
In ethene, the bond angle(s) is/are.
(a) \[10{9^o}28\prime \]
(b) \[12{0^o}\]
(c) \[18{0^o}\]
(d) Different
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Like alkene, graphite also possesses the \[s{p^2}\]hybridization. The ground state electronic configuration of carbon is \[1{s^2},2{s^2},2{p^2}\]. The four valence electrons of carbon are present in \[2s\]and \[2p\]orbital, when these orbitals combine the formation of \[s{p^2}\]hybridized orbitals occurs. Each carbon atom in graphite can be fused with the other three carbon atoms via covalent bonds.
Complete step by step solution:Ethylene is also known as ethene.
Ethene is an organic compound, which is formed by carbon and hydrogen atoms, and it is represented by \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]molecular formula.
Because ethylene contains carbon and hydrogen therefore it belongs to the category of unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Because the ethene has a double bond. Therefore, it comes under the category of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The unsaturated hydrocarbons possess double and triple bonds between carbon atoms.
Because for the formation of a carbon-carbon double bond minimum of two carbon atoms are required. Therefore, in the family of alkenes, the ethene is known as the simplest alkene.
The carbon atom has the property to form carbon-carbon single, double and triple bonds. Due to this property, various covalent compounds of carbon have been reported.
Based on carbon-carbon single, double and triple bonds we can easily predict the hybridization and structure.
When a compound possesses a single carbon-carbon bond, then the structure will be tetrahedral. Whereas, when a compound has carbon-carbon double and triple bond then the structure will be planar and linear respectively.
In each compound, the carbon atom has four valence electrons.
In the structure of the ethylene molecule, the carbon-carbon double bond has four shared pairs of electrons, and the rest two electrons \[C - C\]bond with hydrogen atoms.
An ethene (\[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]) molecule is formed when the ground state configuration (\[1{s^2},2{s^2},2{p^2}\]) of carbon atom change into the excited state configuration (\[1{s^2},2{s^1},2{p_x}^1,2{p_y}^1,2{p_z}^1\]). In the excited state, the carbon atom shifted the \[2{s^2}\]orbital to \[2{p_z}^1\]orbital to provide four unpaired electrons which later overlap with four hydrogen atoms to form the ethene (\[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]) molecule.
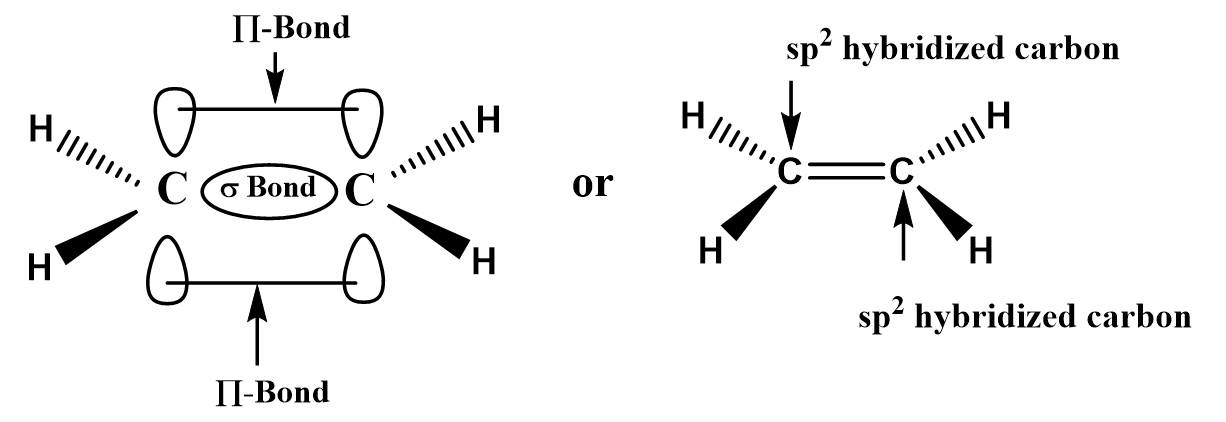
Image: Molecular structure of ethene molecule.
Because ethene molecules have \[s{p^2}\]hybridization and planar structure with \[{120^o}\]bond angle.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: Due to the electronically rich carbon-carbon bond, the ethene molecule gives the electrophilic addition reaction.
The alkenes are considered more reactive than the alkanes.
Ethylene is used as a plant growth and regulator hormone.
Complete step by step solution:Ethylene is also known as ethene.
Ethene is an organic compound, which is formed by carbon and hydrogen atoms, and it is represented by \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]molecular formula.
Because ethylene contains carbon and hydrogen therefore it belongs to the category of unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Because the ethene has a double bond. Therefore, it comes under the category of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
The unsaturated hydrocarbons possess double and triple bonds between carbon atoms.
Because for the formation of a carbon-carbon double bond minimum of two carbon atoms are required. Therefore, in the family of alkenes, the ethene is known as the simplest alkene.
The carbon atom has the property to form carbon-carbon single, double and triple bonds. Due to this property, various covalent compounds of carbon have been reported.
Based on carbon-carbon single, double and triple bonds we can easily predict the hybridization and structure.
When a compound possesses a single carbon-carbon bond, then the structure will be tetrahedral. Whereas, when a compound has carbon-carbon double and triple bond then the structure will be planar and linear respectively.
In each compound, the carbon atom has four valence electrons.
In the structure of the ethylene molecule, the carbon-carbon double bond has four shared pairs of electrons, and the rest two electrons \[C - C\]bond with hydrogen atoms.
An ethene (\[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]) molecule is formed when the ground state configuration (\[1{s^2},2{s^2},2{p^2}\]) of carbon atom change into the excited state configuration (\[1{s^2},2{s^1},2{p_x}^1,2{p_y}^1,2{p_z}^1\]). In the excited state, the carbon atom shifted the \[2{s^2}\]orbital to \[2{p_z}^1\]orbital to provide four unpaired electrons which later overlap with four hydrogen atoms to form the ethene (\[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\]) molecule.

Image: Molecular structure of ethene molecule.
Because ethene molecules have \[s{p^2}\]hybridization and planar structure with \[{120^o}\]bond angle.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: Due to the electronically rich carbon-carbon bond, the ethene molecule gives the electrophilic addition reaction.
The alkenes are considered more reactive than the alkanes.
Ethylene is used as a plant growth and regulator hormone.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




