
Consider the following transformations of a compound P.
Choose the correct option(s).
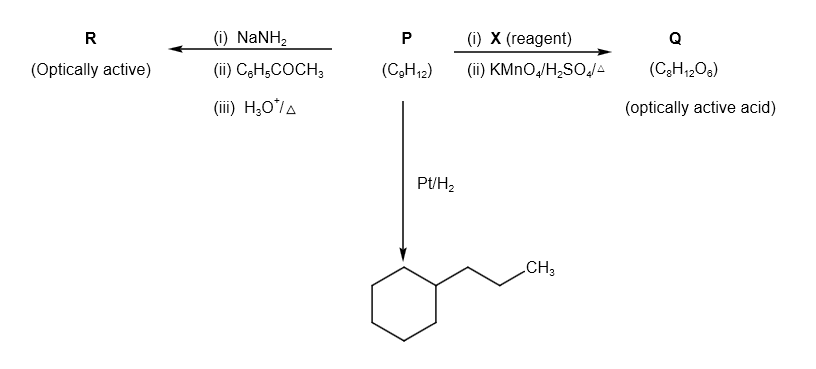
A. P is
B. X is \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\]
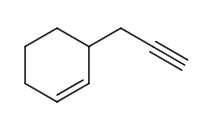
C. P is
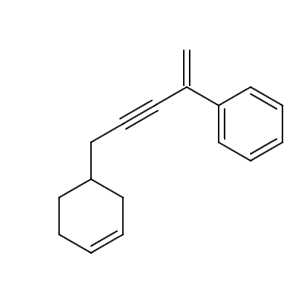
D.R is
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: \[NaN{H_2}\] is a potent nucleophile and strong base. It is employed in elimination reactions as well as the deprotonation of weak acids. Alkenes can be reduced to alkanes with \[{H_2}\] in the presence of metal catalysts such as \[Pt\] .
Complete Step by Step Solution:
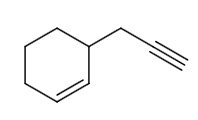
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:
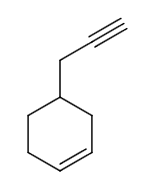
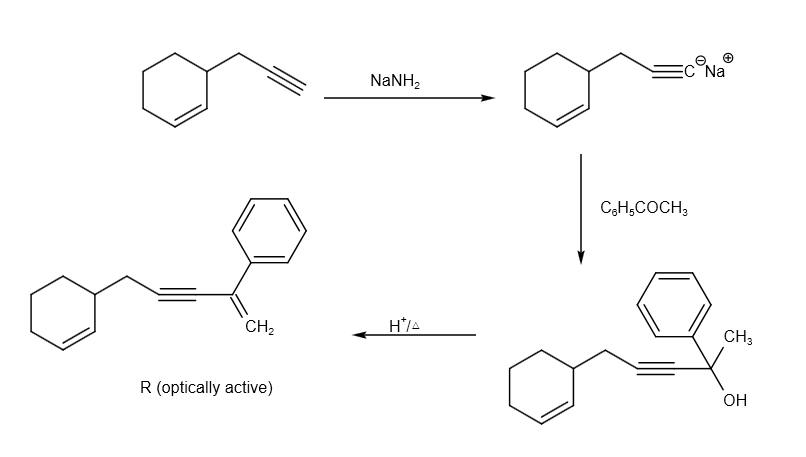
The reaction of P to R can be written as follows:
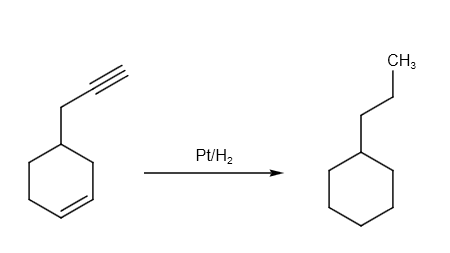
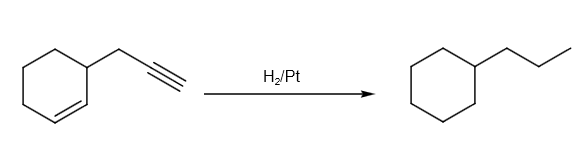
Hydrogenation can be written as follows:
From the options, let us take \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] is Lindlar’s catalyst. The reaction can be written as follows:
Therefore, option A is not the correct answer.
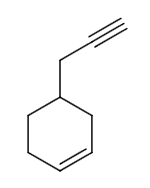
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:
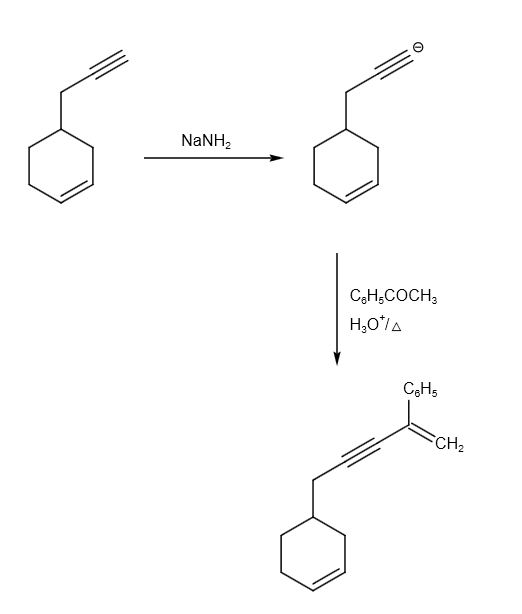
Let us assume \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. The reaction of P to Q can be written as follows:
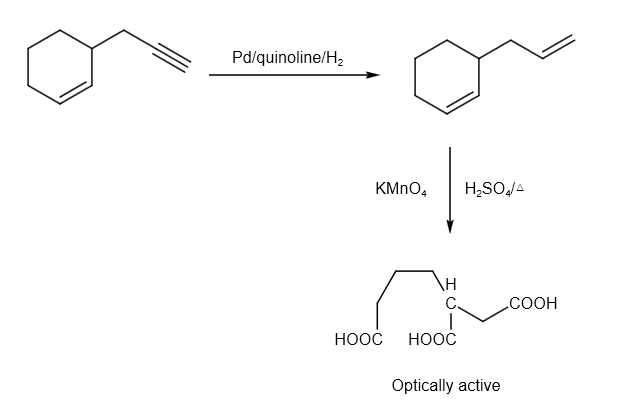
The hydrogenation reaction can be written as follows:
The reaction from P to R can be written as follows:
Therefore, option B and C are correct answer.
Additional Information:
• A heterogeneous catalyst called Lindlar is made of palladium that was created on calcium carbonate and treated with various forms of lead. A heterogeneous catalyst is one that constantly exists in a distinct state from the reactant solution (solid, liquid, or gas solution).
• After Herbert Lindlar, the company's founder, the name "Lindlar" was given. In some places, lead will be required to deactivate the palladium. Lead is present; hence this is frequently referred to as a "poisoned catalyst." When a catalyst's potency starts to decline, it becomes toxic.
Note: Different chemical pollutants, including lead acetate and lead oxide, are utilised to poison the palladium. Normally, just 5% of the weight of the catalyst is made up of the palladium element. Alkenes are subjected to the catalyst in order to hydrogenate alkynes.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:

The reaction of P to R can be written as follows:

Hydrogenation can be written as follows:

From the options, let us take \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] is Lindlar’s catalyst. The reaction can be written as follows:
Therefore, option A is not the correct answer.
From the options, let us assume the structure of P is as follows:

Let us assume \[Pd - C/quinoline/{H_2}\] as reagent X. The reaction of P to Q can be written as follows:

The hydrogenation reaction can be written as follows:

The reaction from P to R can be written as follows:

Therefore, option B and C are correct answer.
Additional Information:
- • A catalyst is a material that modifies or speeds up any chemical reaction without causing any change on its own. Typically, a catalyst is utilised in smaller quantities than the reactants or other reaction participants.
Note: Different chemical pollutants, including lead acetate and lead oxide, are utilised to poison the palladium. Normally, just 5% of the weight of the catalyst is made up of the palladium element. Alkenes are subjected to the catalyst in order to hydrogenate alkynes.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




