
Identify the type of reaction indicated by line A in the diagram.
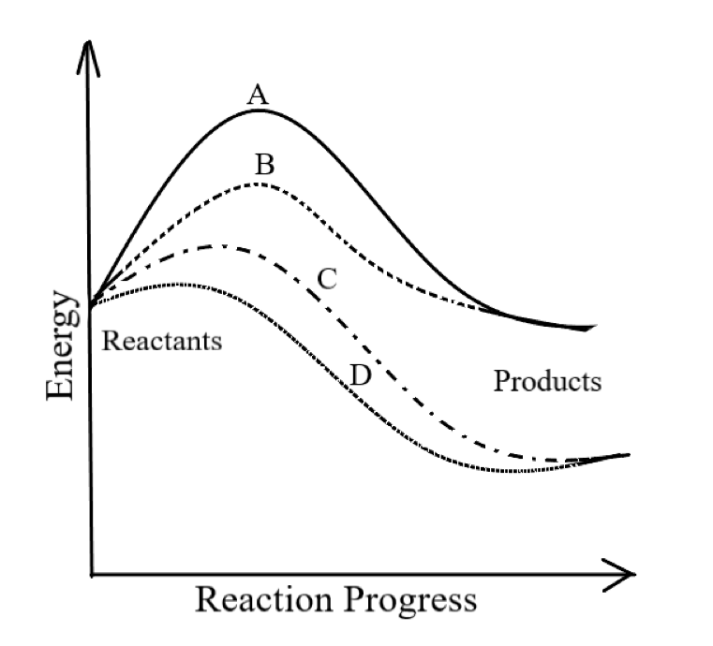
(A) Uncatalyzed exothermic
(B) Catalyzed exothermic
(C) Catalyzed endothermic
(D) Uncatalyzed endothermic
(E) Reversible
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Some substances are sometimes added to a chemical reaction to increase the rate of reaction, those substances are called Catalyst. A catalyst increases the rate of reaction by the process called Catalysis.
Complete step by step solution:
-A catalyst is never consumed in the reaction but fastens the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy of reactants in both, forward and backward directions by:
(i) orienting the reacting particles in such a way that they make more successful collisions
(ii) reacting with the reactants to form an intermediate that requires lower energy for forming the product.
-The minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to proceed is known as Activation energy.
-The uncatalyzed reactions proceed via a one-step mechanism and only one transition state is observed.
-The catalyzed reactions are a two-step mechanism reactions which includes two transition states with
notably lesser activation energy.
-The reactions which take more energy to break the bonds of the reactants are known as an endothermic reaction. In such reactions, the heat from the surroundings is absorbed as a result, the drop is the temperature occurs.
-The reactions which take less energy to break the bonds in the reactants are known as exothermic reactions. The exothermic reactions result in the rise of temperature.
-In the graph given,
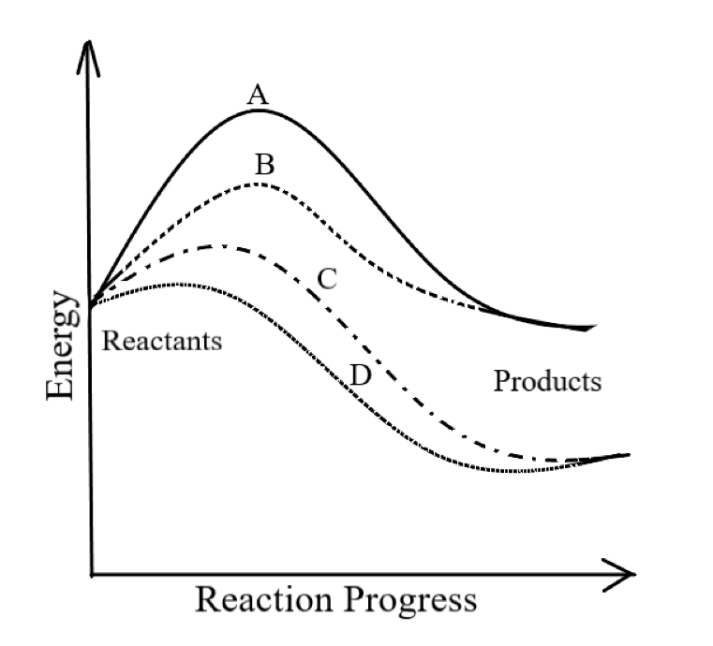
A refers to an uncatalyzed endothermic reaction. As it requires maximum activation energy for initiating the reaction, hence it is an uncatalyzed reaction. Also, as the energy of the product is greater than the energy of the product, hence it is an endothermic reaction.
B refers to a catalyzed endothermic reaction.
C refers to a catalyzed exothermic reaction.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note:-A catalyst may be either a homogenous catalyst or a heterogeneous catalyst.
-If the catalyst is of the same phase as that of the reactant, it is known as a homogeneous catalyst. In this, the catalyst interacts with the reactants forming an intermediate substance which then undergoes decomposition or reacts with another reactant in one or more steps to regenerate and form the product. A typical example of homogenous catalysis is in the earth’s ozone layer.
-If the catalyst to be used is of a different phase (usually a solid) that the other reactants, such catalyst is said to be a heterogeneous catalyst. Heterogeneous catalysis typically involves the following steps during the reaction-
(i) Absorption of the reactant(s) on the surface of the catalyst
(ii) Activation of the adsorbed reactant(s)
(iii) Reaction of the adsorbed reactant(s)
(iv) Desorption of the product(s) from the surface of the catalyst.
Complete step by step solution:
-A catalyst is never consumed in the reaction but fastens the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy of reactants in both, forward and backward directions by:
(i) orienting the reacting particles in such a way that they make more successful collisions
(ii) reacting with the reactants to form an intermediate that requires lower energy for forming the product.
-The minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction to proceed is known as Activation energy.
-The uncatalyzed reactions proceed via a one-step mechanism and only one transition state is observed.
-The catalyzed reactions are a two-step mechanism reactions which includes two transition states with
notably lesser activation energy.
-The reactions which take more energy to break the bonds of the reactants are known as an endothermic reaction. In such reactions, the heat from the surroundings is absorbed as a result, the drop is the temperature occurs.
-The reactions which take less energy to break the bonds in the reactants are known as exothermic reactions. The exothermic reactions result in the rise of temperature.
-In the graph given,

A refers to an uncatalyzed endothermic reaction. As it requires maximum activation energy for initiating the reaction, hence it is an uncatalyzed reaction. Also, as the energy of the product is greater than the energy of the product, hence it is an endothermic reaction.
B refers to a catalyzed endothermic reaction.
C refers to a catalyzed exothermic reaction.
So, the correct answer is option D.
Note:-A catalyst may be either a homogenous catalyst or a heterogeneous catalyst.
-If the catalyst is of the same phase as that of the reactant, it is known as a homogeneous catalyst. In this, the catalyst interacts with the reactants forming an intermediate substance which then undergoes decomposition or reacts with another reactant in one or more steps to regenerate and form the product. A typical example of homogenous catalysis is in the earth’s ozone layer.
-If the catalyst to be used is of a different phase (usually a solid) that the other reactants, such catalyst is said to be a heterogeneous catalyst. Heterogeneous catalysis typically involves the following steps during the reaction-
(i) Absorption of the reactant(s) on the surface of the catalyst
(ii) Activation of the adsorbed reactant(s)
(iii) Reaction of the adsorbed reactant(s)
(iv) Desorption of the product(s) from the surface of the catalyst.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




