Step-by-Step Answers for NCERT Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 (Weigh It Pour It)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 Weigh It Pour It - 2025-26
1. What is included in NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 'Weigh It Pour It'?
NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 include stepwise answers for all textbook exercises, helping students master weights and measurements.
Key features:
- Exercise-wise solutions with detailed explanations
- Important diagrams and examples
- Exam-ready definitions and formulae
- Focus on CBSE 2025–26 marking schemes
- Tips to score full marks and improve conceptual clarity
2. How can I download the free PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths Chapter 8?
You can download the free PDF of Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 'Weigh It Pour It' solutions for offline study.
Steps:
- Visit the NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 page on trusted platforms
- Look for the 'Free PDF Download' button or link
- Click to get the chapter-wise solutions for practice anytime
3. How to write stepwise NCERT answers to score full marks in Class 4 Maths Chapter 8?
To score full marks in Chapter 8, write stepwise answers by:
- Starting with a clear statement of what is to be solved
- Showing each calculation or reasoning step in order
- Including any required units (grams, kilograms, litres, millilitres)
- Drawing neat diagrams where asked
- Writing final answers clearly, underlined if possible
- Using keywords from definitions and textbook terminology
4. Are diagrams and definitions compulsory in NCERT Maths answers for Chapter 8 'Weigh It Pour It'?
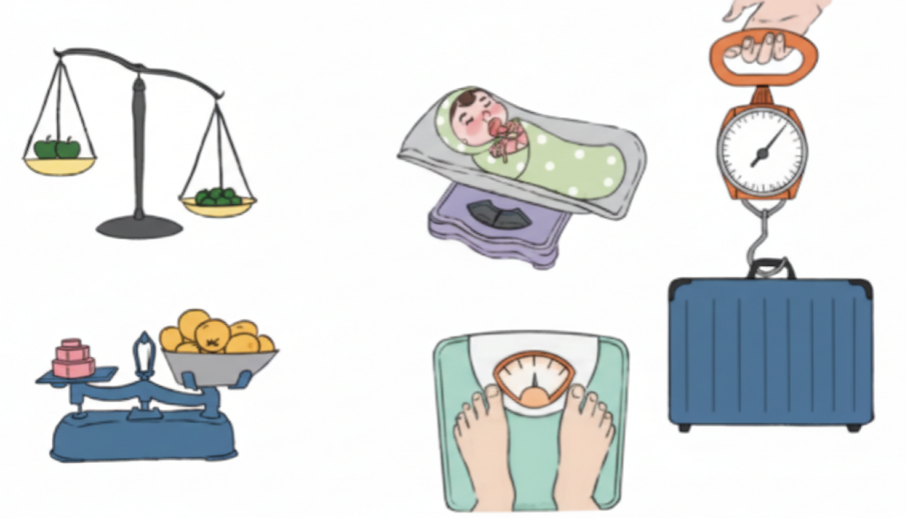
Yes, in Class 4 Maths Chapter 8, diagrams and definitions are essential to:
- Accurately represent weighing and measuring instruments
- Clarify answers and boost marks
- Demonstrate understanding of weight and capacity concepts
Always draw neat, labelled diagrams and write exam-ready definitions in your answers.
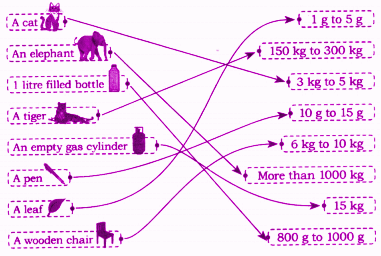
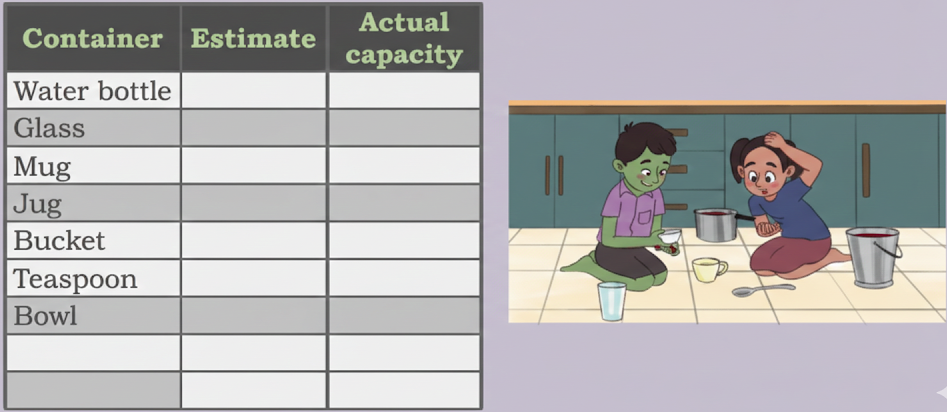
5. What are the most important topics and questions in Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 for CBSE exams?
The most important topics in Chapter 8 'Weigh It Pour It' are:
- Units of measurement (kg, g, L, mL)
- Converting between units (e.g., grams to kilograms, millilitres to litres)
- Reading scales on balances and containers
- Solving real-life word problems involving weights and capacity
Practice sample questions on conversion and practical measurement for best results.
6. Where can I find exercise-wise solutions for Intext and Back Exercises of Class 4 Maths Chapter 8?
You can find exercise-wise NCERT Solutions for both Intext and Back Exercises of Chapter 8 on dedicated educational portals.
- Each exercise is solved step-by-step
- Solutions match the latest CBSE syllabus (2025–26)
- Both practice problems and word problems are covered
- Answers follow the CBSE marking scheme format
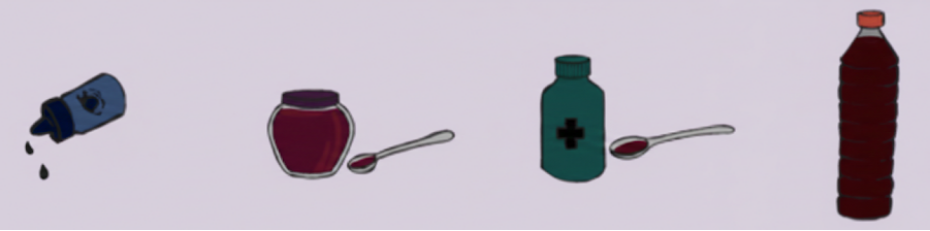
7. What definitions and formulae should I revise for NCERT Class 4 Maths Chapter 8?
Revise key definitions and formulae for Chapter 8 such as:
- Unit of mass: Kilogram (kg), Gram (g)
- Unit of capacity: Litre (L), Millilitre (mL)
- Conversion formulae:
- 1 kg = 1000 g
- 1 L = 1000 mL
- Measuring instruments: balance, measuring cup, jug, glass
Learning these will help in quizzes and exams.
8. How should long answers be structured for CBSE marking in Chapter 8?
To structure long answers for full CBSE marks in Chapter 8, follow these steps:
- Begin with an introduction or definition of the concept
- Break down your answer into bullet points or numbered steps
- Use diagram/labelled illustration where required
- Support your working with examples or calculations
- End with a clear, concise conclusion
9. Do examiners give partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong in CBSE Class 4 Maths?
Yes, CBSE marking scheme often awards step marks for showing the correct method:
- Each correct intermediate step gets partial marks
- Final answer must be correct for full marks
- Neat presentation and proper units add value
- Always show your working to maximise scores, even if unsure of the final answer
10. How can I quickly revise Class 4 Maths Chapter 8 before exams?
To revise Chapter 8 'Weigh It Pour It' efficiently:
- Go through key definitions and conversion formulae
- Practice exercise-wise important questions
- Review labelled diagrams (balance, containers)
- Solve a sample paper or mock test for time management
- Use flash notes and 1-day revision planners if available