
Which of the following is laboratory preparation of dihydrogen?
A. \[3Fe + 4{H_2}{O_{(steam)}} \to F{e_3}{O_4} + 4{H_2}\]
B. \[2Na + 2{H_2}O \to NaOH + 2{H_2}\]
C. \[Ca{H_2} + 2{H_2}O \to Ca{(OH)_2} + 2{H_2}\]
D. \[Zn + {H_2}S{O_{4(dil.)}} \to ZnS{o_4} + {H_2}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Zinc granules are widely preferred for laboratory preparation of hydrogen gas because these granules usually have a small quantity of Cu, which has the ability to act as a catalyst in the given process.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Dihydrogen or just Hydrogen is one of the most widely found gases. Various reactions release hydrogen gas as either a major product or as a by – product. But in most of these cases, the hydrogen gas formed is directly released into the atmosphere. It is very difficult to trap and collect the hydrogen formed because of its light weight and low density.
To collect this hydrogen, a very efficient laboratory method has been developed. The details about this process are as follows:
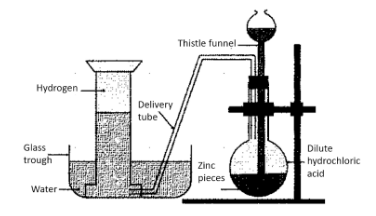
This process involves 4 major steps:
1. First of all, a certain amount of zinc granules is placed in a flask
2. After this, hydrochloric acid needs to be added to these zinc granules. This is done with the help of a thistle funnel. A replacement for hydrochloric acid could be sulphuric acid.
3. The reaction between the acid and the zinc granules would release hydrogen gas. The gas thus produced is transferred to a vessel filled with water, via a delivery tube.
4. The transferred hydrogen is now collected via a method known as downward displacement of water.
The chemical reaction for this process can be given as:
\[Zn + {H_2}S{O_{4(dil.)}} \to ZnS{o_4} + {H_2}\]
Hence, Option D is the correct option.
Note: Before collecting the hydrogen gas with the help of the apparatus, precautions must be taken in order to ensure that all the air inside the apparatus has been displaced. This is because hydrogen gas reacts explosively with air.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Dihydrogen or just Hydrogen is one of the most widely found gases. Various reactions release hydrogen gas as either a major product or as a by – product. But in most of these cases, the hydrogen gas formed is directly released into the atmosphere. It is very difficult to trap and collect the hydrogen formed because of its light weight and low density.
To collect this hydrogen, a very efficient laboratory method has been developed. The details about this process are as follows:

This process involves 4 major steps:
1. First of all, a certain amount of zinc granules is placed in a flask
2. After this, hydrochloric acid needs to be added to these zinc granules. This is done with the help of a thistle funnel. A replacement for hydrochloric acid could be sulphuric acid.
3. The reaction between the acid and the zinc granules would release hydrogen gas. The gas thus produced is transferred to a vessel filled with water, via a delivery tube.
4. The transferred hydrogen is now collected via a method known as downward displacement of water.
The chemical reaction for this process can be given as:
\[Zn + {H_2}S{O_{4(dil.)}} \to ZnS{o_4} + {H_2}\]
Hence, Option D is the correct option.
Note: Before collecting the hydrogen gas with the help of the apparatus, precautions must be taken in order to ensure that all the air inside the apparatus has been displaced. This is because hydrogen gas reacts explosively with air.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




