
Which of the given statement(s) about N, O, P, Q with respect to M is/are correct?
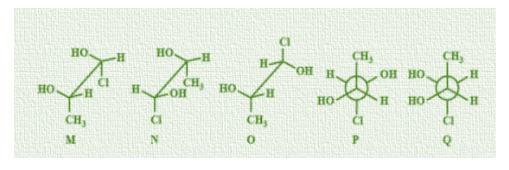
A.M and N are non-mirror image stereoisomers.
B.M and O are identical
C.M and P are enantiomers
D.M and Q are identical
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Stereoisomers are divided into enantiomers and diastereomers. Enantiomers are mirror images and diastereomers are not mirror images but both are non-superimposable with chiral centres. Identical molecules differ from each other only in the spatial orientation of groups in the molecule.
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
Two different molecules are said to be enantiomers if they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have same refractive index, density, boiling and melting points but different direction of rotation in the polarimeter. They interact in different manner with other chiral molecules and are difficult to separate. Enantiomers differ in their configuration such as R or S at the stereogenic centre. We already know that these configurations are assigned by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) rules.
Diastereomers are the non-superimposable non-mirror images but have two or more chiral centres. When four different groups are attached to an asymmetric carbon atom, it is a chiral molecule. They are easy to separate as they have different melting and boiling points. For example, geometric isomers such as cis/trans.
To convert into enantiomers, both chiral carbon atoms must change their configuration. All stereocenters must be different for molecules to be enantiomers. And to convert into diastereomers, only one chiral carbon atom must change configuration. This is an important condition that at least one stereocenter must be different and at least one stereocenter must be same for molecules so as to be diastereomers.
Identical molecules are those two molecules that can be superimposed on each other, through rotation of bonds i.e. conformational changes or via rotation of the molecule itself. These are considered to be the same molecule or identical twins. They differ from each other only in the spatial orientation of groups in the molecule.
Let us write all the given molecules in Fischer projection from sawhorse projections and write the configurations of each chiral carbon as per CIP rules.
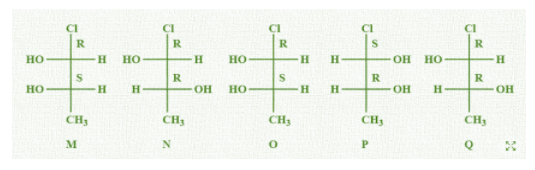
From these configurations we can easily see that M and N are diastereomers as they have different configuration at one chiral carbon and same at another chiral centre. therefore, M and N are non-mirror image stereoisomers. So, option (A) is correct.
Let us look at option (B), M and O are identical. Yes, we can clearly see that both the molecules look identical. The position of every atom and configuration of each chiral carbon is same in both. So it is a correct option.
In option (C), it is stated that M and P are enantiomers. We can see that the configurations are opposite at each chiral carbon in the two molecules. This is the case of enantiomers in which both chiral carbon atoms must change their configuration. So, this option is also correct.
In the last option, it is mentioned that M and Q are identical but they are not because the configurations are changed and not same. So, this option is incorrect.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B) and (C).
Note: Point to be noted here is all molecules are not identical on rotation of a single bond. There exist conformers showing conformational isomers. Conformational isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism in which isomers can only be converted by formally single bond rotations. Also, all enantiomers are known to be optically active.
Complete Step-by-Step answer:
Two different molecules are said to be enantiomers if they are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. They have same refractive index, density, boiling and melting points but different direction of rotation in the polarimeter. They interact in different manner with other chiral molecules and are difficult to separate. Enantiomers differ in their configuration such as R or S at the stereogenic centre. We already know that these configurations are assigned by the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) rules.
Diastereomers are the non-superimposable non-mirror images but have two or more chiral centres. When four different groups are attached to an asymmetric carbon atom, it is a chiral molecule. They are easy to separate as they have different melting and boiling points. For example, geometric isomers such as cis/trans.
To convert into enantiomers, both chiral carbon atoms must change their configuration. All stereocenters must be different for molecules to be enantiomers. And to convert into diastereomers, only one chiral carbon atom must change configuration. This is an important condition that at least one stereocenter must be different and at least one stereocenter must be same for molecules so as to be diastereomers.
Identical molecules are those two molecules that can be superimposed on each other, through rotation of bonds i.e. conformational changes or via rotation of the molecule itself. These are considered to be the same molecule or identical twins. They differ from each other only in the spatial orientation of groups in the molecule.
Let us write all the given molecules in Fischer projection from sawhorse projections and write the configurations of each chiral carbon as per CIP rules.

From these configurations we can easily see that M and N are diastereomers as they have different configuration at one chiral carbon and same at another chiral centre. therefore, M and N are non-mirror image stereoisomers. So, option (A) is correct.
Let us look at option (B), M and O are identical. Yes, we can clearly see that both the molecules look identical. The position of every atom and configuration of each chiral carbon is same in both. So it is a correct option.
In option (C), it is stated that M and P are enantiomers. We can see that the configurations are opposite at each chiral carbon in the two molecules. This is the case of enantiomers in which both chiral carbon atoms must change their configuration. So, this option is also correct.
In the last option, it is mentioned that M and Q are identical but they are not because the configurations are changed and not same. So, this option is incorrect.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B) and (C).
Note: Point to be noted here is all molecules are not identical on rotation of a single bond. There exist conformers showing conformational isomers. Conformational isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism in which isomers can only be converted by formally single bond rotations. Also, all enantiomers are known to be optically active.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




