
Write short notes on the following: carbylamine reaction.
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Carbylamine reaction is used as a test for the identification of primary amines. This test is also referred to as a Saytzeff's isocyanide test. This reaction cannot be used for the identification of secondary and tertiary amines.
Complete step by step answer:
When we heat aliphatic and aromatic primary amines in presence of ethanolic potassium hydroxide and chloroform, carbylamines or isocyanides are generated. The carbylamines have an unpleasant odour. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to this carbylamine reaction test.
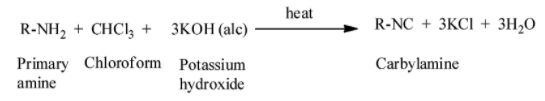
The mechanism of the carbylamine reaction is given as:
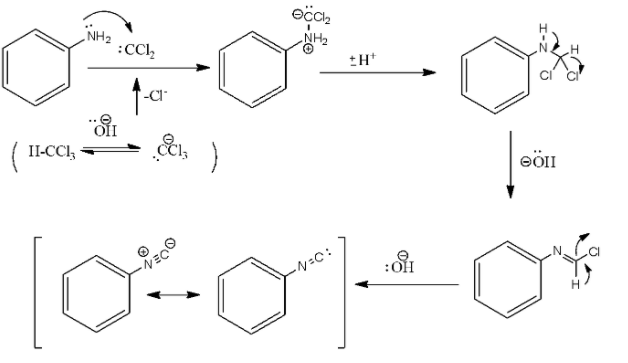
In the above reaction, the addition of the amine to the dichlorocarbene, which is a reactive intermediate that is generated by the chloroform dehydrohalogenation. The formation of the isocyanide involves two successive base-mediated dehydrochlorination.
Additional information:
Carbylamine reaction helps us in testing and distinguish primary amine from that of the secondary and the tertiary amines. We need two protons in this reaction which are provided by the primary amines, but the secondary and the tertiary amines do not give two protons, so they do not show this carbylamine test. Also, secondary and tertiary amines do not form the isocyanides when they are made to undergo the carbylamine reaction, as they have more than one alkyl group that hinders the approach of the group.
Note:
Students may get confused regarding which amine will respond to the carbylamine test. It is important to note that only primary amines respond to this reaction. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to the carbylamine reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
When we heat aliphatic and aromatic primary amines in presence of ethanolic potassium hydroxide and chloroform, carbylamines or isocyanides are generated. The carbylamines have an unpleasant odour. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to this carbylamine reaction test.

The mechanism of the carbylamine reaction is given as:

In the above reaction, the addition of the amine to the dichlorocarbene, which is a reactive intermediate that is generated by the chloroform dehydrohalogenation. The formation of the isocyanide involves two successive base-mediated dehydrochlorination.
Additional information:
Carbylamine reaction helps us in testing and distinguish primary amine from that of the secondary and the tertiary amines. We need two protons in this reaction which are provided by the primary amines, but the secondary and the tertiary amines do not give two protons, so they do not show this carbylamine test. Also, secondary and tertiary amines do not form the isocyanides when they are made to undergo the carbylamine reaction, as they have more than one alkyl group that hinders the approach of the group.
Note:
Students may get confused regarding which amine will respond to the carbylamine test. It is important to note that only primary amines respond to this reaction. Secondary and tertiary amines do not respond to the carbylamine reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




