
Area of right triangle $\Delta AOB$ is 16 square units. If $O$ is the origin and the coordinates of $A$ are (8, 0), what are the coordinates of $B$?
A (0, 4)
B (0, 2)
C (-1, 1)
D (0, $\dfrac{1}{2}$)
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this problem, since the area of the right angle triangle $\Delta AOB$ is given so we have to compare that area with the formula for the area of a triangle which can be written as $\dfrac{1}{2} \times OA \times OB.$ Since the coordinates of $A$ and $O$ are given, we have to calculate the length of the side $OA$. This will give the base of the triangle $\Delta AOB$. Finally, by substituting the value of $OA$ in the area formula of the triangle we can calculate the length $OB$. Once we get the length of $OB$ we can calculate the coordinates of $B$.
Complete step by step answer:
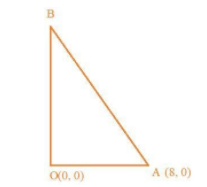
It is given that $O$ is the origin. Thus, coordinates of $O$ is $\left( {0,0} \right)$.
Coordinates of $A$ is given $\left( {8,0} \right)$.
Now we can calculate the length of $OA$ by using the formula $L = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$, where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ are the coordinates.
Substituting $\left( {0,0} \right)$ for $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {8,0} \right)$for $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$.
$\begin{array}{l}OA = \sqrt {{{\left( {8 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OA = \sqrt {{8^2} + {0^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OA = 8\;{\rm{unit}}\end{array}$
Since the point $B$ is in the y – axis, so considering $\left( {0,y} \right)$ is the coordinates of $B$.
Thus length of $OB$ is
$\begin{array}{l}OB = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - y} \right)}^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OB = \sqrt {0 + {y^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OB = y\;{\rm{unit}}\end{array}$
Now, the area of the right angle triangle $\Delta AOB$ is
${\rm{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times OA \times OB$
The area of the triangle is given and we calculated the value of $OA$ and $OB$.
Thus, substituting area $ = 16$, 8 for8 for $OA$ and $y$ for $OB$.
$\begin{array}{l}{\rm{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times OA \times OB\\ \Rightarrow 16 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 8 \times y\\ \Rightarrow 16 = 4y\\ \Rightarrow y = 4\end{array}$
Thus, the required coordinates of $B$ is $\left( {0,4} \right)$.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Here we have to determine the required coordinates of the point $B$ of the triangle $\Delta AOB$. Since the area of triangle coordinates of $O$ and $A$ are given, coordinates of $B$ can be calculated easily.
Complete step by step answer:

It is given that $O$ is the origin. Thus, coordinates of $O$ is $\left( {0,0} \right)$.
Coordinates of $A$ is given $\left( {8,0} \right)$.
Now we can calculate the length of $OA$ by using the formula $L = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}$, where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ are the coordinates.
Substituting $\left( {0,0} \right)$ for $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {8,0} \right)$for $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$.
$\begin{array}{l}OA = \sqrt {{{\left( {8 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OA = \sqrt {{8^2} + {0^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OA = 8\;{\rm{unit}}\end{array}$
Since the point $B$ is in the y – axis, so considering $\left( {0,y} \right)$ is the coordinates of $B$.
Thus length of $OB$ is
$\begin{array}{l}OB = \sqrt {{{\left( {0 - 0} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0 - y} \right)}^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OB = \sqrt {0 + {y^2}} \\ \Rightarrow OB = y\;{\rm{unit}}\end{array}$
Now, the area of the right angle triangle $\Delta AOB$ is
${\rm{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times OA \times OB$
The area of the triangle is given and we calculated the value of $OA$ and $OB$.
Thus, substituting area $ = 16$, 8 for8 for $OA$ and $y$ for $OB$.
$\begin{array}{l}{\rm{Area}} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times OA \times OB\\ \Rightarrow 16 = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 8 \times y\\ \Rightarrow 16 = 4y\\ \Rightarrow y = 4\end{array}$
Thus, the required coordinates of $B$ is $\left( {0,4} \right)$.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: Here we have to determine the required coordinates of the point $B$ of the triangle $\Delta AOB$. Since the area of triangle coordinates of $O$ and $A$ are given, coordinates of $B$ can be calculated easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

JEE Mains 2026 January 21 Shift 2 Question Paper with Solutions PDF - Complete Exam Analysis

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 2 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Circles (2025-26)

Fuel Cost Calculator – Estimate Your Journey Expenses Easily

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas And Volumes Exercise 11.3 (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Heron's Formula (2025-26)





