




Introduction
Organic conversions are simple if you understand organic compounds and reactions. To perform an organic conversion, we must first determine which molecules are necessary for each step. Most of the time, we start thinking from the rear (product) to the front (service) ( initial reactant).
We need to make butanol from ethanol, for example. We begin to consider butanal. We first consider how butanal can be prepared and then choose one of them. Then we consider how that compound can be manufactured in different ways. This process is repeated until we reach ethanol. This procedure should be used frequently.
Important Topics for Differentiations & Conversions - Organic Chemistry
Trends of Periodic Properties in Periodic Table and Reason of Variation
Name Reactions
Important Concepts for Differentiations & Conversions - Organic Chemistry Notes
Following are the important pointers for the differentiation and conversions in organic chemistry
The acidity of phenol and aniline, as well as benzoic acid, is increased by electron-withdrawing groups. NO2, CN, CHO, and other compounds are examples.
Electron donating groups diminish phenol's acidity while increasing aniline's basicity. CH3, NH2, OH, and other compounds are examples.
Electron donating groups are ortho-, para-directing, whereas electron-withdrawing groups are m-directing.
Chiral carbon atoms are those that are linked to four distinct groups.
The stability of the carbocation determines SN1.
The SN2 reaction is favoured by steric hindrance.
Because of steric and electrical differences, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones.
Due to the existence of a lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom, alcohols act as Lewis bases.
Compared to amides and alcohols, amines are more basic.
Because of the existence of highly activating groups, amines and phenols are more reactive than benzene (-OH, -NH2)
Because amines have more electronegative oxygen atoms than alcohols, they are less acidic.
Due to stronger hydrogen bonding, primary amines have a higher boiling point than tertiary amines.
Because of the -I action of alkyl groups, aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines.
The electrical component influences the order of basicity in a solution.
Acetylation protects the NH2 group before nitration. By resonance, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen are less available for donation to the benzene ring. As a result, the -NHCOCH3 group has a stronger activating impact than the amino group.
From top to bottom, each group has a proclivity for forming hydrides.
As the strength of the M-H bond weakens, acidity rises, and the reducing character rises.
From top to bottom, the thermal stability and basicity diminish.
The boiling point rises as the van-der-Waals forces grow in proportion to the size of M.
The electron affinity of halogens rises from top to bottom.
The acidity of halogen hydrides increases from top to bottom.
Because of incompletely filled d-orbitals, d-d transition, and the presence of unpaired electrons, transition metals are coloured paramagnetic and form complexes.
Transition metals have a variety of oxidation states as well.
Solved Examples From Chapter
Question 1: A haloalkane P combines with aq. KOH to form Q, which is then oxidised with K2Cr2O7/H+ to form R, which is then Clemmensen reduced to form S. In the presence of dry ether, the molecule P reacts with sodium metal to create 2,3-dimethyl butane. Write down the chemical reaction with the letters P,Q,R, and S.
Solution:
The reactions mentioned in the question is as follows:
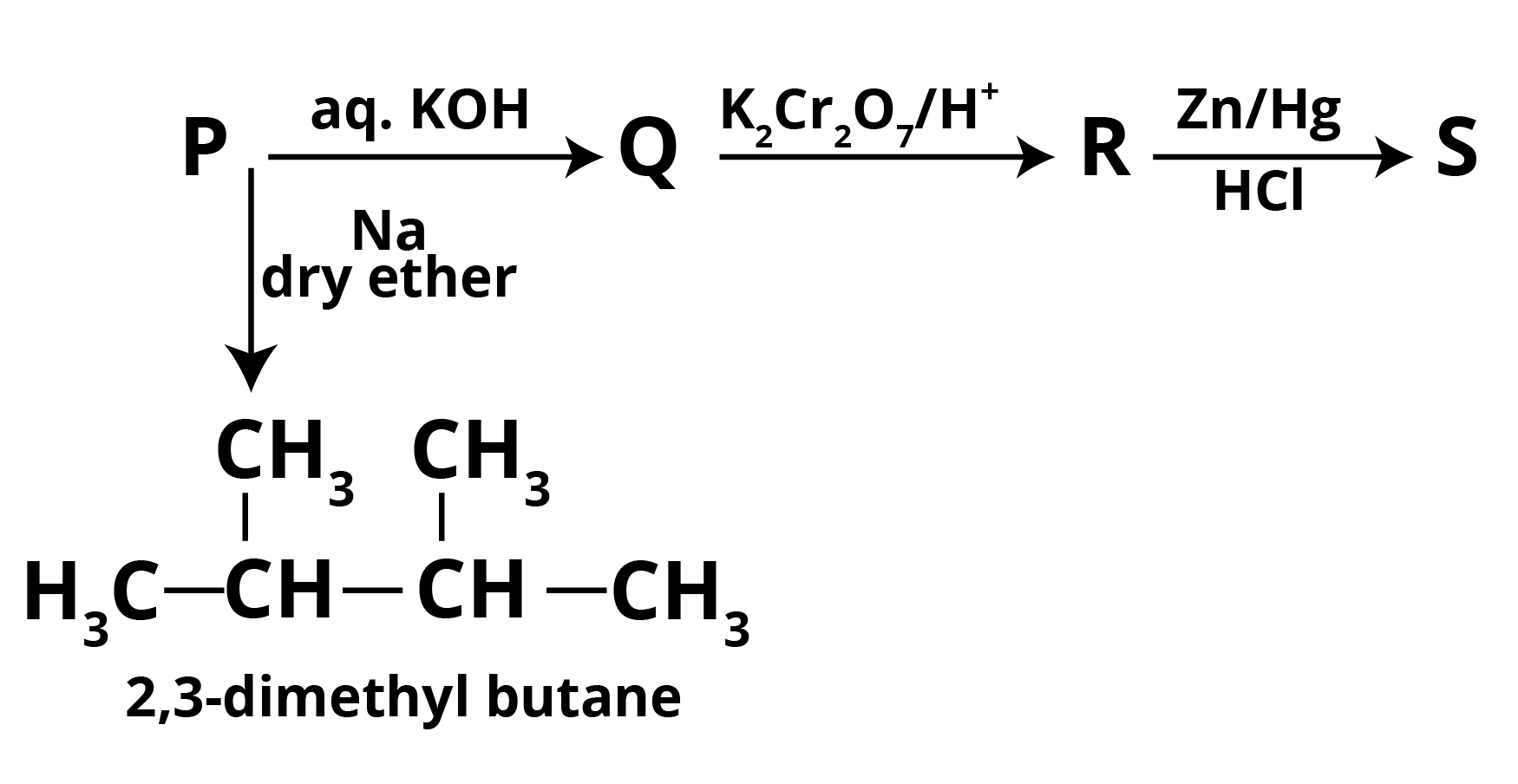
From the given reactions it is clear that,
P = 2 ChloropropaneAs 2-Chloropropane produces 2,3-dimethyl butane in reaction with Dry Ether in presence of sodium which gives NaCl as a by-product along with 2-Chloropropane.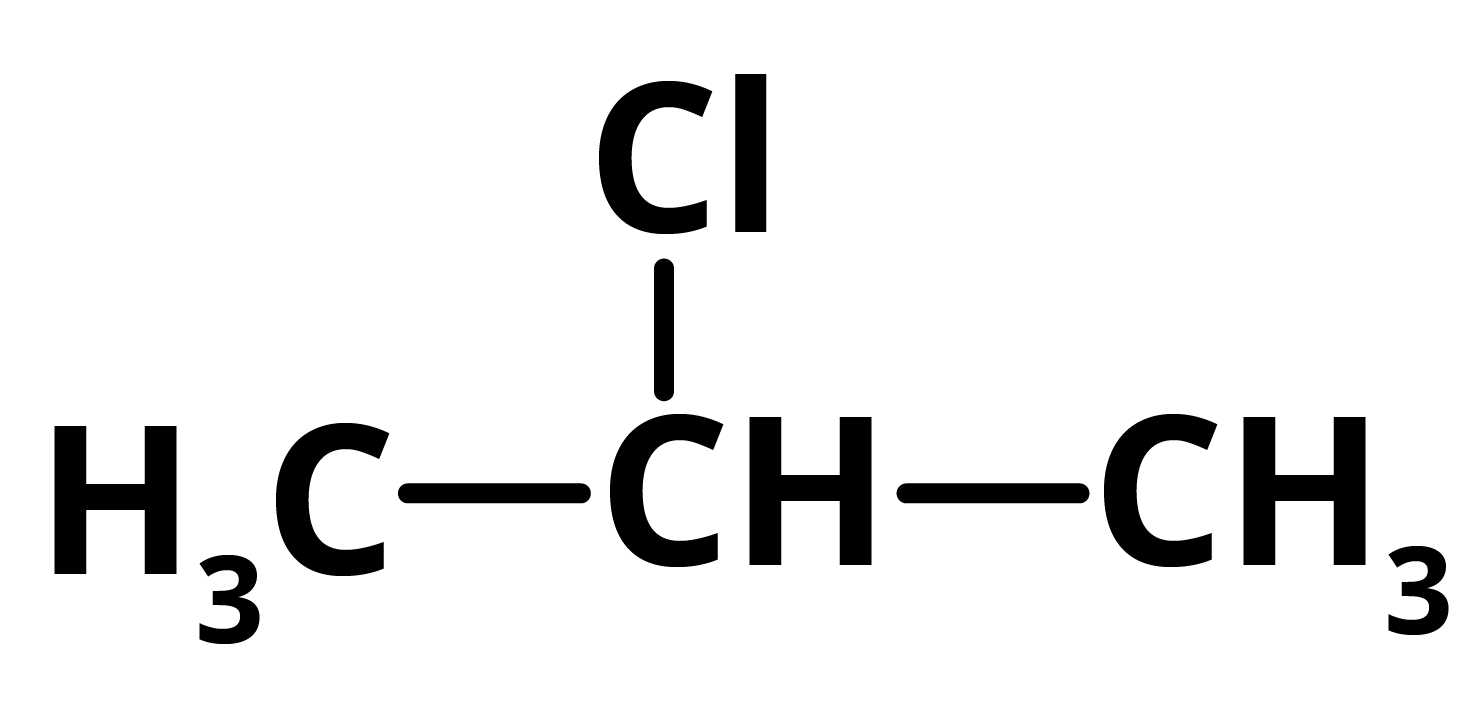
If P = 2 Chloropropane, then under aq KOH it gives,
Q = 2 propanol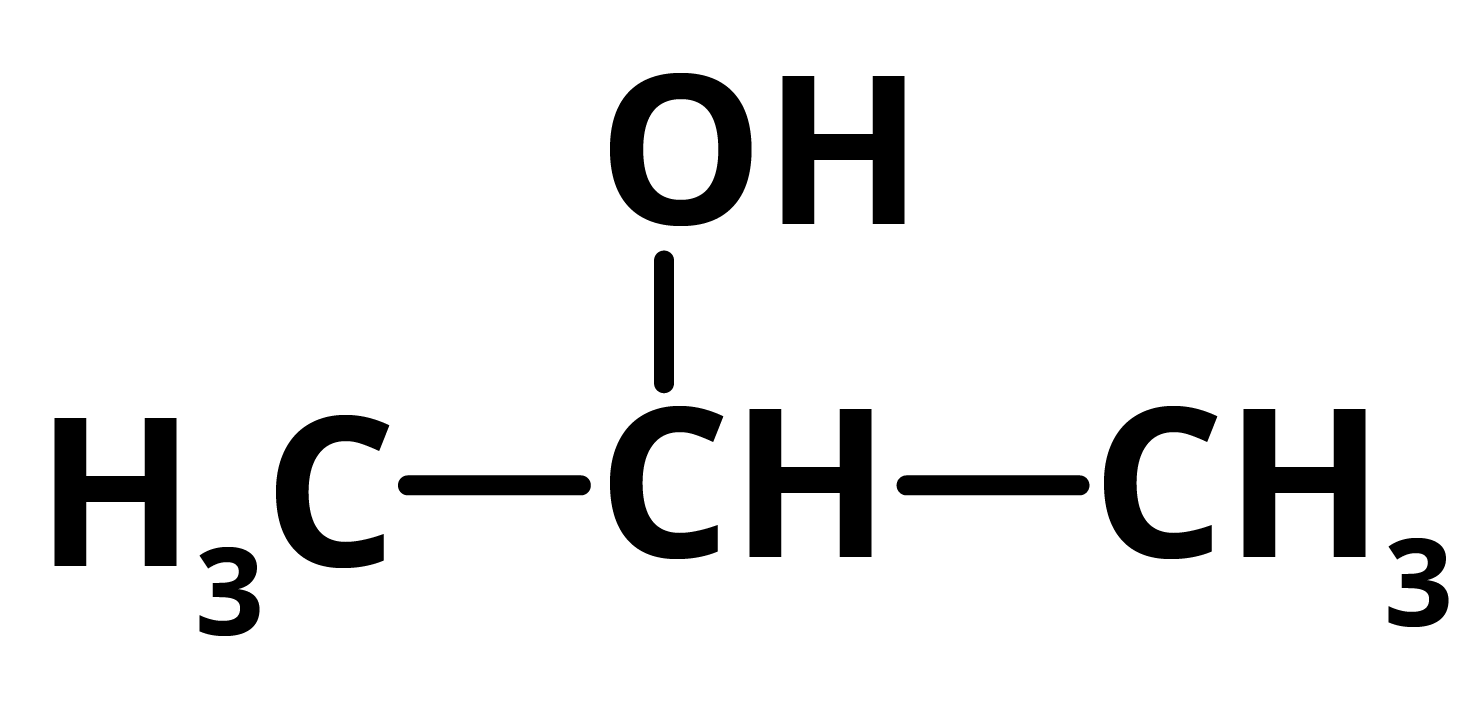
Following which,
R = propanoneAnd S = propane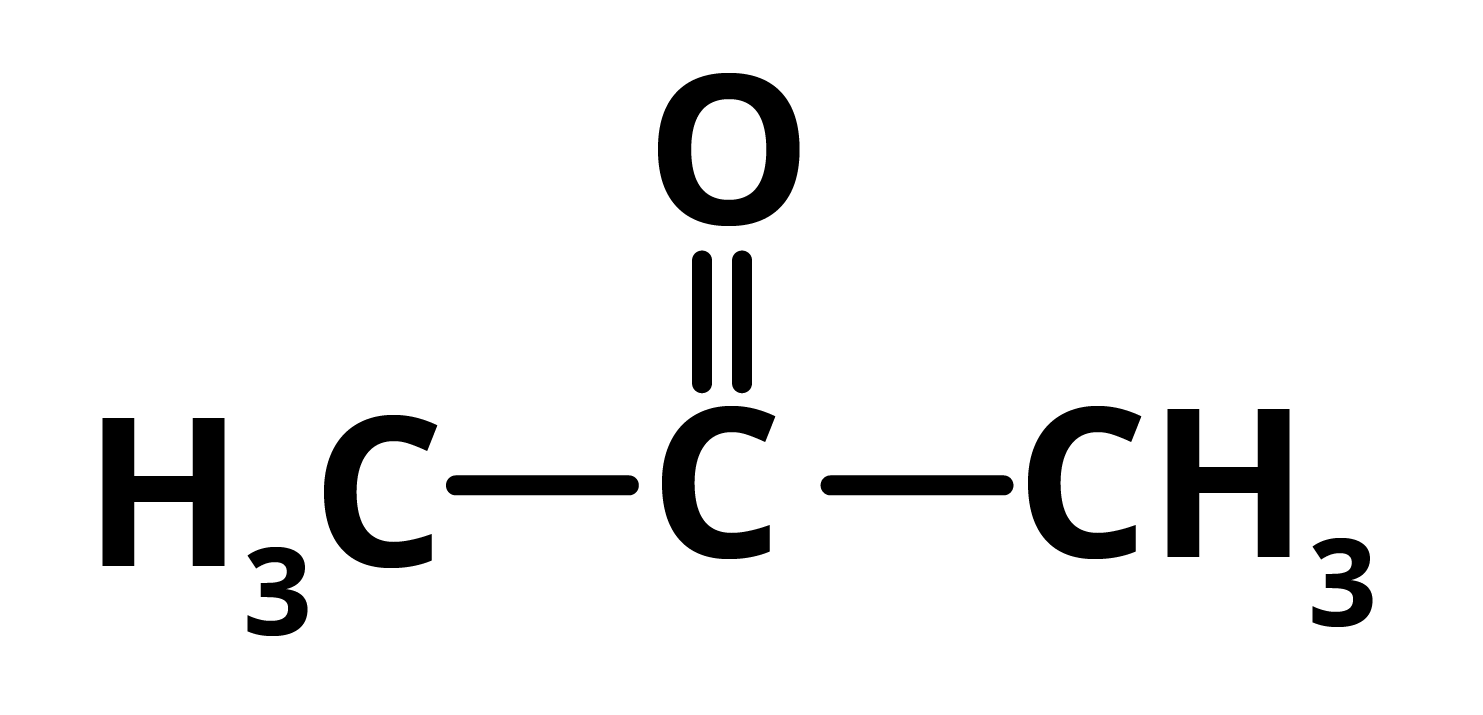
CH3-CH2CH3
Key Points to Remember: Identify one compound and the rest follows. Here, the dimethylbutane can only be formed from the replacement of the chlorine atom of 2-Chloropropane leading to dimerisation.
Question 2: Consider a possible reaction: $A \ \overset{PBr_3}{\rightarrow} \ B \ \overset{KCN}{\rightarrow} \ C \ \overset{H_2O/H^+}{\rightarrow} \ D \ \overset{P_2O_5}{\rightarrow} \ E$ The molecule A is a primary alcohol that causes the primary iodoform test to be positive. To make ethanoic acid, convert component D to ethanoic acid.
Solution:
A primary alcohol that also gives the primary iodoform test is Ethanol.
Hence, compound A = Ethanol = CH3CH2OH.The reaction of ethanol in presence of PBr3 gives Bromoethane as Bromine replaces the hydroxyl group of the alcohol. Hence, B = Bromoethane = CH3CH2Br.
When bromoethane reacts with potassium cyanide, KCN, it gives propane nitrile as the cyanide ion replaces the bromide ion. Therefore, compound C = Propanenitrile = CH3CH2CN.
Similarly, the cyanide ion gets converted by the carboxyl group when Propanenitrile reacts with water in the H+ solution. Hence, D = Propanoic Acid = CH3CH2COOH.
In the presence of phosphorus pentoxide, propanoic acid gets converted to propanoic anhydride. Hence, E = Propanoic Anhydride
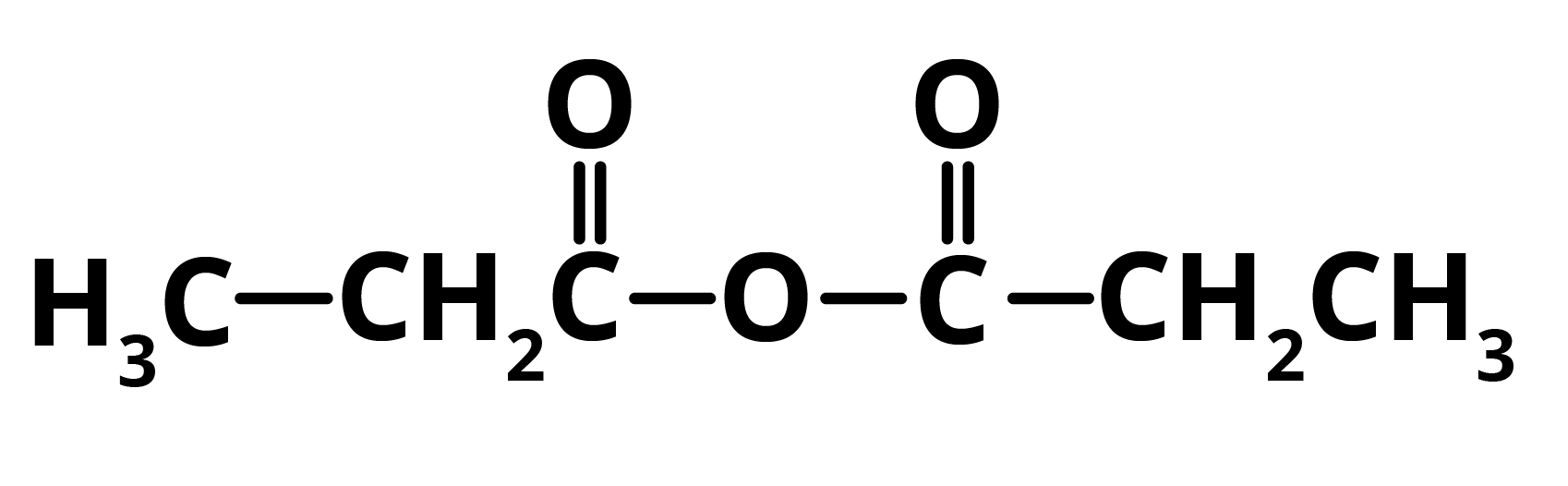
The compound D, propanoic acid is converted into Ethanoic Acid by the following set of reactions:
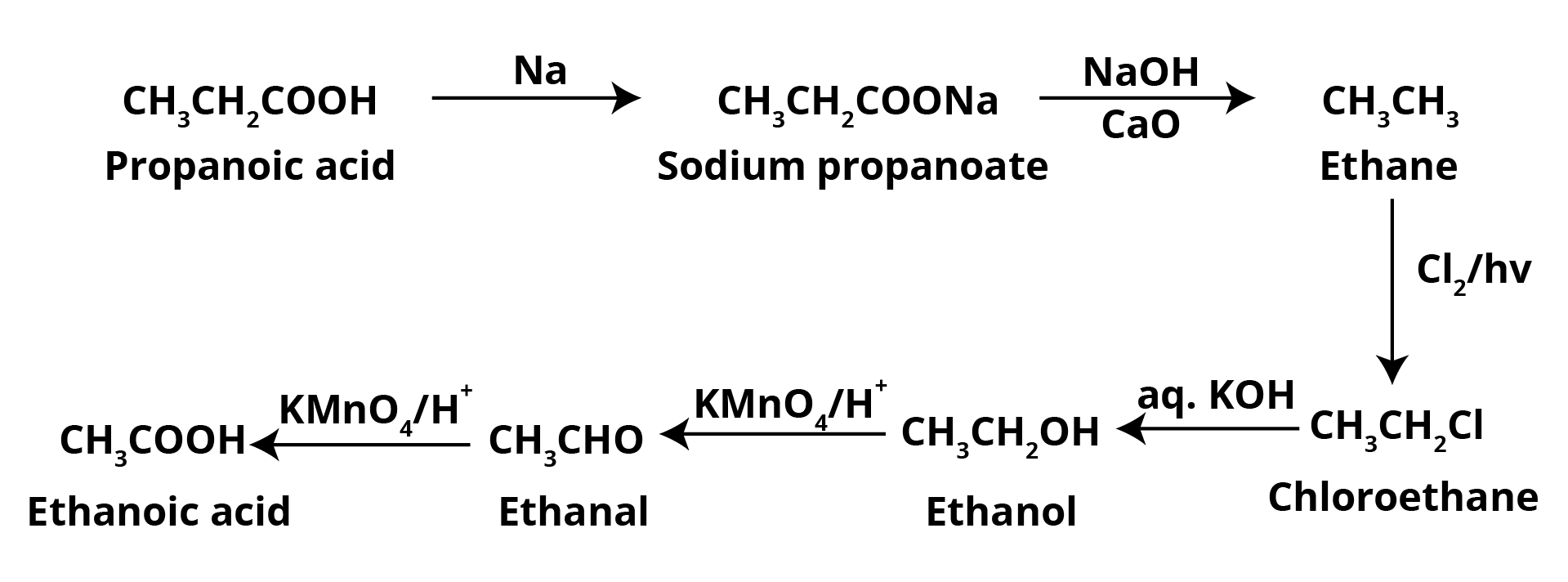
Key Points to Remember: Iodoform tests are the essential tests for the determination of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Solved Examples from Previous Year Question Papers
Question 1: To prepare a pure sample of n-hexane using sodium metal as one reactant, the other reactant will be
(a) n-propyl bromide
(b) Ethyl bromide and n-butyl bromide
(c) Ethyl chloride and n-butyl chloride
(d) Methyl bromide and n -pentyl chloride
Solution:
According to the reaction of Wurtz,
2CH3CH2CH2Br + 2Na− → CH3(CH2)4CH3 + 2NaBr.As a result, (a) is the correct response.
Question 2: Sodium acetate can be converted to ethane by
(a) Heating with LiAlH4
(b) Electrolysing its aqueous solution
(c) Heating with soda lime
(d) Heating with calcium acetate
Solution:
The reaction given in the question,
$2CH_3COONa \ + \ 2H_2O \ \overset{\text{Electrolysis}}{\rightarrow} \ CH_3-CH_3 + 2CO_2 + 2NaOH + H_2$Hence, the given answer is (b) Electrolysing its aqueous solution.
Question 3: Which of the following is oxidised by KMnO4
(a) Methane
(b) Pentane
(c) Isobutane
(d) Neopentane
Solution:
The reaction asked in the above question when trying with isobutane is:
$\left ( CH_3\right )_3CH \ \overset{KMnO_4}{\rightarrow} \ \left ( CH_3 \right )_3C-OH$.As a result, (c) is the correct response.
Practice Organic Chemistry Conversions Questions
Question 1: A nitrogenous substance X is treated with HNO2, and the resulting product is then treated with NaOH solution, resulting in a blue coloration. X can be any nitrogenous substance.
(a) CH3CH2NH2
(b) CH3CH2NO2
(a) CH3CH2ONO
(a) (CH3)2CHNO2
Answer: (a) (CH3)2CHNO2
Question 2: At room temperature, the molecule that interacts with Lucas reagent the fastest is
(a) Butan-1-ol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) 2-methylpropan-1-ol
(d) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Answer: (d) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Conclusion
If you understand organic molecules and reactions, organic conversions are simple. To carry out an organic conversion, we must first figure out which molecules are required for each step. We frequently shift our focus from the back (product) to the front (service) (initial reactant). Organic chemistry conversions chart pdf can be prepared for examination preparation based on different types of reactions and the interconnections between them.
FAQs on NEET Chapter Page - Differentiations & Conversions - Organic Chemistry
1. In organic chemistry, what are the four types of reactions?
Additions, eliminations, replacements, and rearrangements are the four main reaction classes. The number of -bonds in the substrate molecule rise in an additional reaction, usually at the price of one or more -bonds.
2. What is the difference between a reagent and a substrate?
A molecule that serves as a reactant in a process is referred to as a substrate. The enzyme operates on a molecule called a substrate. The substrate is transformed into a product by the action of enzymes. A reagent is a chemical molecule that can be a single substance or a combination of substances.
3. In organic chemistry, what is conversion?
An organic conversion is a process of converting one organic chemical to another organic compound utilising one or more other organic compounds or reagents in a single or several processes. Questions about organic conversions play an essential part in organic chemistry. Class 12 organic chemistry conversions are difficult questions to solve in exams. Organic conversions are simple if you understand organic compounds and reactions. To perform an organic conversion, we must first determine which molecules are necessary for each step.
4. What is the procedure for converting propanol to propene?
In the presence of peroxide, combine propene with hydrogen bromide. Propan-1-ol is obtained by adding an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide to the resulting and heating it. Propene–2–ol is formed when propene is treated with water in the presence of an acid as a catalyst.























