
Which of the following is an anhydride ?
(A)
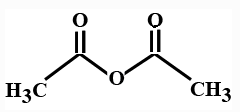
(B)
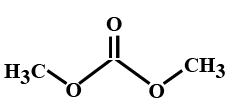
(C)
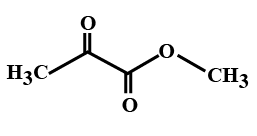
(D)
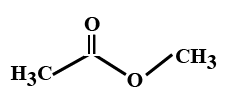
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint : We can define an anhydride compound as a compound that is formed from another compound by dehydration or elimination of water. Anhydrides have functional groups which used to be derivatives of either acid or bases. Basic anhydrides have a different pattern from acid anhydrides. Anhydrides can be organic and inorganic both.
Complete step by step solution:
> In organic chemistry acid anhydrides contain the functional group \[R\left( {CO} \right)O\left( {CO} \right)R'\]. Hence an acid anhydride compound contains two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common example of acid anhydride is carboxylic anhydride whose parent acid is a carboxylic acid. The organic anhydrides introduces the acyl group $(RCO)$ in organic synthesis. Anhydrides reacts with water and produces carboxylic acids.
> In the options all are organic compounds. In the given organic compounds we have to identify the functional group \[R\left( {CO} \right)O\left( {CO} \right)R'\]. If in the given compounds we consider $C{H_3} - $ group as $R - $ group then analysis will become easy. In the first option we have found this compound satisfy the formula\[R\left( {CO} \right)O\left( {CO} \right)R'\] of anhydride compounds where $R = R' = C{H_3}$, hence this is a symmetric type of anhydride. The rest of the option does not satisfy the chemical formula of anhydrides so they are not anhydrides.
So here option A is the correct answer to this question. Compound ( A) is acetic anhydride.
Note : Anhydrides produces ester when it reacts with alcohol or phenol and with ammonia and amines it produces amides. Symmetric acid anhydrides can be prepared easily and have a wide range of applications. These are used in synthesis of other useful organic compounds and used as reagents for amines.
Complete step by step solution:
> In organic chemistry acid anhydrides contain the functional group \[R\left( {CO} \right)O\left( {CO} \right)R'\]. Hence an acid anhydride compound contains two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common example of acid anhydride is carboxylic anhydride whose parent acid is a carboxylic acid. The organic anhydrides introduces the acyl group $(RCO)$ in organic synthesis. Anhydrides reacts with water and produces carboxylic acids.
> In the options all are organic compounds. In the given organic compounds we have to identify the functional group \[R\left( {CO} \right)O\left( {CO} \right)R'\]. If in the given compounds we consider $C{H_3} - $ group as $R - $ group then analysis will become easy. In the first option we have found this compound satisfy the formula\[R\left( {CO} \right)O\left( {CO} \right)R'\] of anhydride compounds where $R = R' = C{H_3}$, hence this is a symmetric type of anhydride. The rest of the option does not satisfy the chemical formula of anhydrides so they are not anhydrides.
So here option A is the correct answer to this question. Compound ( A) is acetic anhydride.
Note : Anhydrides produces ester when it reacts with alcohol or phenol and with ammonia and amines it produces amides. Symmetric acid anhydrides can be prepared easily and have a wide range of applications. These are used in synthesis of other useful organic compounds and used as reagents for amines.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




