
Which of the following is the most reactive in Friedel craft acylation reaction?
(A) 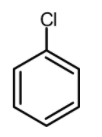
(B) 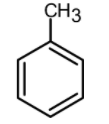
(C) 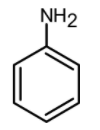
(D) 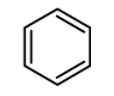
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: The Friedel craft reactions are electrophilic substitution reactions. The activation or deactivation of the benzene ring towards the electrophilic substitution reaction depends on the substituents. The electron-donating group activates the ring towards the electrophilic substitution reaction and the electron-withdrawing groups like $\text{-Cl}$ or nitro deactivates the ring. The amine reacts differently in Friedel's craft reaction. It forms the complex and does not give the acylated product.
Complete step by step solution:
-The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction. It is used for the synthesis of monoacetylated products.it is a reaction between arene and the acyl chloride $\text{(R-COCl)}$ to give the acylated products.
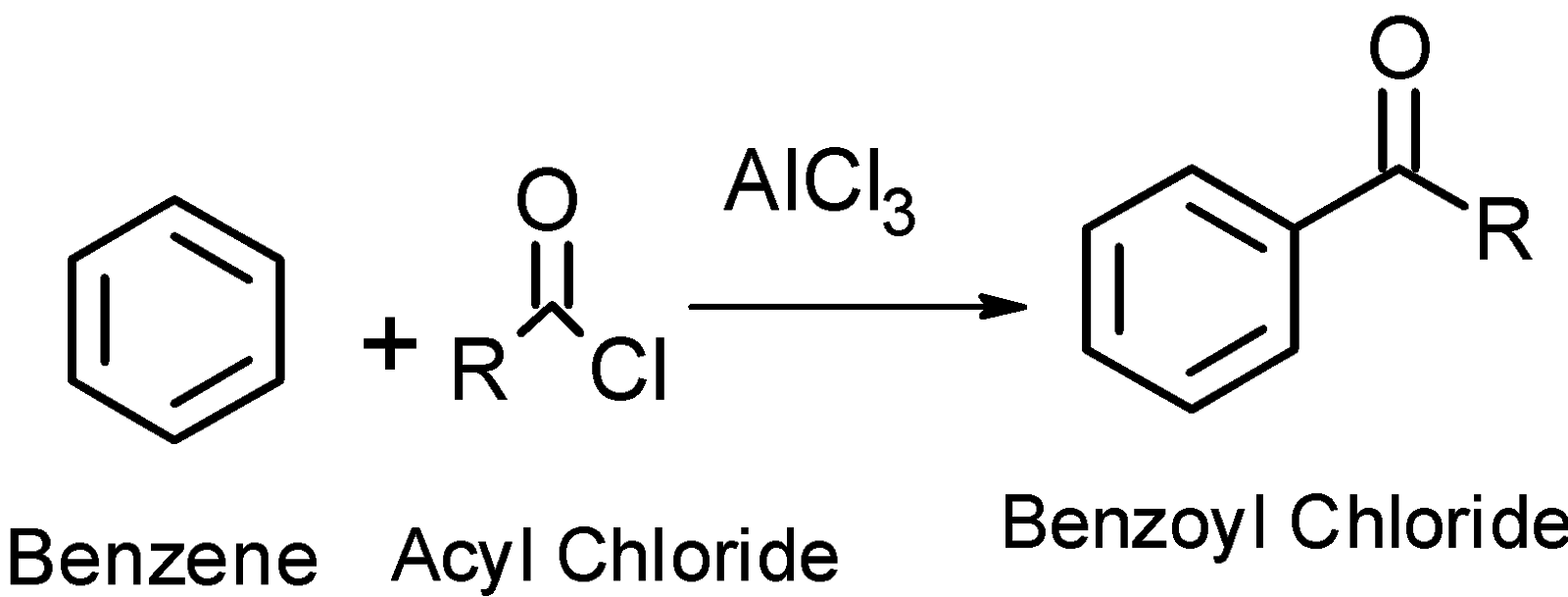
-The Friedel Craft reaction is electrophilic substitution reactions.in which the electrophile displaces the functional group existing on the ring.
In the Friedel crafts, the acylation reaction \[\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]acts as a catalyst that further reacts with the acyl group to convert it into the electrophile.
-This electrophile attacks on the electron-rich positions. This is para and Meta positions in the ring. This results in the formation of the product.
-Friedel-Crafts reactions cannot be performed for the aromatic system which contains a \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{, NHR, or N}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\] substituent. Such as aniline, etc. This is because the lone pair on the amines makes it Lewis base and thus the lone pair of electrons react with the Lewis acid which is $\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$.
The reaction generates a positive charge at the next to the ring results in the deactivation of the ring. Thus the Friedel craft acylation does not occur.
Therefore from the given compounds, the aniline does not undergo the Friedel crafts acylation. $\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ reacts with the amino group $\text{(-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$ and forms an insoluble complex.
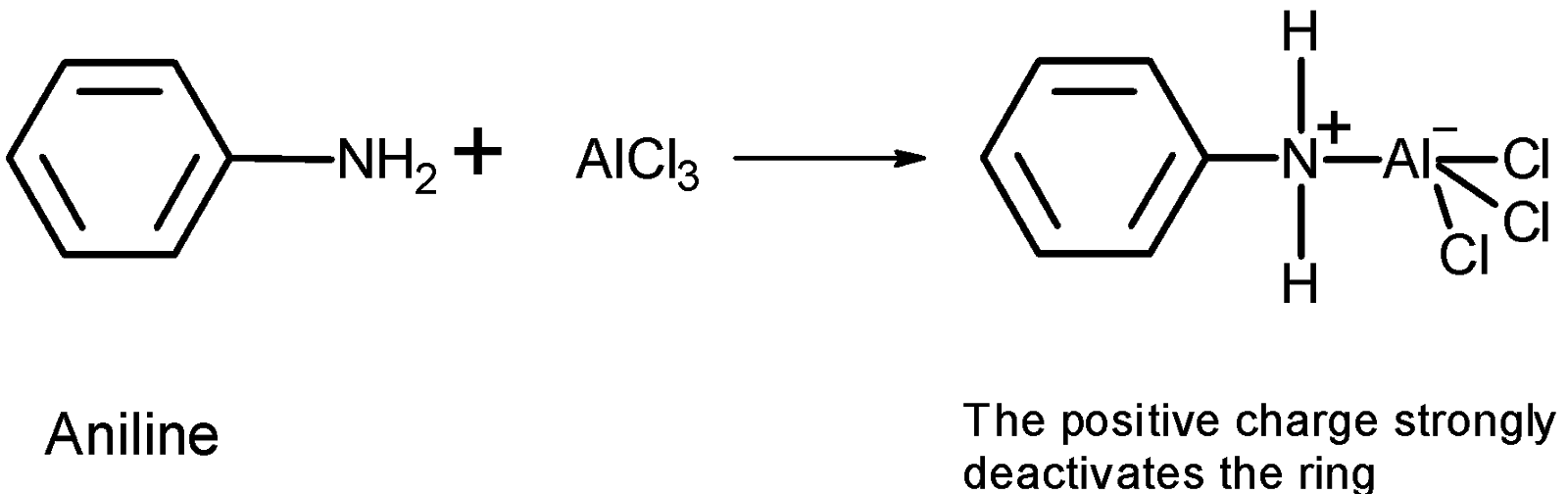
Now let us have a look at chlorobenzene, benzene, and the toluene. The order of reactivity of the rings towards the electrophilic substitution is found to be greater for toluene than benzene than the chlorobenzene. The ortho and para positions are reactive towards the electrophile. The reaction takes place even in presence of poor electrophile. Hence the methyl group is 25 times more reactive than the benzene.
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
\text{Toluene}\rangle \text{Benzene}\rangle \text{Chlorobenzene} \\
\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ } \\
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the group which is highly reactive towards Friedel craft acylation is the toluene.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: $\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ acts as a catalyst. In such a question remember the electron-donating and electron-withdrawing group. Friedel-Crafts fails when we use the compound with a nitro group such as nitrobenzene. Unlike polyalkylation in Friedel craft alkylation, the acylation reaction does not for poly acylated products.
Complete step by step solution:
-The Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction. It is used for the synthesis of monoacetylated products.it is a reaction between arene and the acyl chloride $\text{(R-COCl)}$ to give the acylated products.

-The Friedel Craft reaction is electrophilic substitution reactions.in which the electrophile displaces the functional group existing on the ring.
In the Friedel crafts, the acylation reaction \[\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\]acts as a catalyst that further reacts with the acyl group to convert it into the electrophile.
-This electrophile attacks on the electron-rich positions. This is para and Meta positions in the ring. This results in the formation of the product.
-Friedel-Crafts reactions cannot be performed for the aromatic system which contains a \[\text{N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{, NHR, or N}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\] substituent. Such as aniline, etc. This is because the lone pair on the amines makes it Lewis base and thus the lone pair of electrons react with the Lewis acid which is $\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$.
The reaction generates a positive charge at the next to the ring results in the deactivation of the ring. Thus the Friedel craft acylation does not occur.
Therefore from the given compounds, the aniline does not undergo the Friedel crafts acylation. $\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ reacts with the amino group $\text{(-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$ and forms an insoluble complex.

Now let us have a look at chlorobenzene, benzene, and the toluene. The order of reactivity of the rings towards the electrophilic substitution is found to be greater for toluene than benzene than the chlorobenzene. The ortho and para positions are reactive towards the electrophile. The reaction takes place even in presence of poor electrophile. Hence the methyl group is 25 times more reactive than the benzene.
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
\text{Toluene}\rangle \text{Benzene}\rangle \text{Chlorobenzene} \\
\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ } \\
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the group which is highly reactive towards Friedel craft acylation is the toluene.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: $\text{AlC}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$ acts as a catalyst. In such a question remember the electron-donating and electron-withdrawing group. Friedel-Crafts fails when we use the compound with a nitro group such as nitrobenzene. Unlike polyalkylation in Friedel craft alkylation, the acylation reaction does not for poly acylated products.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




