
1-methyl ethylene oxide when treated with an excess of HBr produces:
A.
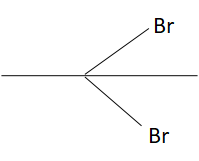
B.
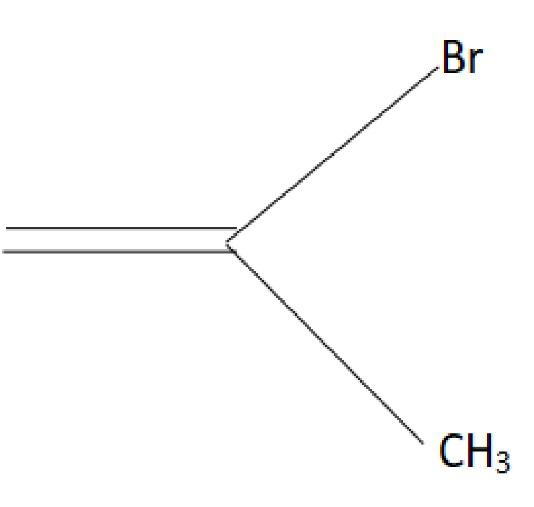
C.
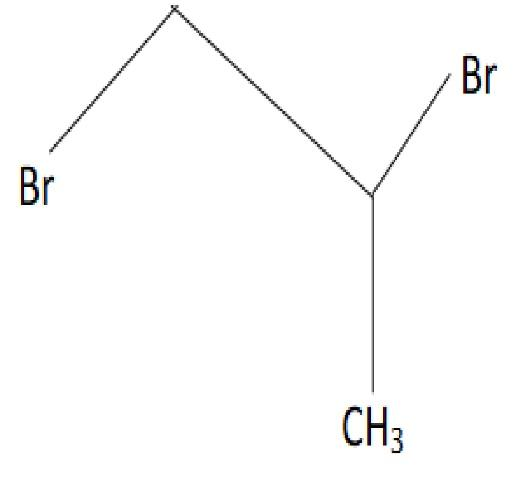
D.
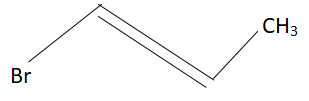
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The three-membered ring epoxides can also be opened by anhydrous acids (like \[HBr\]) to form trans halohydrins. A halogen anion will attack the less substituted carbon in an \[{S_N}2\] like the reaction when both epoxide carbons are primary or secondary.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
1. 1-methyl ethylene oxide is a type of cyclic ether that reacts with strong acid to form a linear compound.
2. 1-methyl ethylene oxide undergoes a reaction with Hydrogen bromide in which a partial hydrogen ion attaches to the Oxygen atom with the lone pair and the Bromide ion is eliminated.
3. There are two possibilities to break this cyclic structure: one has only alpha Hydrogen and another has five alpha Hydrogen. So, the stability is higher for more alpha Hydrogen.
4. The negative charge Bromide ion attaches to the positive charge Carbon atom.
5. The excess Hydrogen Bromide reacts with the compound in which a positive charge Hydrogen atom makes a bond with the lone pair of an Oxygen atom and forms\[OH_2^ + \].
5. The negative charge Bromide ion attacks the positive position and forms 1,2-Dibromopropane with the elimination of water molecules.
6. The reaction of 1-methyl ethylene oxide with the excess Hydrogen bromide is expressed below:
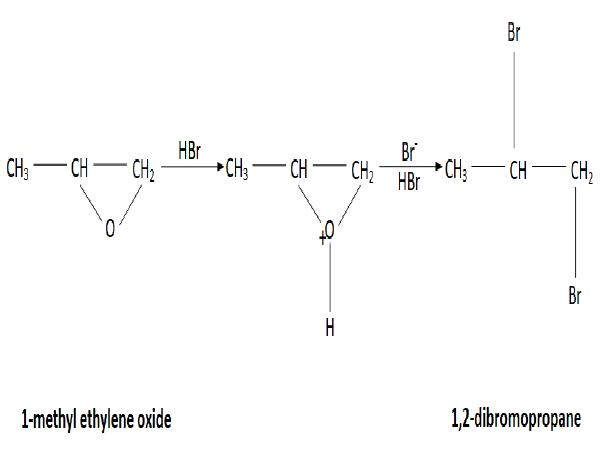
Image: Preparation of 1,2-dibromopropane
The correct option is (3).
Additional information:
The opening of epoxides under acidic conditions occurs in two ways:
1. The epoxide should be protonated first.
2. The nucleophilic attacks at the most substituted position.
Note: The three-membered ring is highly strained and readily open when it acts with strong acid under mild conditions.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
1. 1-methyl ethylene oxide is a type of cyclic ether that reacts with strong acid to form a linear compound.
2. 1-methyl ethylene oxide undergoes a reaction with Hydrogen bromide in which a partial hydrogen ion attaches to the Oxygen atom with the lone pair and the Bromide ion is eliminated.
3. There are two possibilities to break this cyclic structure: one has only alpha Hydrogen and another has five alpha Hydrogen. So, the stability is higher for more alpha Hydrogen.
4. The negative charge Bromide ion attaches to the positive charge Carbon atom.
5. The excess Hydrogen Bromide reacts with the compound in which a positive charge Hydrogen atom makes a bond with the lone pair of an Oxygen atom and forms\[OH_2^ + \].
5. The negative charge Bromide ion attacks the positive position and forms 1,2-Dibromopropane with the elimination of water molecules.
6. The reaction of 1-methyl ethylene oxide with the excess Hydrogen bromide is expressed below:

Image: Preparation of 1,2-dibromopropane
The correct option is (3).
Additional information:
The opening of epoxides under acidic conditions occurs in two ways:
1. The epoxide should be protonated first.
2. The nucleophilic attacks at the most substituted position.
Note: The three-membered ring is highly strained and readily open when it acts with strong acid under mild conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




