
Which of these is correct in regards to a magnet?
A) \[\text{Geometric length = 0}\text{.8 times the magnetic length}\]
B) \[\text{Magnetic length = 0}\text{.8 times the geometric length}\]
C) \[\text{Magnetic length = Geometric length}\]
D) \[\text{Geometric length = 10/9 of magnetic length}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A bar magnet consists of two equal and opposite magnetic poles separated by a small distance. Poles are not exactly at the ends. The smallest distance between two poles is known as the effective length and is less than the geometric length. The distance between two magnetic poles is called magnetic length whereas the Geometric length is a measure of the total length of the magnet. Since the magnetic poles are not exactly at the ends, the magnetic length is slightly less than the geometrical length.
Complete step by step solution:
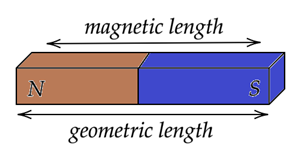
Due to end effects, the poles of a bar magnet are assumed to be slightly inside the ends of the magnet. The distance between the two poles (north and south) gives the magnetic length of the magnet. The actual size of the magnet gives us its geometric length. The magnetic length of a bar magnet is nearly \[\text{0}\text{.8}\] times that of the geometric length, which looks quite valid if you refer to the figure given above.
Hence we can say that \[\text{Magnetic length = 0}\text{.8 times the geometric length}\] or option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: This ratio of the magnetic length to the geometric length remains constant in all situations. It is due to this constant property that when a magnet is cut transversely, the magnetic strength remains constant. The effective length of the magnet is the inter-polar distance of the magnet and is always less than the geometric length of the magnet. Although the actual relationship between them depends on the shape of the magnet.
Complete step by step solution:

Due to end effects, the poles of a bar magnet are assumed to be slightly inside the ends of the magnet. The distance between the two poles (north and south) gives the magnetic length of the magnet. The actual size of the magnet gives us its geometric length. The magnetic length of a bar magnet is nearly \[\text{0}\text{.8}\] times that of the geometric length, which looks quite valid if you refer to the figure given above.
Hence we can say that \[\text{Magnetic length = 0}\text{.8 times the geometric length}\] or option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: This ratio of the magnetic length to the geometric length remains constant in all situations. It is due to this constant property that when a magnet is cut transversely, the magnetic strength remains constant. The effective length of the magnet is the inter-polar distance of the magnet and is always less than the geometric length of the magnet. Although the actual relationship between them depends on the shape of the magnet.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

JEE Main Syllabus 2026: Download Detailed Subject-wise PDF

Other Pages
MOSFET: Definition, Working Principle, Types & Applications

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning

One Day International Cricket- India Vs New Zealand Records and Score

Highest T20 Scores in Cricket: Top Records & Stats 2025




