
Write Faraday’s second law of electrolysis
Draw labelled diagram of standard hydrogen electrode
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: Faraday’s law is the basic law of electromagnetism which helps to predict how a magnetic field would interact with an electric current to produce an electromotive force. Moreover, a standard hydrogen electrode is a redox electrode which forms the basis of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potentials.
Complete step by step answer:
Faraday’s law was proposed in the year 1831 by a physicist and chemist named Michael Faraday. This further consists of two laws. The first law describes the induction of emf in a conductor and the second law quantifies the emf produced in the conductor. Now let’s discuss Faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction in detail.
Now, the second law states that the induced emf in a coil is equal to the rate of change of the flux linkage. Further, the flux is the product of the number of turns in the coil and the flux associated with the coil. The formula is given below:
${\rm E} = - N\dfrac{{\Delta \phi }}{{\Delta t}}$
Where, E is the electromotive force
N is the number of turns,
$\phi $ is the magnetic flux
Moreover, the negative sign indicates that the direction of the induced emf and change in the direction of magnetic fields have the opposite signs.
Now, we will discuss the standard hydrogen electrode. Basically, this electrode is used as a reference electrode while calculating the standard electrode potential of a half cell. Its standard electrode potential is declared to be zero at a temperature of 298K because it acts as a reference for comparison with any other electrode. The redox half-cell of the standard hydrogen electrode is where the following reaction takes place:
$2{H^ + }(aq) + 2{e^ - } \to {H_2}(g)$
This reaction generally takes place on a platinum electrode. The diagram is as shown:
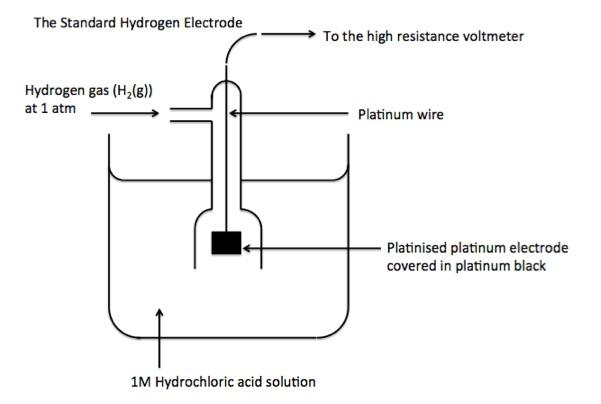
Note:
Platinum is used in the hydrogen electrode due to many reasons. It is a relatively inert metal which does not corrode easily and has a catalytic quality which further promotes the proton reduction. Moreover, it also improves the reaction kinetics by adsorbing hydrogen at the surface.
Complete step by step answer:
Faraday’s law was proposed in the year 1831 by a physicist and chemist named Michael Faraday. This further consists of two laws. The first law describes the induction of emf in a conductor and the second law quantifies the emf produced in the conductor. Now let’s discuss Faraday’s second law of electromagnetic induction in detail.
Now, the second law states that the induced emf in a coil is equal to the rate of change of the flux linkage. Further, the flux is the product of the number of turns in the coil and the flux associated with the coil. The formula is given below:
${\rm E} = - N\dfrac{{\Delta \phi }}{{\Delta t}}$
Where, E is the electromotive force
N is the number of turns,
$\phi $ is the magnetic flux
Moreover, the negative sign indicates that the direction of the induced emf and change in the direction of magnetic fields have the opposite signs.
Now, we will discuss the standard hydrogen electrode. Basically, this electrode is used as a reference electrode while calculating the standard electrode potential of a half cell. Its standard electrode potential is declared to be zero at a temperature of 298K because it acts as a reference for comparison with any other electrode. The redox half-cell of the standard hydrogen electrode is where the following reaction takes place:
$2{H^ + }(aq) + 2{e^ - } \to {H_2}(g)$
This reaction generally takes place on a platinum electrode. The diagram is as shown:

Note:
Platinum is used in the hydrogen electrode due to many reasons. It is a relatively inert metal which does not corrode easily and has a catalytic quality which further promotes the proton reduction. Moreover, it also improves the reaction kinetics by adsorbing hydrogen at the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




