
Which of the following pairs has the same structure
A. \[PH_3\] and \[BCl_3\]
B. \[SO_2\] and \[NH_3\]
C. \[PCl_5\] and \[SF_6\]
D. \[NH_4^{+}\] and \[SO_4^{2 - }\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: the geometry of molecules described by the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory.
It is established on the repulsion between the electron pairs in the valence shell of the atoms which decides the shape of the molecules.
Complete step by step solution:VSEPR theory was provided by Sidgwick and Powell back in 1940 and some changes were brought in by Nyholm and Gillespie in 1957.
The shape of the molecule pivots on the bonded and non-bonded valence shell electron pairs around the central atom.
Pairs of electrons in the valence shell repelled by one another and thus remain distant and separated from each other.
Lone pair-lone pair repel each other sizably. Then comes lone pair-bond pair repulsion and bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
We have to find out which of the following pairs have the same structure.
A. \[PH_3\] and \[BCl_3\]
P has five electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making and two other electrons pair up.
So, it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
So, it has a trigonal pyramidal structure.
Boron has three electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making.
So, it has three bond pairs.
So, it has a trigonal planar structure.
So, A is incorrect.
B. \[SO_2\] and \[NH_3\]
Sulfur has six electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making and
two other electrons pair up.
So, it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
So, it has a bent structure.
NH3
Nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making and two other electrons pair up.
So, it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
So, it has a trigonal pyramidal structure.
So, B is incorrect.
C. \[PCl_5\] and \[SF_6\]
P has five electrons in its valence shell. All five electrons take part in bond-making.
So, there are five bond pairs.
It has a trigonal bipyramidal structure.
S has six electrons in its valence shell. All six electrons take part in bond-making.
So, there are six bond pairs.
It has an octahedral structure.
So, C is incorrect.
D. \[NH_4^{+}\] and \[SO_4^{2 - }\]
In this ammonium ion, the positive charge is on N which thus has four electrons and all of which take part in bond-making. So, the structure is tetrahedral.
In sulfate anion, sulfur is bonded to four oxygen atoms, 2 of the oxygen atoms constitute double bonds, and the other two constitute single bonds. These two oxygen atoms have a negative charge on them.
So, it has tetrahedral geometry.
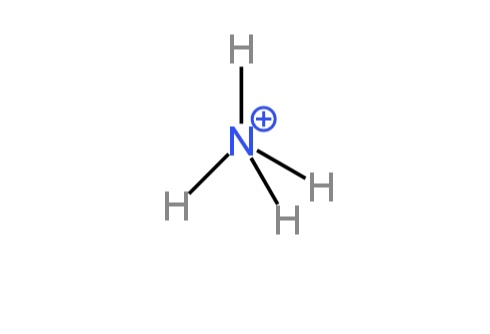
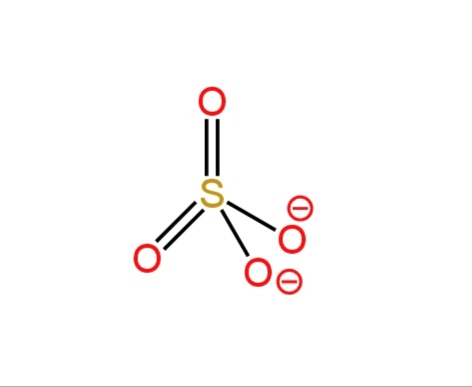
Image: Structures of ammonium cation and sulfate anion.
So, ammonium cation and sulfate anion both have tetrahedral geometry.
So, option D is correct.
Note: The ammonium ion is developed when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Bronsted acids like protons.
The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Bronsted bases to yield the uncharged ammonia molecule.
The extent to which ammonia constitutes the ammonium ion relies on the pH of the solution.
It is established on the repulsion between the electron pairs in the valence shell of the atoms which decides the shape of the molecules.
Complete step by step solution:VSEPR theory was provided by Sidgwick and Powell back in 1940 and some changes were brought in by Nyholm and Gillespie in 1957.
The shape of the molecule pivots on the bonded and non-bonded valence shell electron pairs around the central atom.
Pairs of electrons in the valence shell repelled by one another and thus remain distant and separated from each other.
Lone pair-lone pair repel each other sizably. Then comes lone pair-bond pair repulsion and bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
We have to find out which of the following pairs have the same structure.
A. \[PH_3\] and \[BCl_3\]
P has five electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making and two other electrons pair up.
So, it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
So, it has a trigonal pyramidal structure.
Boron has three electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making.
So, it has three bond pairs.
So, it has a trigonal planar structure.
So, A is incorrect.
B. \[SO_2\] and \[NH_3\]
Sulfur has six electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making and
two other electrons pair up.
So, it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
So, it has a bent structure.
NH3
Nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell.
Three electrons take part in bond-making and two other electrons pair up.
So, it has three bond pairs and one lone pair.
So, it has a trigonal pyramidal structure.
So, B is incorrect.
C. \[PCl_5\] and \[SF_6\]
P has five electrons in its valence shell. All five electrons take part in bond-making.
So, there are five bond pairs.
It has a trigonal bipyramidal structure.
S has six electrons in its valence shell. All six electrons take part in bond-making.
So, there are six bond pairs.
It has an octahedral structure.
So, C is incorrect.
D. \[NH_4^{+}\] and \[SO_4^{2 - }\]
In this ammonium ion, the positive charge is on N which thus has four electrons and all of which take part in bond-making. So, the structure is tetrahedral.
In sulfate anion, sulfur is bonded to four oxygen atoms, 2 of the oxygen atoms constitute double bonds, and the other two constitute single bonds. These two oxygen atoms have a negative charge on them.
So, it has tetrahedral geometry.


Image: Structures of ammonium cation and sulfate anion.
So, ammonium cation and sulfate anion both have tetrahedral geometry.
So, option D is correct.
Note: The ammonium ion is developed when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Bronsted acids like protons.
The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Bronsted bases to yield the uncharged ammonia molecule.
The extent to which ammonia constitutes the ammonium ion relies on the pH of the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




