
Which of the following products is obtained, when chloroethane reacts with silver oxide suspended in boiling water?
(A) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
(B) \[C{H_3}C{H_3}\]
(C) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\]
(D) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}OC{H_2}C{H_3}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In the given reaction, the leaving group is being eliminated to produce an unsaturated hydrocarbon as the main product and a salt as a side product. The base in this situation is silver oxide.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The answer to the question is that silver oxide suspended in boiling water reacts with chloroethane.
As is well known, silver hydroxide is produced when silver oxide combines with water.
\[A{g_2}O + {H_2}O \to 2AgOH\]
The reaction of chloroethane with a silver oxide is shown below:
\[{C_2}{H_5}Cl{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}AgOH \to \;{C_2}{H_5}OH\; + {\text{ }}AgCl\]
In this process, silver oxide and chloroethane combine to generate ethanol with a double bond and silver chloride.
The following diagram illustrates the mechanism of chloroethane with a silver hydroxide:
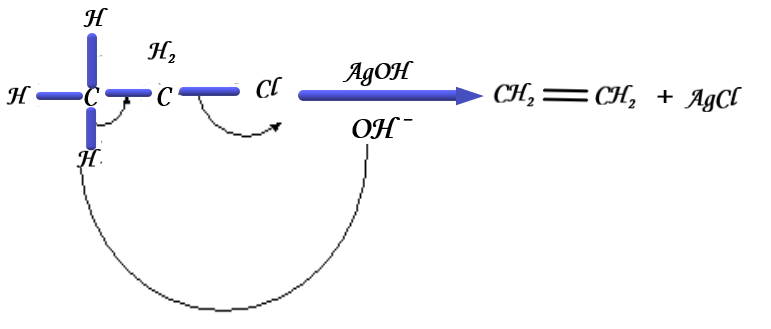
In this reaction, the alcoholic \[AgOH\] acts as the base which will attack the hydrogen atom to form water. After the removal of hydrogen, the bond will shift to form an ethene and remove the chlorine. The chlorine acts as a nucleophile which will attack the positive silver ion to form silver chloride.
Anhydrous silver oxide is dissolved in ethanol to produce alcoholic silver hydroxide. It is utilised in water-sensitive elimination processes. An illustration of an elimination reaction is this one. A molecule with a saturated carbon (single bond) can become an unsaturated carbon through the elimination reaction (double bond).
In this reaction the leaving group from the reactant, which is removed to form an unsaturated carbon compound.
Therefore, the correct answer is: (C) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\].
Note: Dehydrohalogenation is another name for this process. Make that the silver oxide being utilised in the reaction is of the alcoholic variety. When chloroethane and aqueous silver oxide combine, the major product that results after the silver chloride is removed is alcohol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The answer to the question is that silver oxide suspended in boiling water reacts with chloroethane.
As is well known, silver hydroxide is produced when silver oxide combines with water.
\[A{g_2}O + {H_2}O \to 2AgOH\]
The reaction of chloroethane with a silver oxide is shown below:
\[{C_2}{H_5}Cl{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}AgOH \to \;{C_2}{H_5}OH\; + {\text{ }}AgCl\]
In this process, silver oxide and chloroethane combine to generate ethanol with a double bond and silver chloride.
The following diagram illustrates the mechanism of chloroethane with a silver hydroxide:

In this reaction, the alcoholic \[AgOH\] acts as the base which will attack the hydrogen atom to form water. After the removal of hydrogen, the bond will shift to form an ethene and remove the chlorine. The chlorine acts as a nucleophile which will attack the positive silver ion to form silver chloride.
Anhydrous silver oxide is dissolved in ethanol to produce alcoholic silver hydroxide. It is utilised in water-sensitive elimination processes. An illustration of an elimination reaction is this one. A molecule with a saturated carbon (single bond) can become an unsaturated carbon through the elimination reaction (double bond).
In this reaction the leaving group from the reactant, which is removed to form an unsaturated carbon compound.
Therefore, the correct answer is: (C) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}OH\].
Note: Dehydrohalogenation is another name for this process. Make that the silver oxide being utilised in the reaction is of the alcoholic variety. When chloroethane and aqueous silver oxide combine, the major product that results after the silver chloride is removed is alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




