
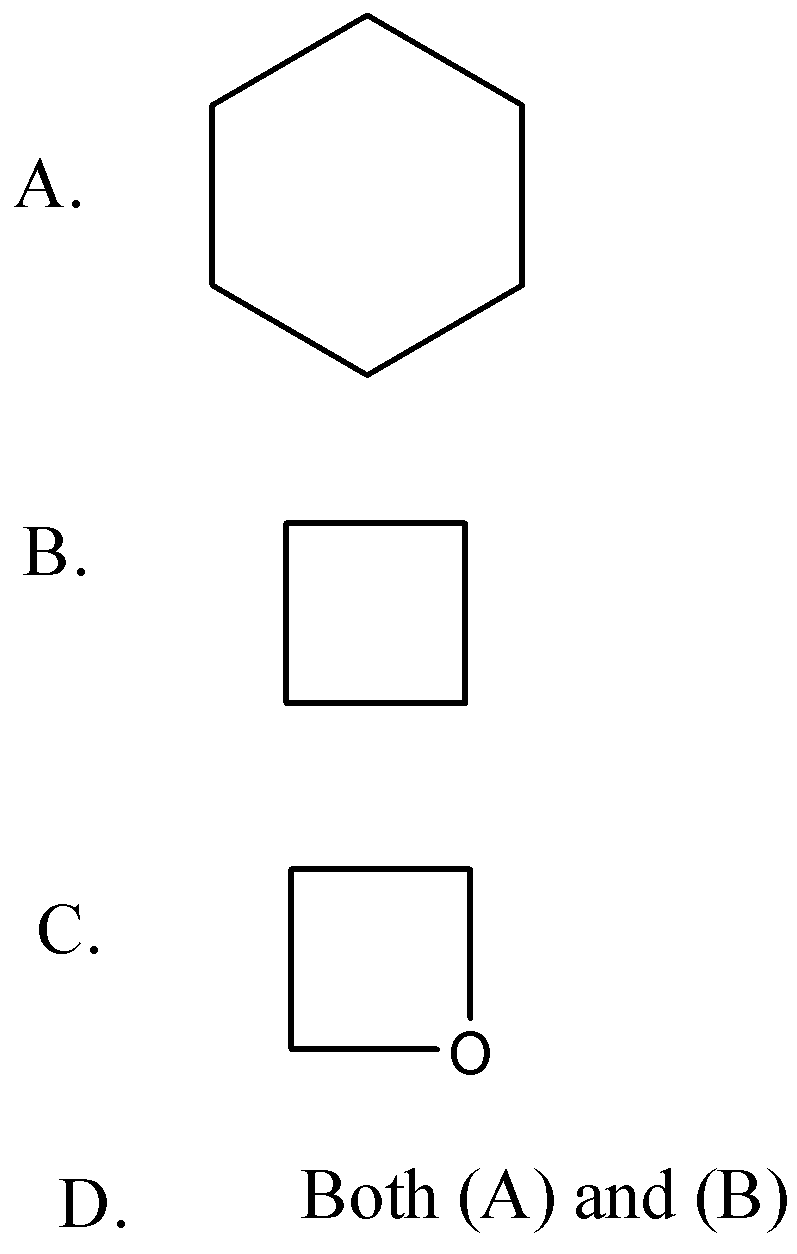
Which of the following is a homocyclic compound?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: All the above options are cyclic compounds. Cyclic compounds can be homocyclic compounds as well as heterocyclic compounds depending upon the type of atoms present in the ring.
Complete step by step answer:
When one or more series of atoms in a compound are connected to form a ring, they are called cyclic compounds. They can be homocyclic or heterocyclic. In homocyclic compounds, the atoms present in the ring only belong to one element. When these atoms are carbon, then they are called carbocycles. Whereas, in heterocyclic compounds, the atoms forming the ring belong to at least two different elements. Generally in heterocyclic compounds both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present. Both carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds can be fully saturated, have multiple bonds within the ring or can be aromatic in nature.
Cycloalkanes are the simplest carbocycles. Some of the examples are given below: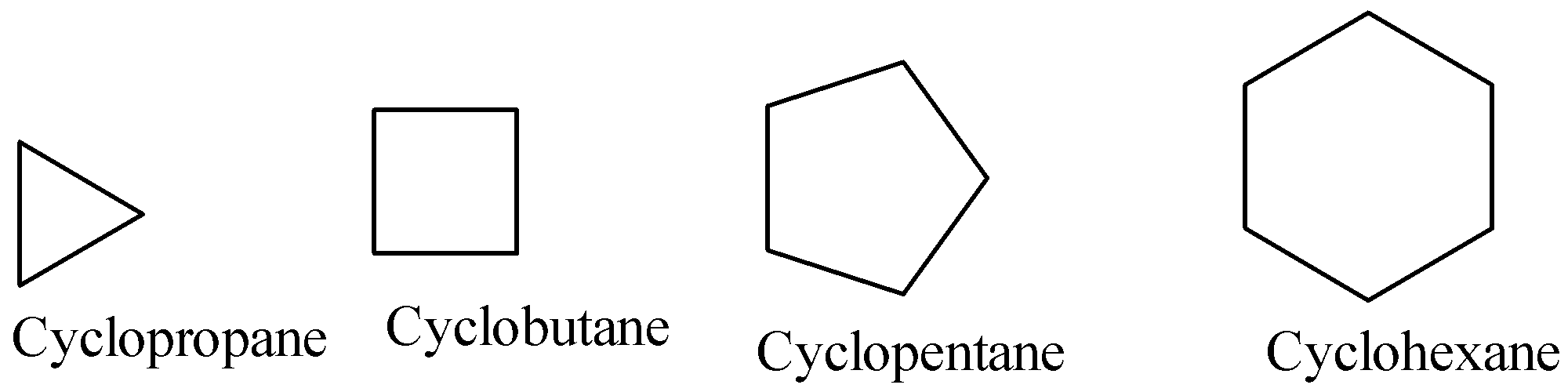
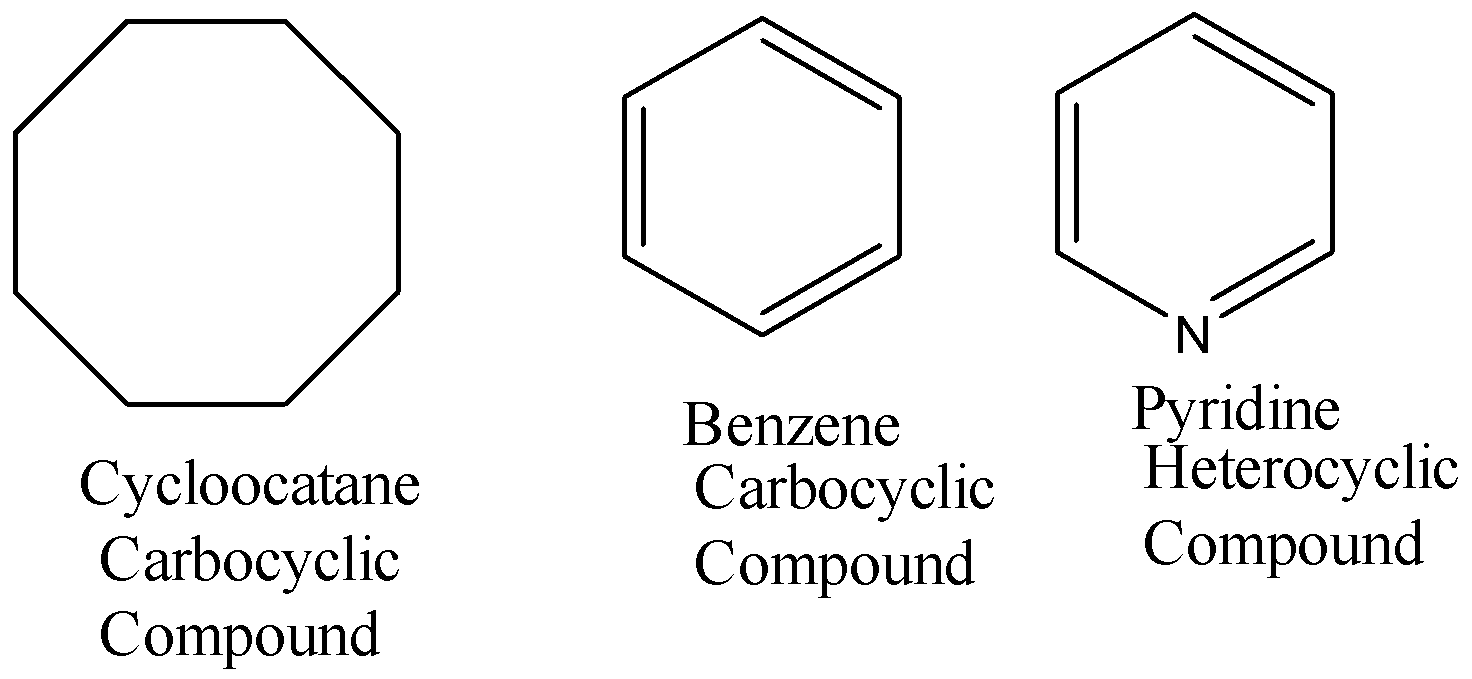
Monocyclic compounds are the compounds that consist of only one ring in their structure. Some of the examples are shown below:
Macrocycle compounds are the compounds that have a ring composed of eight or more atoms. They can be carbocyclic or heterocyclic. Some of the examples are given below: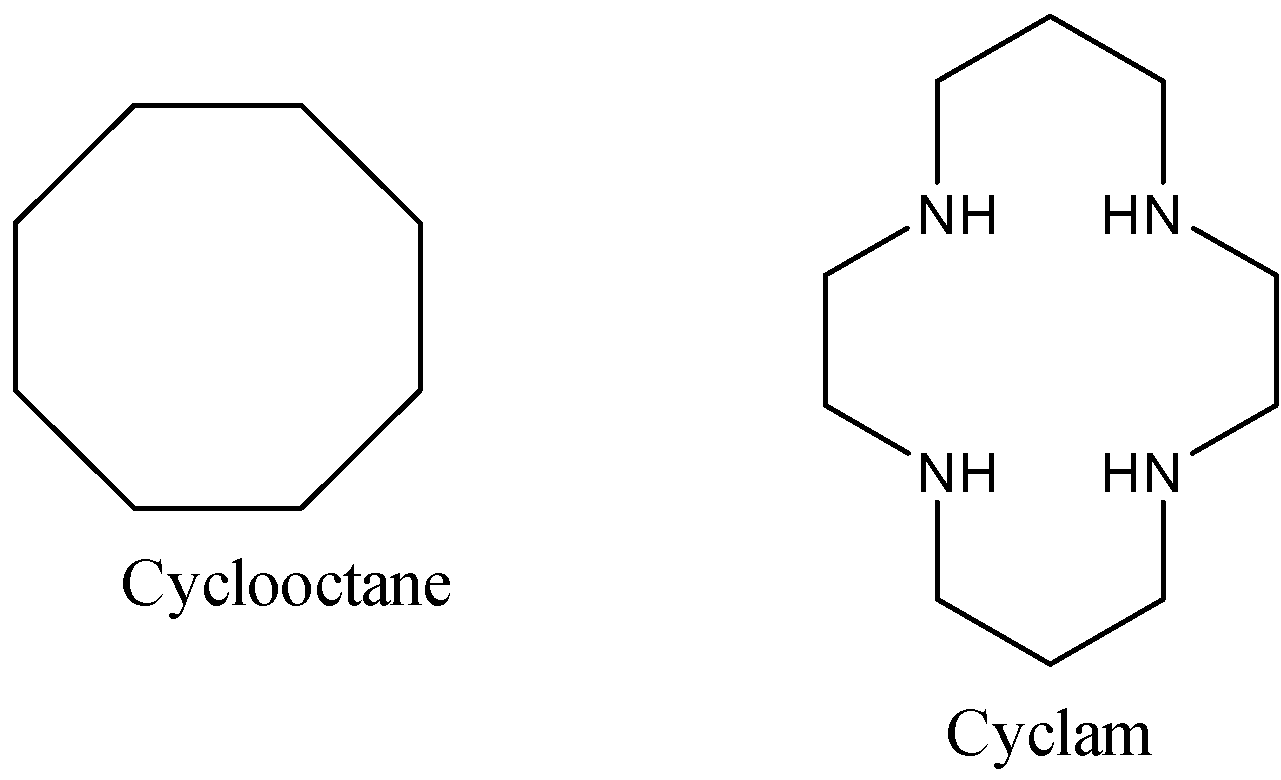
Polycyclic compounds consist of more than one ring structures that are fused to one another. They can be bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic etc. Some of the examples are given below:
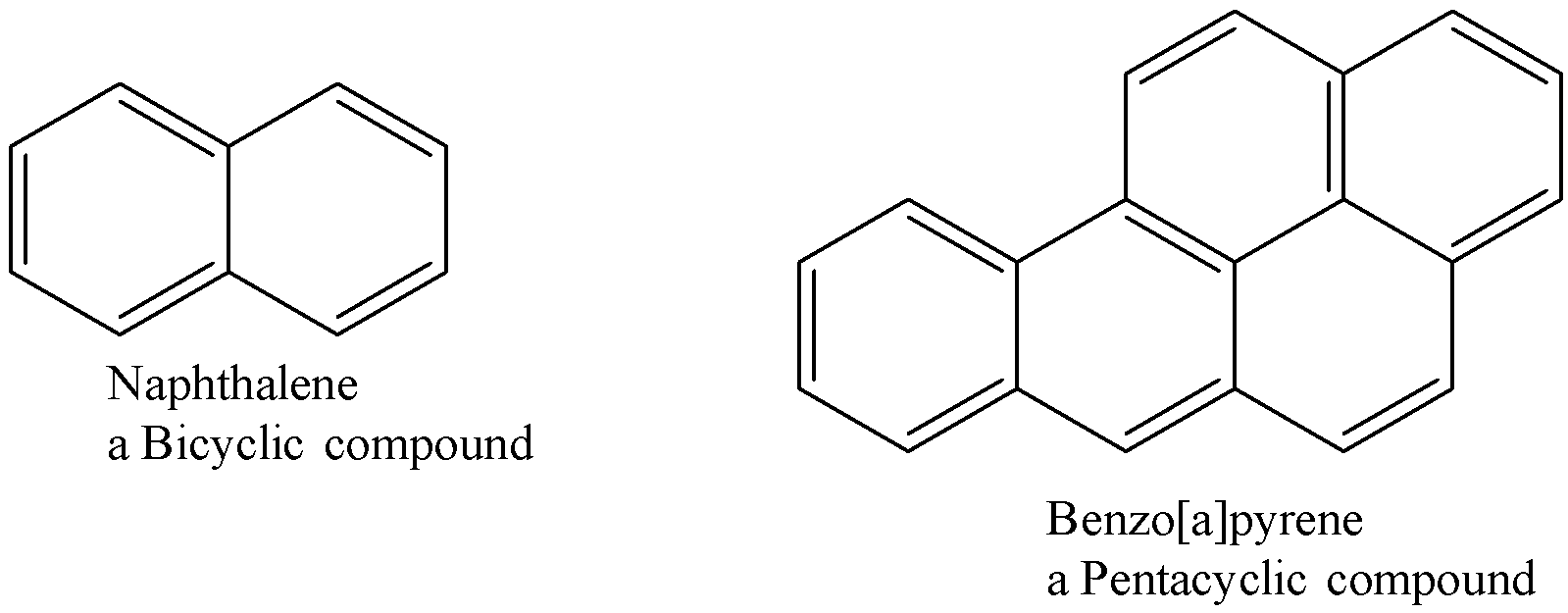
In the above question both A. and B. consist of a ring only composed of one element i.e. carbon therefore both of them are homocyclic compounds. Whereas in option C. The atoms present in the ring are carbon and oxygen therefore it is a heterocyclic compound.
Therefore option D. Both (A) and (B) are correct.
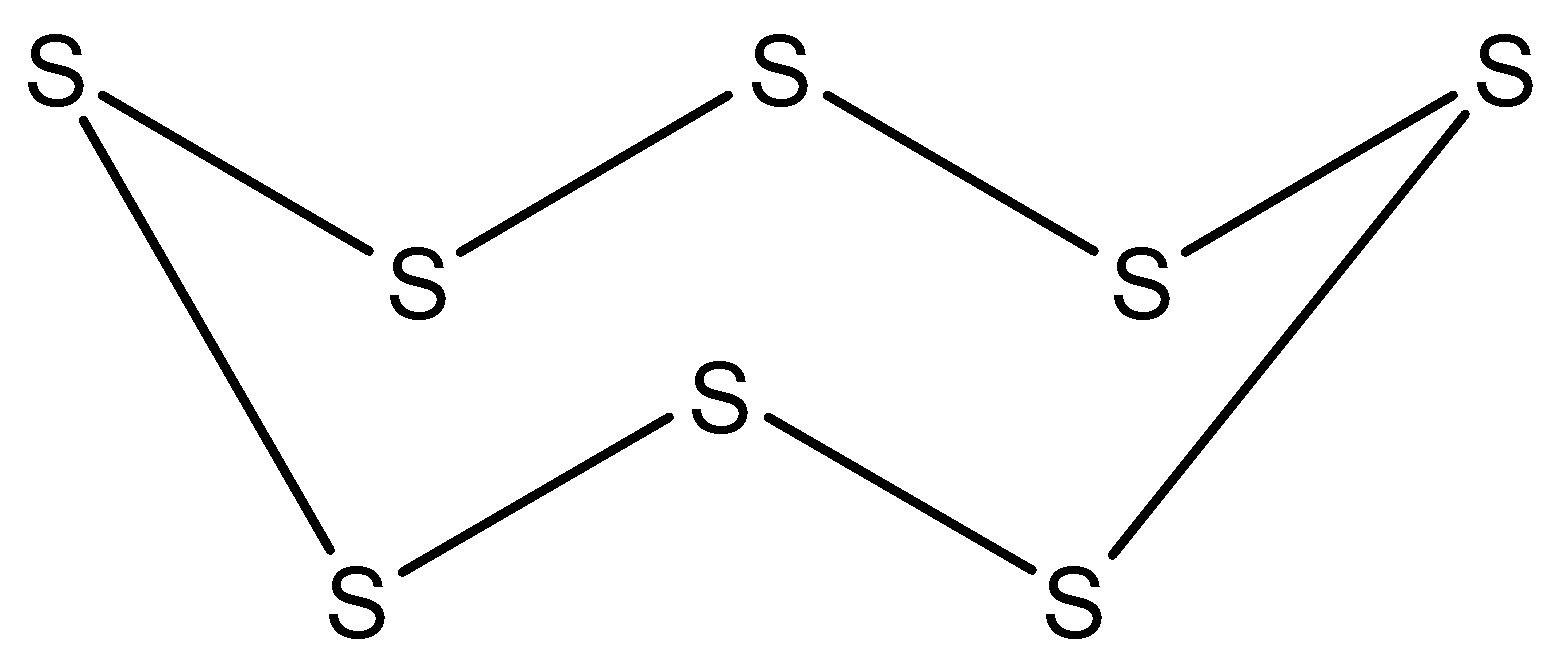
Note: Homocyclic compounds can also be composed of atoms belonging to an element other than carbon. For example cyclo-octasulfur is an eight membered inorganic homocyclic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
When one or more series of atoms in a compound are connected to form a ring, they are called cyclic compounds. They can be homocyclic or heterocyclic. In homocyclic compounds, the atoms present in the ring only belong to one element. When these atoms are carbon, then they are called carbocycles. Whereas, in heterocyclic compounds, the atoms forming the ring belong to at least two different elements. Generally in heterocyclic compounds both carbon and non-carbon atoms are present. Both carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds can be fully saturated, have multiple bonds within the ring or can be aromatic in nature.
Cycloalkanes are the simplest carbocycles. Some of the examples are given below:

Monocyclic compounds are the compounds that consist of only one ring in their structure. Some of the examples are shown below:

Macrocycle compounds are the compounds that have a ring composed of eight or more atoms. They can be carbocyclic or heterocyclic. Some of the examples are given below:

Polycyclic compounds consist of more than one ring structures that are fused to one another. They can be bicyclic, tricyclic, tetracyclic etc. Some of the examples are given below:

In the above question both A. and B. consist of a ring only composed of one element i.e. carbon therefore both of them are homocyclic compounds. Whereas in option C. The atoms present in the ring are carbon and oxygen therefore it is a heterocyclic compound.
Therefore option D. Both (A) and (B) are correct.
Note: Homocyclic compounds can also be composed of atoms belonging to an element other than carbon. For example cyclo-octasulfur is an eight membered inorganic homocyclic compound.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




