Stepwise Answers and Physical vs Chemical Changes Explained
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 5 The World Of Metals And Non-Metals - 2025-26
1. What are physical and chemical changes?
Physical and chemical changes are two types of changes observed in science, especially in NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 5.
Physical Change:
- No new substance is formed
- Often reversible (e.g., melting ice)
- Properties like shape or state may change
Chemical Change:
- New substance(s) are produced
- Generally irreversible (e.g., rusting of iron)
- Accompanied by changes in colour, heat, gas, or precipitate
Understanding these changes helps in differentiating between various processes around us, which is crucial for CBSE exams.
2. How to differentiate between physical and chemical changes?
To differentiate, observe the outcome and process characteristics:
Physical Changes:
- No new substance formed
- May be reversible
- Change mainly in state, shape, or size
Chemical Changes:
- Accompanied by production of new substance(s)
- Usually irreversible
- Signs: change in colour, formation of gas, heat, or precipitate
Use these criteria in your NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 answers for full CBSE marks.
3. Is burning a physical or chemical change?
Burning is a chemical change because it forms new substances and cannot be reversed.
Key points:
- Produces new substances (ash, gases like CO₂)
- Heat and light are released
- Original material is changed permanently
This concept is explained in detail in Class 7 Science Chapter 5: Changes Around Us.
4. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in answers?
Yes, in CBSE Class 7 Science exams, including diagrams and definitions is important for full marks.
- Accurate, labelled diagrams can fetch step marks
- Definitions help in answering theory-based questions confidently
- Follow NCERT language and marking guidelines
Always check the question type: diagrams are necessary for practical/process questions.
5. What are the most important topics from Class 7 Science Chapter 5?
Key topics for Chapter 5: Changes Around Us include:
- Definition and examples of physical and chemical changes
- Differences between the two
- Everyday examples (dissolving salt, burning paper, melting wax, rusting)
- Indicators of chemical change (gas, colour change, precipitate)
- Effects of heating and cooling
Focus on these areas to prepare well for board exams and NCERT-based questions.
6. How to write stepwise NCERT answers to score full marks?
To score full marks in CBSE and NCERT exercises:
- Write in clear, sequential steps
- Start with definitions or key statements
- Give relevant examples from the textbook
- Use neat diagrams and labels where required
- Follow the CBSE word limit and marking scheme
Use the stepwise format in your Class 7 Science Chapter 5 answers for best results.
7. Where can I download the Class 7 Science Chapter 5 NCERT Solutions PDF?
You can download free PDF NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 5 from trusted educational platforms.
- Look for the 'Free PDF Download' button on the solutions page
- PDFs are useful for offline revision and last-minute preparation
- Ensure the solutions match the 2025–26 CBSE syllabus
8. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 7 Science exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science provide a strong foundation and cover almost all exam questions.
- Syllabus-aligned answers
- Stepwise explanations and examples
- Include definitions, diagrams, and revision tips
- For higher scores, practice with additional worksheets and exemplars
9. How do I structure long answers in CBSE Science to get better marks?
For long answers in Class 7 Science Chapter 5:
- Begin with an introduction or definition
- Use headings, sub-points, and examples
- Include relevant diagrams and label them clearly
- Summarise with a concluding line
- Use correct scientific terms and CBSE keywords
Organised answers help you secure full or stepwise marks.
10. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong?
Yes, in CBSE exams, partial marks are awarded for correct steps or methods shown, even if the final answer is incorrect.
- Write every step clearly
- Show diagrams, calculations, and key reasoning
- Attempt all parts for best scoring
This method encourages thorough understanding and rewards effort.
11. How do I learn diagrams and map labelling for this chapter?
To master diagrams in Class 7 Science Chapter 5:
- Practice drawing labelled diagrams as in NCERT
- Use sharp pencils and clear labels
- Learn standard conventions (arrows, titles)
- Refer to solved NCERT examples
Accurate diagrams help gain easy marks in board and school exams.
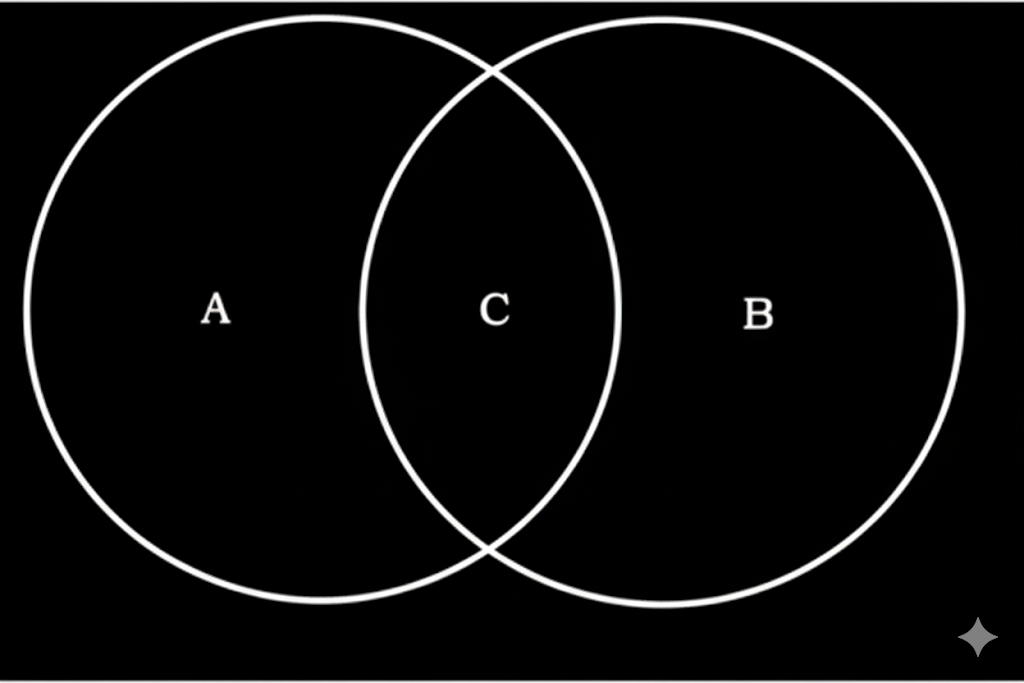
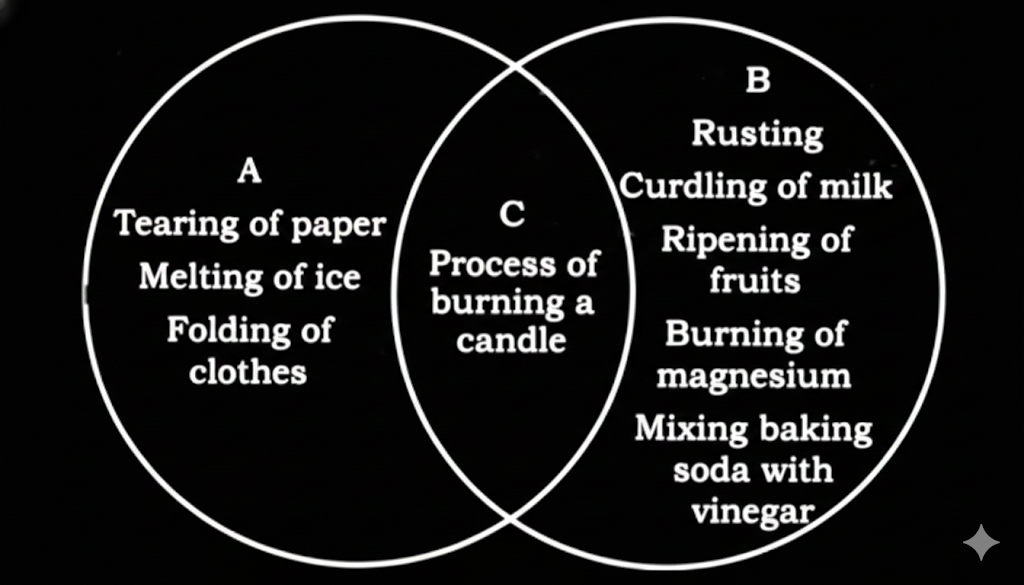
12. What are some examples of physical and chemical changes from Class 7 Science Chapter 5?
Examples found in Chapter 5 NCERT Solutions:
Physical Changes:
- Melting of ice
- Dissolving salt in water
- Tearing paper
Chemical Changes:
- Burning of paper
- Rusting of iron
- Formation of curd from milk
Use these in answers to demonstrate understanding during exams.