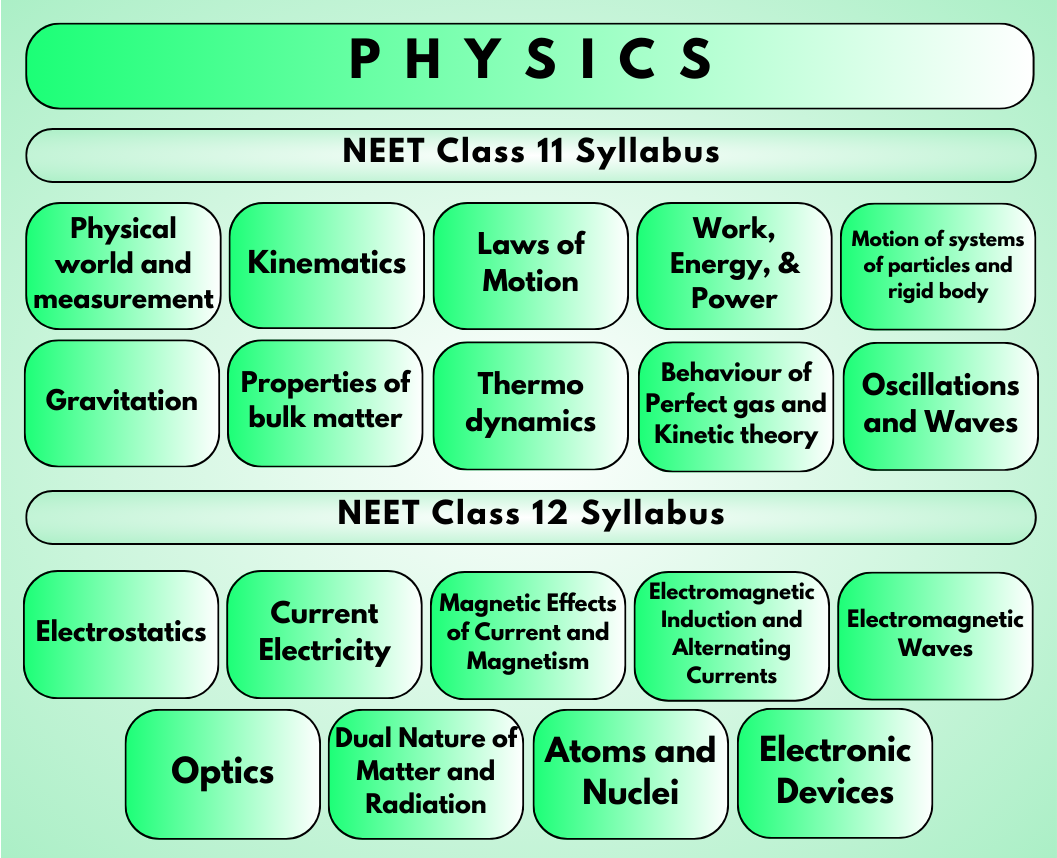
NTA NEET Physics Syllabus PDF Download: Chapter-wise





















FAQs on NEET Physics Syllabus 2024
1. How can one score good marks in NEET Physics using NEET Physics Syllabus PDF?
The exam paper of NEET Physics consists of questions from both classes (i.e., XI and XII). So, in order to achieve good marks, students will have to study from good sources and reference books like NCERT, etc. After going through the chapters thoroughly, students are also advised to attempt the exercise questions from the same. After having a brief run-through of the above, students can write their own references of different formulae and important points, which is also known as Fact Sheet.
After you have finished referring to the NCERT books, you can go for some similar reference books which will help you understand the concepts even better. Students should also get their doubts cleared regularly in order to avoid last-minute confusion that leads to stress. It is also advised to practice previous years’ question papers. This not only gives the students an idea about the format of the paper but also helps the students gain confidence to solve the papers during their exams.
2. What is a useful source to learn NEET Physics-related Concepts?
Vedantu website or app is the best study source for students who are willing to appear for NEET exams. You can find everything you need to study on this website or app as the sources on this website are thoroughly created and edited by professionals, which makes the learning even more interactive and easy to understand. Also, there is no need to worry about the fees required since the content on this website is absolutely free! All you need to do is create an account and further take advantage of all the study materials offered to you, which will surely help you gain a good score in your exams.
3. Does solving Previous Years’ Question Papers really prove to be useful?
The answer to your question is Yes. The choice of solving question papers of previous years’ is a good habit to cultivate while preparing for NEET exams. The reason is that it gives a clear idea about the format of the question paper and also what questions are repeated more often and which chapters contain more weightage and which chapters contain less weightage. About roughly 10-15 questions are repeated in some modified versions of the exam papers. So it is best to include solving the previous papers in your study habits.
4. Is it possible to score 700 in NEET Exams using NEET 2024 Physics Syllabus?
As the proverb goes, “Practice makes a man perfect”, you have to keep on practising. It is difficult but not impossible. You have to avoid making some mistakes if you are willing to score such good marks. First of all, you need to drop the thinking of doing hard work. That does not mean that you shouldn’t study hard. It simply means you also need to include some smart work in order to score 700 in NEET exams.
You need to score somewhere between 170 to 180 in just physics, meaning you need to get 43 to 45 questions correct out of 45 questions. For that, you need to study at least one full chapter with proper dedication and also get your concepts cleared in a proper manner. You need to also study with the help of reliable sources which are provided by the Vedantu app or website.
5. Is the NEET Physics exam easy to crack using the NEET 2024 physics syllabus?
The most difficult section in the NEET exam is that of Physics. In the NEET Physics exam, 45 questions carry 180 marks. The questions that are asked in physics exams are often lengthy, and tricky calculations are involved. Hence, they require lots of practice. And proper study materials in order to ace the NEET physics exams. Fortunately, there is no need to worry since an enriching experience is provided by the Vedantu app or website. It provides the students with professionalised sources that contain solutions that are explained in simple and user-friendly language.
6. Which chapters have more weightage in NEET Physics?
Chapters with higher weightage in NEET Physics include mechanics, laws of motion, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, optics, modern physics, and nuclear physics. Understanding these topics thoroughly is crucial for scoring well in the exam.
7. How many chapters are there in Physics NEET 2024?
The NEET Physics syllabus for 2024 comprises chapters from both Class 11 and Class 12. In total, there are approximately 22 chapters covering a wide range of topics, including mechanics, electromagnetism, optics, thermodynamics, modern physics, and nuclear physics.
8. What are the new changes in NEET 2024?
For precise details on any new changes in NEET 2024, it's best to refer to official notifications or announcements from the National Medical Commission (NMC) or Vedantu as they update information based on the updates given by exam conducting authority. Changes could include modifications in the syllabus, exam pattern, or eligibility criteria.
9. Which are the toughest chapters of Physics for NEET?
The difficulty level can vary depending on your strengths and weaknesses. However, some chapters generally considered more challenging include:
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Magnetism
Optics (especially wave optics)
Modern Physics
10. How to complete NEET Physics in 30 days?
Completing the entire NEET Physics syllabus in 30 days is quite ambitious. It's more realistic to focus on revision and strengthening your grasp of important concepts if you're nearing the exam. Here are some tips for a 30-day NEET Physics sprint:
Identify the high-weightage chapters and focus on revising those thoroughly.
Solve previous years' NEET question papers and mock tests to identify your weak areas and practice time management.
Don't try to memorize everything. Understand the core principles and how to apply them.
If you get stuck on a concept, seek clarification from teachers or online resources.