
Write chemical reaction to affect the following transformations:
Cyclohexene to hexane −1,6− dioic acid
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The carbon-carbon double bond in cyclohexene can be oxidised by Potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) on heating under acidic conditions. This results in the formation of hexane-1,6-dial which is further oxidised by Potassium permanganate to hexane-1,6-diol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
To convert cyclohexene into hexane-1,6-dioic acid, the carbon-carbon double bond must oxidise as well as cleave. Only then will the cyclic alkene convert into a straight chain. Such reactions can be performed by concentrated Potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) under acidic conditions on heating.
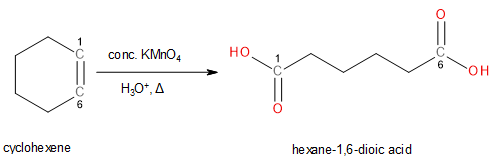
Image: Conversion of cyclohexane to hexane-1,6-dioic acid
In the first step of this reaction, the permanganate ion (\[MnO_4^ - \]) from Potassium permanganate reacts with the carbon-carbon double bond of cyclohexene in a cycloaddition reaction to form a cyclic manganate ester as shown below:

Image: Formation of cyclic manganate ester through cycloaddition of permanganate ion to cyclohexene.
The cyclic manganate ester so formed is unstable and under hot conditions, in the presence of an acid, the single bond between C1 and C6 cleaves, and this results in the formation of hexane-1,6-dial as shown below:
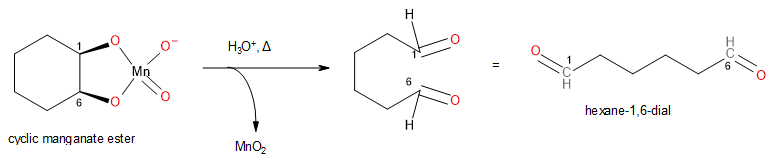
Image: Conversion of cyclic manganate ester to hexane-1,6-dial.
Since the Potassium permanganate is concentrated, the reaction does not stop with the formation of hexane-1,6-dial. Instead, hexane-1,6-dial is further oxidized by Potassium permanganate into hexane-1,6-dioic acid (which is also known as Adipic acid).
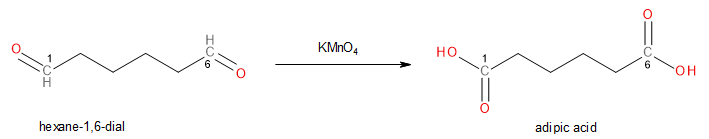
Image: Oxidation of Hexane-1,6-dial to Adipic Acid.
Thus, cyclohexene can be converted into hexane-1,6-dioic acid by heating with concentrated Potassium permanganate under acidic conditions.
Note: It is very important to remember that the above-mentioned reaction occurs only under hot conditions in the presence of an acid. If the reaction is carried out under cold conditions in a basic medium, the cyclic manganate ester will convert into a syn-diol instead of an aldehyde. This reaction is called syn-dihydroxylation.
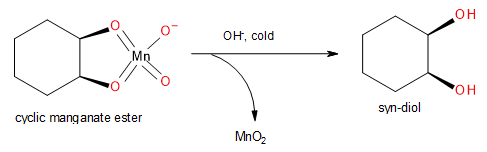
Image: Syn-Dihydroxylation of Cyclic Manganate Ester.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
To convert cyclohexene into hexane-1,6-dioic acid, the carbon-carbon double bond must oxidise as well as cleave. Only then will the cyclic alkene convert into a straight chain. Such reactions can be performed by concentrated Potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) under acidic conditions on heating.

Image: Conversion of cyclohexane to hexane-1,6-dioic acid
In the first step of this reaction, the permanganate ion (\[MnO_4^ - \]) from Potassium permanganate reacts with the carbon-carbon double bond of cyclohexene in a cycloaddition reaction to form a cyclic manganate ester as shown below:

Image: Formation of cyclic manganate ester through cycloaddition of permanganate ion to cyclohexene.
The cyclic manganate ester so formed is unstable and under hot conditions, in the presence of an acid, the single bond between C1 and C6 cleaves, and this results in the formation of hexane-1,6-dial as shown below:

Image: Conversion of cyclic manganate ester to hexane-1,6-dial.
Since the Potassium permanganate is concentrated, the reaction does not stop with the formation of hexane-1,6-dial. Instead, hexane-1,6-dial is further oxidized by Potassium permanganate into hexane-1,6-dioic acid (which is also known as Adipic acid).

Image: Oxidation of Hexane-1,6-dial to Adipic Acid.
Thus, cyclohexene can be converted into hexane-1,6-dioic acid by heating with concentrated Potassium permanganate under acidic conditions.
Note: It is very important to remember that the above-mentioned reaction occurs only under hot conditions in the presence of an acid. If the reaction is carried out under cold conditions in a basic medium, the cyclic manganate ester will convert into a syn-diol instead of an aldehyde. This reaction is called syn-dihydroxylation.

Image: Syn-Dihydroxylation of Cyclic Manganate Ester.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




