Drainage Questions and Answers for Class 9 Students
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 3 Drainage - 2025-26
1. What topics are covered in Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3, Drainage?
These NCERT Solutions provide step-by-step answers for all the exercise questions in Chapter 3, Drainage. The key topics covered include India's major river systems (both Himalayan and Peninsular), different drainage patterns, the concept of a water divide, the formation and importance of lakes, the role of rivers in the economy, and the causes and effects of river pollution.
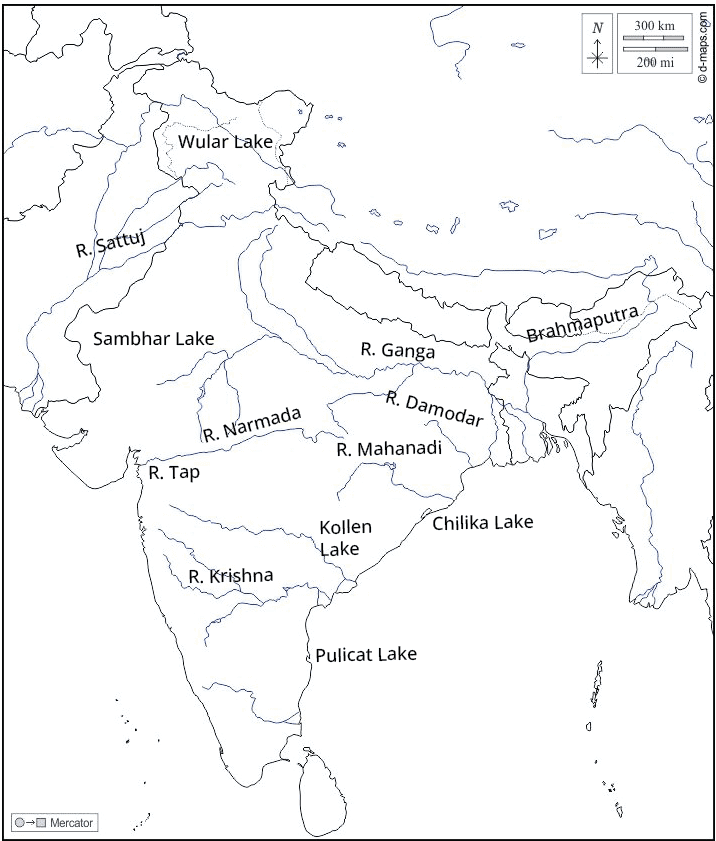
2. How do these NCERT Solutions help in solving the map-based questions for the Drainage chapter?
The solutions provide clear guidance for the map-pointing tasks in the NCERT textbook. They help you accurately identify and mark major rivers like the Ganga, Brahmaputra, Narmada, and Godavari, as well as significant lakes such as Wular, Chilika, and Pulicat. Following these solutions ensures you learn the correct locations as per the CBSE curriculum.
3. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 3 explain the main differences between Himalayan and Peninsular rivers?
The solutions provide a clear, point-wise comparison to help you answer this question effectively. They explain that:
- Origin: Himalayan rivers originate from snow-clad mountains and are perennial, while Peninsular rivers are mostly rain-fed and seasonal.
- Course: Himalayan rivers have long, meandering courses and form large deltas, whereas Peninsular rivers have shorter, straighter courses and often form estuaries.
- Basins: The solutions clarify that Himalayan rivers have larger drainage basins compared to their Peninsular counterparts.
4. Why is a step-by-step answering method, as shown in the solutions, important for explaining different drainage patterns?
A step-by-step method is crucial because drainage patterns are a direct result of the region's topography and rock structure. The solutions break down the logic for each pattern:
- Dendritic: Explained as a tree-branch-like pattern that develops on gentle slopes with uniform rock types.
- Trellis: Shown to form where hard and soft rocks exist parallel to each other.
- Radial: Clarified as a pattern where streams flow in different directions from a central peak, like a dome.
5. What is the correct way to define a 'water divide' as per the NCERT exercise questions?
According to the solutions for the NCERT exercises, a water divide is defined as any elevated area, such as a mountain or an upland, that separates two distinct drainage basins. The solutions explain that water flowing on one side of the divide enters one river system, while water on the other side flows into another, helping to clearly demarcate the catchment areas of different rivers.
6. Beyond just listing facts, how do the NCERT solutions help in comparing the economic importance of rivers versus lakes?
The solutions guide you to form a comparative analysis. While both are important, the answers highlight their distinct roles:
- Rivers are crucial for generating hydroelectricity, large-scale irrigation through canals, and inland navigation, forming the backbone of agricultural economies.
- Lakes are vital for regulating river flow, moderating climate, preserving aquatic ecosystems, and promoting tourism. The solutions help you structure an answer that compares these unique contributions rather than just stating them separately.
7. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 updated for the 2025-26 CBSE session?
Yes, all NCERT Solutions provided by Vedantu, including those for Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 (Drainage), are meticulously prepared by subject experts to align with the latest CBSE guidelines and syllabus for the 2025-26 academic year. This ensures the answers are accurate, relevant, and follow the current curriculum standards.
8. While solving questions on river pollution, what common mistakes do these NCERT solutions help students avoid?
Students often list causes of pollution without explaining the impact. These solutions help you avoid this by structuring answers that connect cause and effect. For example, they clarify how industrial effluents lead to the death of aquatic life, and how untreated domestic sewage increases biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), making the water unfit for use. This ensures a comprehensive and scientifically accurate answer.
9. How do the NCERT solutions for this chapter explain the formation of different types of lakes in India?
The solutions provide clear explanations for the formation of various lakes as asked in the textbook exercises. They describe how oxbow lakes are formed by meandering rivers, how lagoons like Chilika are formed by coastal deposition, and how glacial lakes are a result of glacier movement. For each type, the solutions offer a concise definition and a relevant example, making the concept easy to understand and remember.
10. How does solving the NCERT questions for the Drainage chapter help in understanding other Social Science topics?
Mastering the concepts in this chapter through the NCERT solutions provides a strong foundation for other topics. Understanding river systems is essential for studying India's climate (Chapter 4), as rivers influence weather patterns. It is also directly linked to agriculture and the economy, as river plains are the most fertile and densely populated regions. The solutions help build these crucial inter-disciplinary connections.