
Which products are obtained when phenyl ethanoate reacts in presence of Anh $AlC{l_3}$ ?
A.$\sigma $ -Ethoxy acetophenone and p-Ethoxy acetophenone.
B.O-Hydroxy acetophenone and p-Hydroxy acetophenone
C.$\sigma $ -Methyl acetophenone and p-Methyl acetophenone
D.$\sigma $ Methoxy acetophenone and p-Methoxy acetophenone.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Phenyl ethanoate is basically the ester of phenol and acetic acid. It can further be produced by decarboxylation of aspirin or by reacting phenol with acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride. Moreover, aluminium chloride is used as a Lewis acid catalyst for a variety of reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
Ester is basically a chemical compound that is derived from an organic or inorganic acid in which hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkyl group. Moreover, esters are a group of chemical compounds which are formed by bonding of an alcohol group with a group of organic acids by losing water molecules.
Now, the products obtained when phenyl ethanoate reacts in presence of Anh. $AlC{l_3}$are o-hydroxy acetophenone and p-hyroxy acetophenone. This is known as Fries Rearrangement. Further, it is an organic rearrangement reaction in which an aryl ester is transformed into a hydroxyl aryl ketone with the help of a Lewis acid catalyst and an aqueous acid.
Moreover, this rearrangement is ortho and para selective i.e. the acyl group attaches itself at the ortho or para positions of the aryl ring. The reaction is as shown:
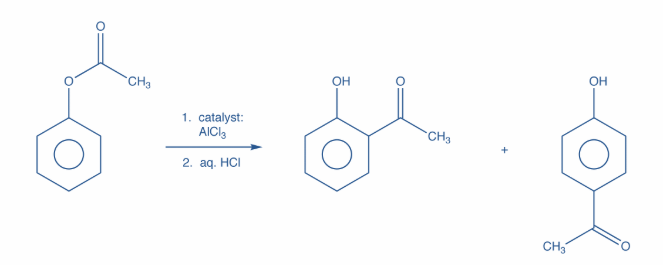
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: There are few limitations of this reaction. Owing to its relatively harsh reaction conditions, only esters with relatively stable acyl components can be used in this reaction. Moreover, the presence of deactivating or meta-directing groups on the aromatic ring results in low yields.
Complete step by step answer:
Ester is basically a chemical compound that is derived from an organic or inorganic acid in which hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkyl group. Moreover, esters are a group of chemical compounds which are formed by bonding of an alcohol group with a group of organic acids by losing water molecules.
Now, the products obtained when phenyl ethanoate reacts in presence of Anh. $AlC{l_3}$are o-hydroxy acetophenone and p-hyroxy acetophenone. This is known as Fries Rearrangement. Further, it is an organic rearrangement reaction in which an aryl ester is transformed into a hydroxyl aryl ketone with the help of a Lewis acid catalyst and an aqueous acid.
Moreover, this rearrangement is ortho and para selective i.e. the acyl group attaches itself at the ortho or para positions of the aryl ring. The reaction is as shown:

Hence, option B is correct.
Note: There are few limitations of this reaction. Owing to its relatively harsh reaction conditions, only esters with relatively stable acyl components can be used in this reaction. Moreover, the presence of deactivating or meta-directing groups on the aromatic ring results in low yields.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




