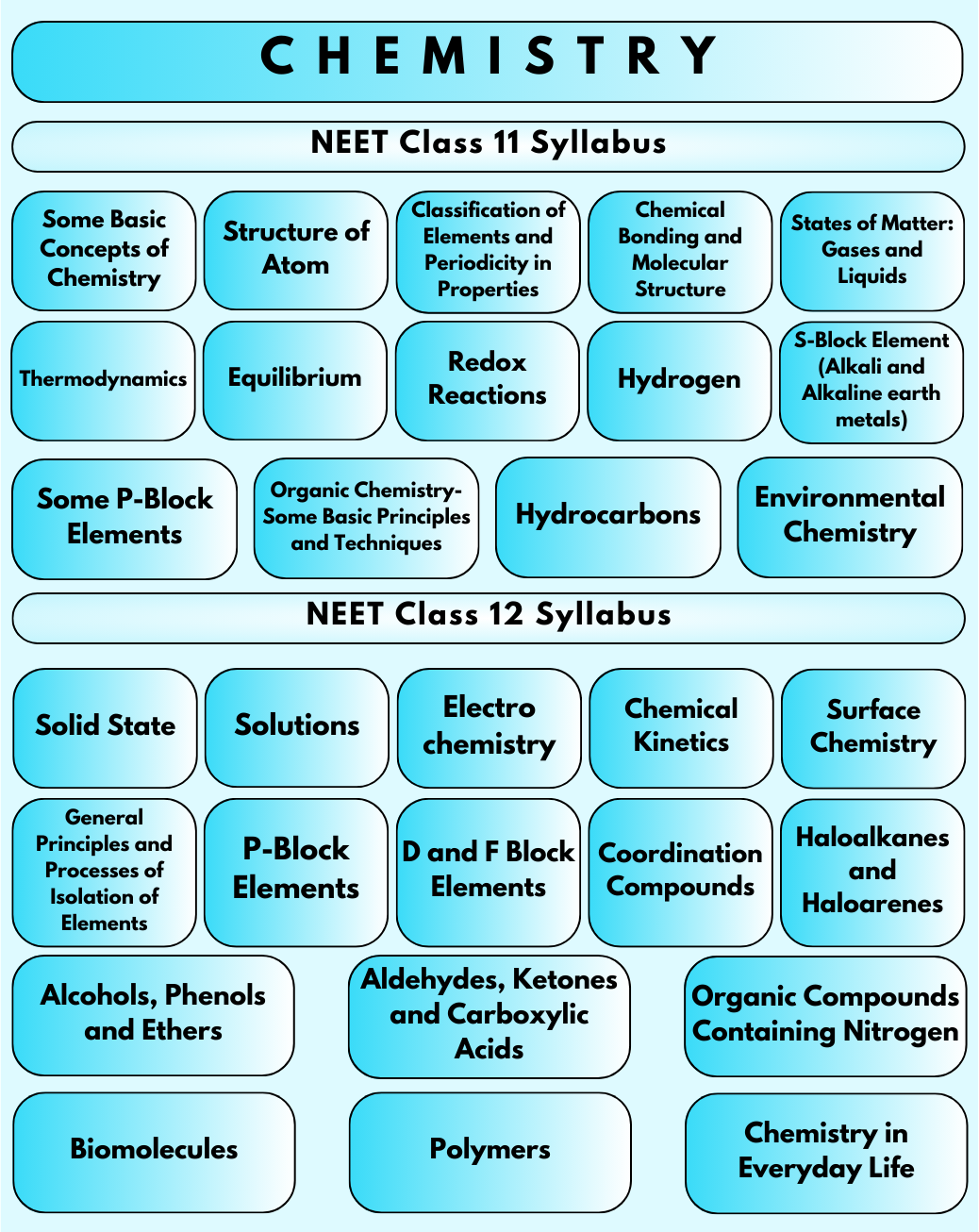
Chemistry Syllabus for NEET UG 2024 - Free PDF Download





















FAQs on NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2024
1. How is the NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for Medical Entrance Examination designed?
The design of the NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for the Medical Entrance Examination is as per the high school courses that the aspirants already have. No matter if their board is CBSE, ICSE, or any else, the syllabus is designed to fit all the courses in one. The aspirants also get a hold of the topics easily, with them already being familiar with them. This makes their preparations slightly easier as well. Hence, they can do well in their exams.
2. Are the topics mentioned in detail in the Chemistry NEET Syllabus 2024 for Medical Entrance Examination?
The aspirants who are preparing for their NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for Medical Entrance Examination must be thorough. To do that, they must be familiar with the many topics that they are going to have to prepare for. This can be done with the help of a syllabus for the NEET Medical Entrance Exam. Good thing is that the syllabus is pretty descriptive and mentions all the details that a student must know about to stay on top of their exam preparations.
3. Why must an aspirant prepare from the NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for Medical Entrance Examination?
One thing that is already established is the fact that an aspirant must be fully prepared for their NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for Medical Entrance Examination. This can only be done when they have a piece of thorough knowledge of the topic. Hence, the best way to go about it is by being thorough through the syllabus of the respective year. And more than that, getting to know the detailed info about what topics must be covered during the preparations for one to prepare for their entrance exam.
4. What kind, of course, is covered in the NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for Medical Entrance Examination?
Once an aspirant starts considering going for NEET 2023-24 Chemistry Syllabus for Medical Entrance Examination, they will observe that the syllabus only covers the topics from various boards for Class 11 and Class 12. This is the only undergraduate program that the students can give in the country for starting their career in medicine. Hence, they must be well prepared for such an exam and be thorough with every single detail of the topics that are being covered as part of the syllabus for such exams.
5. How can a student prepare for the NEET 2023-24 Chemistry for Medical Entrance Examination with the help of a syllabus?
When it comes to preparing for the NEET 2023-24 Chemistry for Medical Entrance Examination, it is quite easy to access the syllabus online. The aspirants can register on Vedantu’s website or app and search for the syllabus and download it on any of their devices. This can easily be one of the best ways in which they prepare for their exams. The key is to check the topics in the syllabus and then prepare for the upcoming exams to ace them.
6. How many chapters are in chemistry for NEET?
The NEET Chemistry syllabus typically consists of around 30 chapters.
7. What is the syllabus of NEET Chemistry 2024?
The syllabus of NEET Chemistry 2024 includes various topics such as Organic Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, and Physical Chemistry. Some specific topics may vary slightly each year.
8. What is the level of chemistry in NEET?
The level of chemistry in NEET is generally considered moderate. It requires a good understanding of basic concepts and thorough preparation to score well.
9. What is the main topic in chemistry for NEET?
One of the main topics in the NEET Chemistry syllabus is Organic Chemistry, which covers a wide range of concepts including hydrocarbons, biomolecules, and polymers.
10. What are some essential concepts covered in the Class 11 NEET Syllabus for Chemistry?
In Chemistry, the Class 11 NEET Syllabus introduces fundamental concepts such as atomic structure, chemical bonding, states of matter, thermodynamics, and classification of elements. These concepts lay the groundwork for advanced topics in Chemistry.
11. What does the NEET Organic Chemistry Syllabus cover?
The NEET Organic Chemistry Syllabus focuses on the study of carbon compounds and their reactions. It includes topics such as hydrocarbons, organic compounds containing oxygen and nitrogen, biomolecules, polymers, and chemistry in everyday life.
12. Are there any recent updates or changes in the Inorganic Chemistry NEET Syllabus?
Three chapters are deleted from the Inorganic Chemistry NEET Syllabus 2024. They are Hydrogen, Metallurgy and S-block.