
Which of the following tests is given by both aldehydes as well as ketones?
(A) Tollen’s reagent test
(B) 2,4-DNP test
(C) Schiff’s reagent test
(D) All of the above
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Both aldehyde and ketone are pure carbonyl compounds and so they undergo nucleophilic addition reactions to form the compounds. So all the reactions of acetaldehyde and acetone are nucleophilic addition reactions only. Both are colourless compounds but can be easily distinguished by a few tests.
Complete step by step solution:
-Aldehydes and ketones have the functional groups of –CHO and =O respectively. These groups are responsible for different characteristics present in the compounds containing these functional groups.
-They form different products on oxidation, reaction with 1 mole of Grignard’s reagent, reaction with Tollen’s reagent, the reaction of Benedict’s solution and many more reactions.
-Aldehydes give black silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent $\left( AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH \right)$ and red precipitate with Fehling’s solution while ketones do not give this test. The reactions can be given as
$\begin{align}
& R-CHO\xrightarrow{AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH}R-CO{{O}^{-}}+Ag\downarrow (\text{Tollen }\!\!'\!\!\text{ s test)} \\
& \text{R-CHO+C}{{\text{u}}^{2+}}\xrightarrow{O{{H}^{-}}}R-CO{{O}^{-}}+C{{u}_{2}}O\downarrow (Fehling's\text{ test)} \\
\end{align}$
-When 2,4-DNP or Brady’s reagent is reacted with pure carbonyls, it forms precipitate which is yellow-orange in colour. This colour shows the presence of the carbonyl compounds (both aldehydes and ketones). Brady’s reagent is red to orange in colour in pure form. The reaction can be shown as
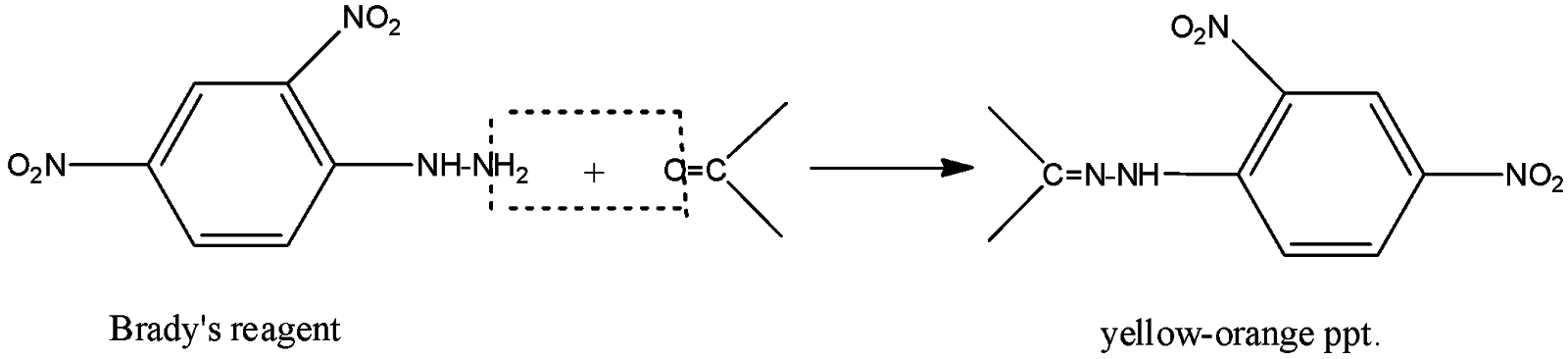
Thus, the correct answer is (B).
Note: Brady’s reagent only reacts with pure carbonyls which are aldehydes and ketones. It does not react with the impure carbonyls like acid halides, esters, anhydrides, etc to give the yellow-orange precipitate. It gives elimination reactions with the aldehydes and ketones.
Complete step by step solution:
-Aldehydes and ketones have the functional groups of –CHO and =O respectively. These groups are responsible for different characteristics present in the compounds containing these functional groups.
-They form different products on oxidation, reaction with 1 mole of Grignard’s reagent, reaction with Tollen’s reagent, the reaction of Benedict’s solution and many more reactions.
-Aldehydes give black silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent $\left( AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH \right)$ and red precipitate with Fehling’s solution while ketones do not give this test. The reactions can be given as
$\begin{align}
& R-CHO\xrightarrow{AgN{{O}_{3}}+N{{H}_{4}}OH}R-CO{{O}^{-}}+Ag\downarrow (\text{Tollen }\!\!'\!\!\text{ s test)} \\
& \text{R-CHO+C}{{\text{u}}^{2+}}\xrightarrow{O{{H}^{-}}}R-CO{{O}^{-}}+C{{u}_{2}}O\downarrow (Fehling's\text{ test)} \\
\end{align}$
-When 2,4-DNP or Brady’s reagent is reacted with pure carbonyls, it forms precipitate which is yellow-orange in colour. This colour shows the presence of the carbonyl compounds (both aldehydes and ketones). Brady’s reagent is red to orange in colour in pure form. The reaction can be shown as

Thus, the correct answer is (B).
Note: Brady’s reagent only reacts with pure carbonyls which are aldehydes and ketones. It does not react with the impure carbonyls like acid halides, esters, anhydrides, etc to give the yellow-orange precipitate. It gives elimination reactions with the aldehydes and ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




