
Which will form two oximes with $N{H_2}OH$?
(A) $C{H_3}CHO$
(B) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}C{H_3}$
(C) $HCHO$
(D) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_2}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When aldehyde or ketones react with hydroxylamine ($N{H_2}OH$), then oximes are formed. Symmetrical ketones form a single oxime while asymmetrical ketones and aldehydes can form two isomeric oximes.
Complete step by step solution:
An oxime is a chemical compound belonging to the class of imines. General formulas of oximes are $RR'C =$ $NOH$, where R is an alkyl group. If R’ is hydrogen, then oxime formed is aldoxime because an aldehyde reacted with hydroxylamine. If R’ is another organic group, then the oxime is ketoxime because a ketone group reacted with hydroxylamine.
Oximes are generally synthesized by the condensation reaction of aldehydes or ketones with hydroxylamine. This reaction of hydroxylamine with aldehydes/ketones is nucleophilic addition reaction followed by the elimination of a molecule of water. The reaction is reversible and is catalysed by acids. Oxime is a combination of the words oxygen and imine.
Now, the reaction of acetaldehyde that is, $C{H_3}CHO$ with hydroxylamine:
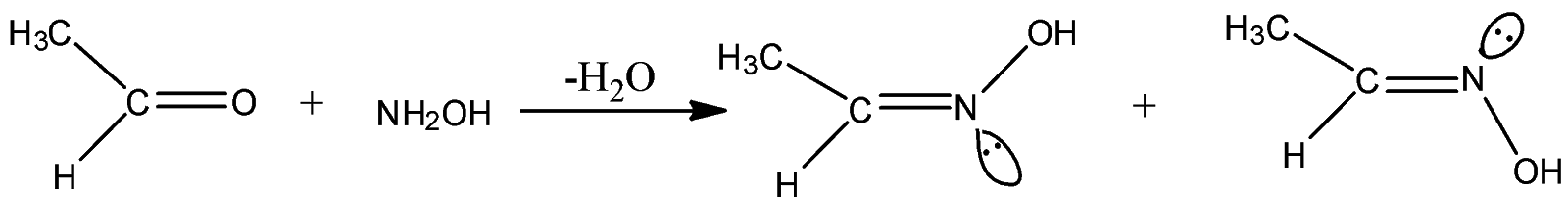
Thus, the product ethanol oxime formed in the reaction has two isomeric forms. This is because the lone pair of nitrogen can occupy two positions in space as can be seen in the above chemical reaction. $HCHO$ is a symmetrical aldehyde, so it will not form isomeric oxime and other options are also incorrect, that is they will not form isomeric oximes.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note: The addition of hydroxylamine to aldehydes or ketones is catalysed by acids. To maintain a controlled acidic medium, these reactions are carried out at an optimum value of pH. Usually, a pH of around 3.5 is needed. Oximes can also be obtained from the reaction of nitriles with the compounds containing an acidic hydrogen atom.
Complete step by step solution:
An oxime is a chemical compound belonging to the class of imines. General formulas of oximes are $RR'C =$ $NOH$, where R is an alkyl group. If R’ is hydrogen, then oxime formed is aldoxime because an aldehyde reacted with hydroxylamine. If R’ is another organic group, then the oxime is ketoxime because a ketone group reacted with hydroxylamine.
Oximes are generally synthesized by the condensation reaction of aldehydes or ketones with hydroxylamine. This reaction of hydroxylamine with aldehydes/ketones is nucleophilic addition reaction followed by the elimination of a molecule of water. The reaction is reversible and is catalysed by acids. Oxime is a combination of the words oxygen and imine.
Now, the reaction of acetaldehyde that is, $C{H_3}CHO$ with hydroxylamine:

Thus, the product ethanol oxime formed in the reaction has two isomeric forms. This is because the lone pair of nitrogen can occupy two positions in space as can be seen in the above chemical reaction. $HCHO$ is a symmetrical aldehyde, so it will not form isomeric oxime and other options are also incorrect, that is they will not form isomeric oximes.
Hence, option (A) is correct.
Note: The addition of hydroxylamine to aldehydes or ketones is catalysed by acids. To maintain a controlled acidic medium, these reactions are carried out at an optimum value of pH. Usually, a pH of around 3.5 is needed. Oximes can also be obtained from the reaction of nitriles with the compounds containing an acidic hydrogen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




