
Which of the following is/are polyamide?
(A) Terylene
(B) Rayon
(C) Nylon-6
(D) Polystyrene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In polymer chemistry, the term polyamide refers to the category of condensation polymers which have amide linkages. These polyamides are synthesized by the condensation polymerization of dibasic acids with diamines or their equivalents. These polymers are also called nylons.
Complete step by step answer: Let us check the given options one by one.
The first option is terylene also known as Dacron. It is the best known example of a polyester, i.e., it contains ester linkages. It is prepared by the condensation polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid with the elimination of water. The reaction is shown below.
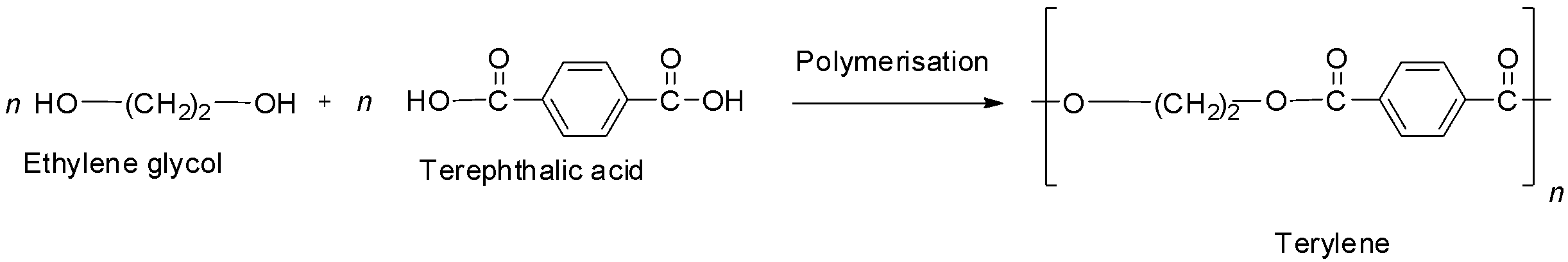
So, it is not a polyamide and hence option A is not correct.
Rayon is a kind of cellulose fibre made up from natural sources. It has the same structure as cellulose and so it does not have any polyamide linkages and hence, it is not a polyamide. So, option B is not correct.
Nylon – 6 is a polyamide prepared from a single monomer called caprolactum. The caprolactum is manufactured from cyclohexane. When caprolactum is heated with water, it forms an aminocaproic acid that undergoes polymerization to give nylon – 6. The reaction is shown below.
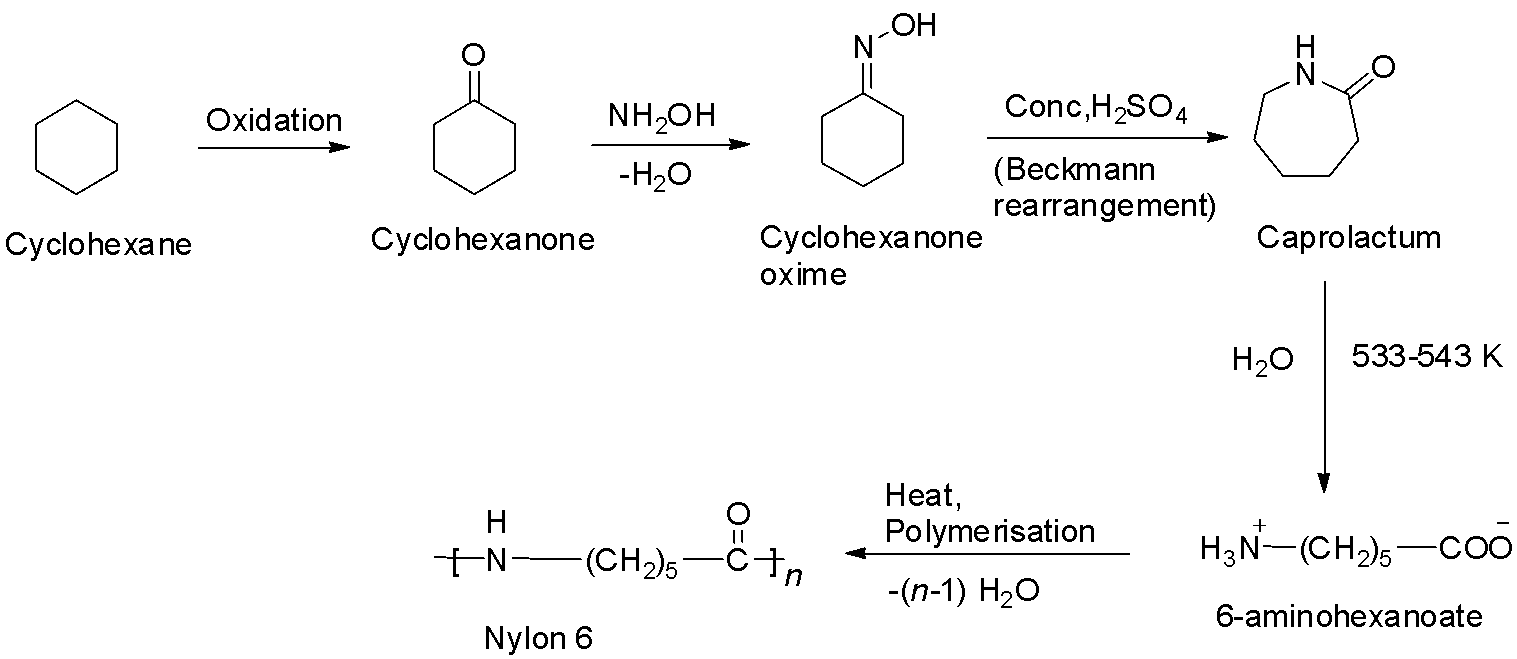
So, option C is correct.
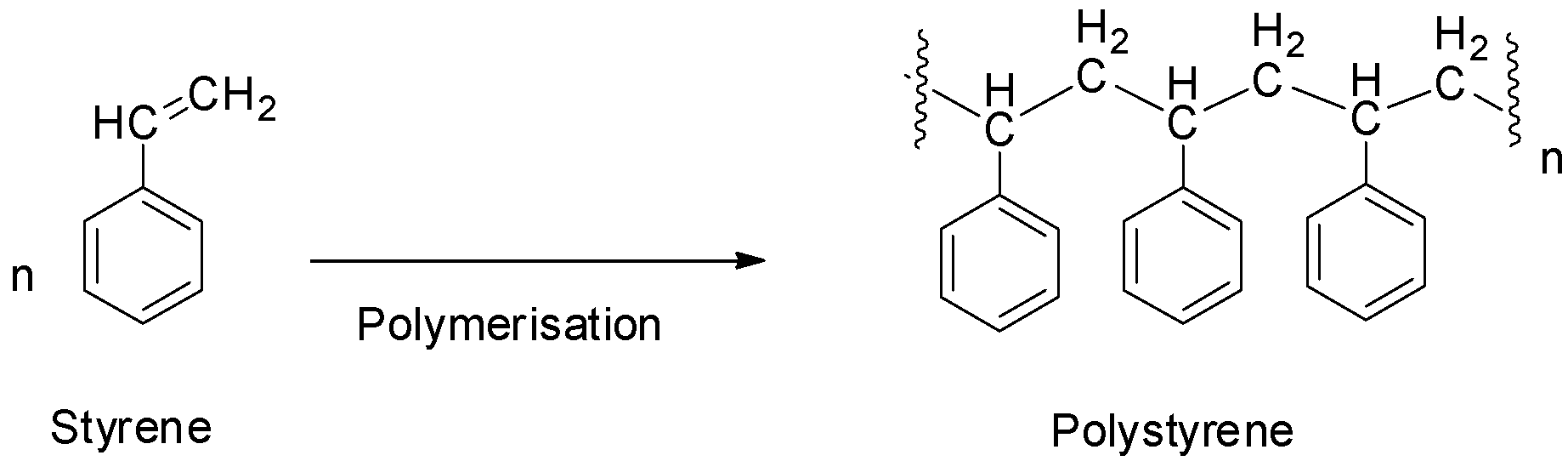
Polystyrene is an addition polymer formed by the polymerization of styrene monomers. It does not contain any polyamide linkage and hence, it is not a polyamide. So, option D is also not correct.
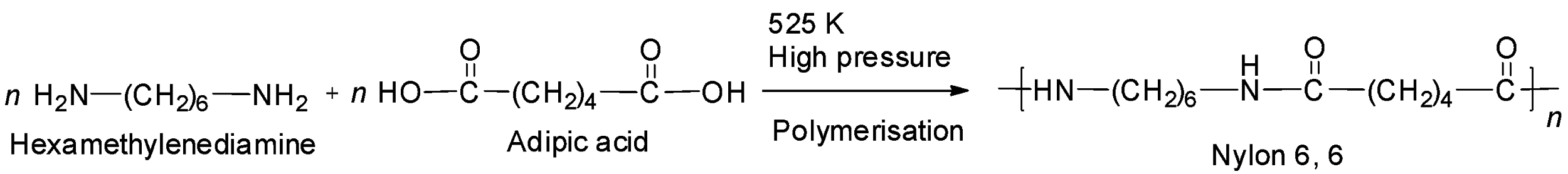
Note: Another example of a well-known polyamide is nylon -6, 6. It is prepared by the condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. It is called nylon -6, 6 because both adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine has six carbon atoms each. The reaction is:
Complete step by step answer: Let us check the given options one by one.
The first option is terylene also known as Dacron. It is the best known example of a polyester, i.e., it contains ester linkages. It is prepared by the condensation polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid with the elimination of water. The reaction is shown below.

So, it is not a polyamide and hence option A is not correct.
Rayon is a kind of cellulose fibre made up from natural sources. It has the same structure as cellulose and so it does not have any polyamide linkages and hence, it is not a polyamide. So, option B is not correct.
Nylon – 6 is a polyamide prepared from a single monomer called caprolactum. The caprolactum is manufactured from cyclohexane. When caprolactum is heated with water, it forms an aminocaproic acid that undergoes polymerization to give nylon – 6. The reaction is shown below.

So, option C is correct.
Polystyrene is an addition polymer formed by the polymerization of styrene monomers. It does not contain any polyamide linkage and hence, it is not a polyamide. So, option D is also not correct.

Note: Another example of a well-known polyamide is nylon -6, 6. It is prepared by the condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. It is called nylon -6, 6 because both adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine has six carbon atoms each. The reaction is:

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




