
If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a polar molecule, a possible geometry of \[A{B_4}\] is:
A. Square planar
B. Tetrahedral
C. Square pyramidal
D. Rectangular planar
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When the atoms of a molecule are arranged in a three-dimensional structure it gives the molecular geometry of that molecule. Various geometrical parameters like bond length, torsional angles, molecular bond angles, etc., determine the shape of a molecule and the position of the atoms in it. The geometry of molecules is dependent on various factors like the presence or absence of lone pair in the central atom.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A. If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a square planar then it should be non-polar because the vector sum of the dipole moment here is zero.
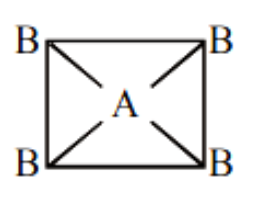
Image caption – Square planar geometry
B. If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is tetrahedral then it has no lone pair and their structure should be represented as follows:
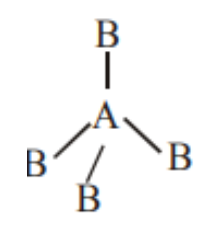
Image caption - Tetrahedral geometry
Here also it should be non-polar as it has perfect symmetry.
C. If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a square pyramidal then it has one lone pair and their structure should be represented as:
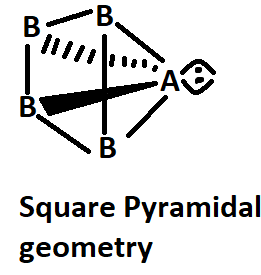
Image caption - Square pyramidal geometry
Here, in fact, the molecule is polar because the dipole moment of the lone pair of A is not affected by others.
(4) If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a rectangular plane then it should be non-polar because the vector sum of the dipole moment is zero.
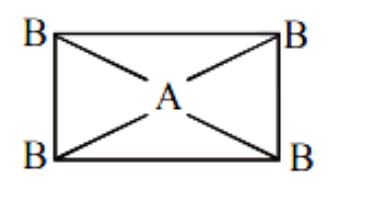
Image caption - Rectangular planar geometry
From the above analysis, it is evident that only the square pyramidal geometry satisfies the polar nature of the molecule. So it is our correct answer.
Hence, the correct answer is, option (C).
Note: It should be noted that the geometry of a molecule can be determined using the VSEPR model. The VSEPR model of organisation aids in making molecules more stable and less energetic.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
A. If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a square planar then it should be non-polar because the vector sum of the dipole moment here is zero.

Image caption – Square planar geometry
B. If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is tetrahedral then it has no lone pair and their structure should be represented as follows:

Image caption - Tetrahedral geometry
Here also it should be non-polar as it has perfect symmetry.
C. If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a square pyramidal then it has one lone pair and their structure should be represented as:

Image caption - Square pyramidal geometry
Here, in fact, the molecule is polar because the dipole moment of the lone pair of A is not affected by others.
(4) If \[A{B_4}\] molecule is a rectangular plane then it should be non-polar because the vector sum of the dipole moment is zero.

Image caption - Rectangular planar geometry
From the above analysis, it is evident that only the square pyramidal geometry satisfies the polar nature of the molecule. So it is our correct answer.
Hence, the correct answer is, option (C).
Note: It should be noted that the geometry of a molecule can be determined using the VSEPR model. The VSEPR model of organisation aids in making molecules more stable and less energetic.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




