
Which of the following is planar?
(A) \[Xe{F_2}\]
(B) $Xe{O_3}F$
(C) $Xe{O_2}{F_2}$
(D) $Xe{F_4}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes) suitable for pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds. Hybrid orbitals are the combination of standard atomic orbitals resulting in the formation of new atomic orbitals.
Complete step by step solution:
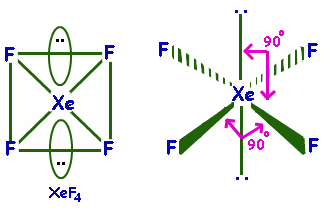
$Xe{F_4}$ Is planar as it has a square planar structure and $s{p^3}{d^2}$ hybridization.
Xenon tetrafluoride was the first discovered binary compound of a noble gas. It was produced by the chemical reaction of xenon with fluoride. The reaction is as shown:
$Xe + 2{F_2} \to Xe{F_4}$
This is an exothermic reaction releasing an energy of $250KJmo{l^{ - 1}}$.
Its molecular geometry is square planar. The bond angles are ${90^ \circ }$ or ${180^ \circ }$. The lone pairs lie on the opposite sides of the molecule basically at ${180^ \circ }$ from each other.
Hence, option D is correct
Note: $Xe{F_4}$ Molecule is nonpolar. It has octahedral geometry and square planar shape. The bonds are polar but the vector sum of the bond dipole is zero. The lone pair dipoles are equal in strength and oppose each other. Hence, it is a nonpolar molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
$Xe{F_4}$ Is planar as it has a square planar structure and $s{p^3}{d^2}$ hybridization.
Xenon tetrafluoride was the first discovered binary compound of a noble gas. It was produced by the chemical reaction of xenon with fluoride. The reaction is as shown:
$Xe + 2{F_2} \to Xe{F_4}$
This is an exothermic reaction releasing an energy of $250KJmo{l^{ - 1}}$.
Its molecular geometry is square planar. The bond angles are ${90^ \circ }$ or ${180^ \circ }$. The lone pairs lie on the opposite sides of the molecule basically at ${180^ \circ }$ from each other.

Hence, option D is correct
Note: $Xe{F_4}$ Molecule is nonpolar. It has octahedral geometry and square planar shape. The bonds are polar but the vector sum of the bond dipole is zero. The lone pair dipoles are equal in strength and oppose each other. Hence, it is a nonpolar molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




