




Essential Geometry Terms and Problem-Solving Strategies
Introduction
2D forms like triangles, squares, rectangles, and circles are examples of flat shapes in plane geometry. Solid geometry also refers to three-dimensional forms like cubes, cuboids, etc. as solids. Fundamental geometry is built on the coordinate geometry of points, lines, and planes. The area of mathematics known as geometry is concerned with the dimensions, sizes, forms, and angles of a wide range of common objects. Geometry comes from the Ancient Greek terms "geo" and "metron," which both imply "measuring." There are two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional forms in Euclidean geometry.
Geometry's many sorts of forms make it easier for us to comprehend the shapes we encounter every day. Geometric ideas allow us to compute the area, perimeter, and volume of forms.
Basic Terms Used in Geometry are:
Line
Angle
Point
On a plane, a point is a particular area or position. Usually, a dot represents them. It's important to understand that a point is not an object, but rather a position. Remember that a point has just one location and, ideally, no dimensions.
Line
The line has no thickness, is straight (no curves), and goes in both directions without coming to an end (infinitely). It is significant to remember that an unlimited number of points come together to form a line.
Line Segment - A line is referred to as a Line Segment if it has a starting point and an ending point.
Ray - If there is a starting point and no ending point in a line then it becomes a ray.
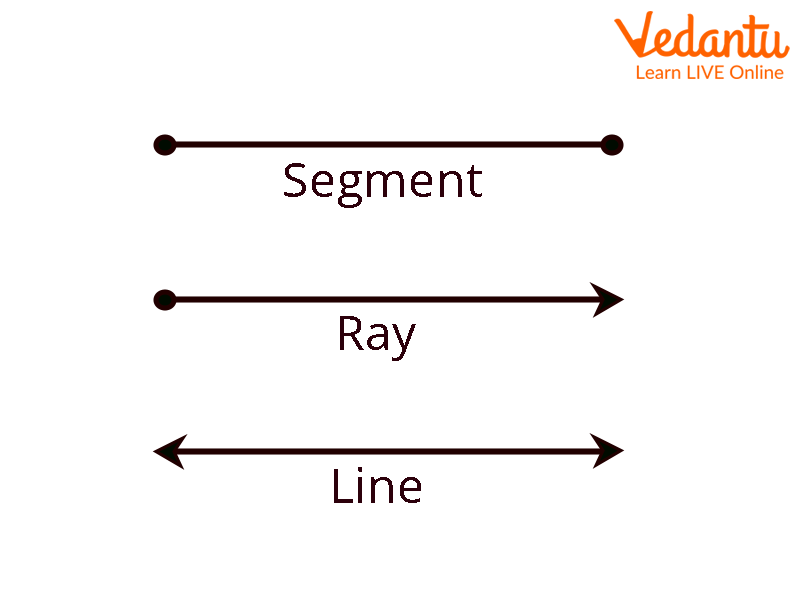
Line segment, Ray, Line
Class 5 Shapes and Angles
Two rays that share a termination and are collectively referred to as the angle's sides and vertices form an angle in planar geometry.
Acute Angle - A Acute angle is a smaller angle than a straight angle, i.e. It can be in the \[0^\circ \] to \[90^\circ \].
Obtuse Angle: Obtuse angles are those that are greater than \[90^\circ \] but less than \[180^\circ \].
Right Angle: A right angle is a \[90^\circ \]of angle.
Straight Angle - A straight angle is an angle created by a straight line, and it has a \[180^\circ \].
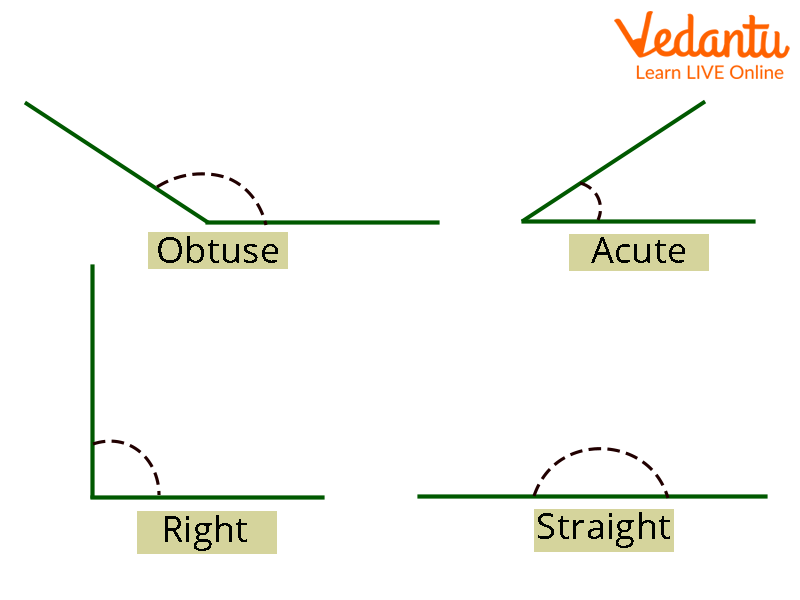
Angles
Basic Geometrical Figures and Shapes
Some basic geometrical figures are given below:
1. Triangle
The polygonal shape known as a triangle has three sides, three edges, and three vertices. Additionally, the total of its interior angles is \[180^\circ \].
2. Circle
A circle is a collection of all points that are all at the same set distance from a common central point.
3. Square
The quadrilateral known as the "square" has four equal sides and angles, and each of its vertices has a \[90^\circ \] angle.
4. Rectangle
The internal angles of a rectangle, which has four sides, are all exactly 90 degrees. At each corner or vertex, the two sides come together at a straight angle. The rectangle differs from a square because its two opposite sides are of equal length.
5. Polygon
A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional structure with straight line segments in mathematics. It does not have three dimensions. There aren't any curved surfaces in a polygon. A polygon must have three sides at a minimum. Only at its terminal must each side of a line segment cross another line segment.
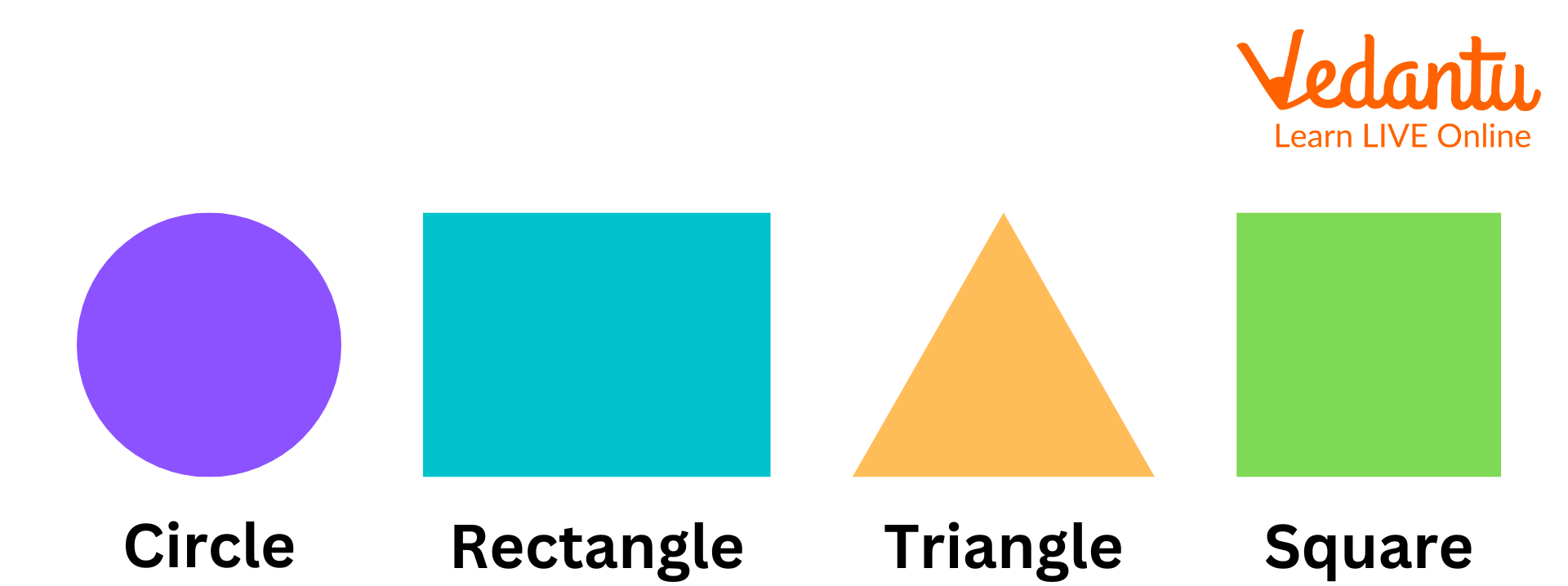
Different Geometrical Shapes
Conclusion:
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that focuses on measuring, describing, and relating points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids. The four fundamental components of geometry are a point, a line, an angle, and a plane. Flat forms in plane geometry include 2-dimensional shapes including triangles, squares, rectangles, and circles. Three-dimensional forms like a cube, cuboid, cone, etc. are also referred to as solids in solid geometry. The coordinate geometry of points, lines, and planes is the foundation of fundamental geometry.
Solved Examples
1. What is the total angle of the triangle?
Ans: The Total of angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
2. What kind of shape is a cone?
Ans: A cone is a solid, three-dimensional shape having a single vertex and a circular base. From the base to the vertex, the cone's surface narrows.
3. Give a few differences between a square and a rectangle.
Ans:
FAQs on Geometry for Class 5: Key Concepts and Examples
1. What is geometry for class 5?
In class 5, geometry is a branch of mathematics that introduces students to the study of shapes, sizes, and the properties of figures. At this level, students learn about basic geometric concepts such as points, lines, angles, and shapes. The focus is on helping young learners visualize and understand how these forms appear in everyday life and solve simple geometry-related problems under guided instruction as offered in Vedantu’s interactive online classes.
2. What is fifth grade geometry?
Fifth grade geometry builds a foundation for understanding geometric ideas required for higher mathematics. Usually, it includes:
- Identifying and classifying basic shapes (triangles, rectangles, circles, etc.)
- Understanding the properties of shapes such as sides, angles, and symmetry
- Measuring and drawing angles using protractors
- Learning about perimeter and area
3. How to teach geometry to 5th graders?
Effective methods to teach geometry to 5th graders include:
- Using visual aids and hands-on activities to explore shapes and figures
- Incorporating games, puzzles, or drawing exercises to make concepts more interactive
- Breaking down abstract concepts into simple, relatable examples
- Practicing real-life applications like measuring classroom objects or observing patterns in nature
4. What are the 7 basic geometric forms?
The 7 basic geometric forms commonly introduced in class 5 geometry are:
- Point
- Line
- Line Segment
- Ray
- Angle
- Polygon (e.g., triangle, square, rectangle)
- Circle
5. What types of shapes are taught in geometry for class 5?
In class 5 geometry, students are introduced to a variety of 2D and 3D shapes, including:
- 2D Shapes: Triangle, square, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezium, rhombus, circle
- 3D Shapes: Cube, cuboid, sphere, cylinder, cone
6. How do Vedantu’s online classes help students master geometry in grade 5?
Vedantu's online classes make grade 5 geometry engaging and easy to understand through:
- Interactive live sessions with expert teachers
- Step-by-step explanations and visuals
- Personalized doubt-solving sessions
- Practice assignments and quizzes
- Real-life examples and activities to build spatial reasoning
7. What are some real-world applications of geometry for 5th graders?
Geometry for 5th graders relates to everyday life in many ways, such as:
- Measuring the area and perimeter of a garden or room
- Identifying shapes in architecture and household items
- Understanding symmetry in art or nature
- Arranging objects based on geometric patterns
8. How can parents support 5th graders in learning geometry at home?
Parents can enhance their child’s geometry learning at home by:
- Discussing everyday geometric shapes while shopping or cooking
- Encouraging drawing and labeling of various forms
- Providing opportunities for hands-on projects like making models or origami
- Using Vedantu’s worksheets and online quizzes for extra practice
9. What key skills do students develop through geometry lessons in class 5?
Through geometry lessons in class 5, students develop:
- Visual-spatial skills
- Logical reasoning
- Problem-solving ability
- Understanding of measurement and calculation
- Critical thinking for analyzing patterns and relationships
10. What topics are covered under class 5 geometry according to the latest curriculum?
The latest class 5 geometry syllabus typically includes:
- Types of lines and angles
- Properties of triangles and quadrilaterals
- Circles and their parts (radius, diameter, chord)
- Symmetry and patterns
- Introduction to perimeter and area formulas, such as:
Perimeter of a rectangle: $P = 2(l + b)$
Area of a rectangle: $A = l \times b$

















