
Which of the following has \[s{p^3}\] hybridization.
(a) \[Xe{O_3}\]
(b) \[BC{l_3}\]
(c) \[Xe{F_3}\]
(d) \[BB{r_3}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The intermixing of atomic orbitals (\[s,p,\]and \[d\]orbitals) of compatible energies to form a new kind of atomic orbitals of different energy. This phenomenon is known as hybridization and the resulting orbitals are called hybrid orbitals. Both half and full-filled atomic orbitals can be involved in the formation of hybrid orbitals.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
During the process of hybridization, the resulting hybridised molecule has a different size, shape, and energy from the unhybridized atomic orbitals. The concept of hybridization is considered as the expansion of the valence bond theory.
By means of the concept of hybridization, we can easily predict the geometry of the molecule. The hybridization process of orbitals involves the proper overlapping. To determine the hybridization of any given molecule we can use the following equation:
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{V + M - C + A}}{2}\] (Eq.1)
Whereas V = number of valence electrons on the central atom
M = a number of monovalent atoms
C = charge on the cation
A =charge on anion
Now using above equation will be used to explore the hybridization of the given molecules
(a) \[Xe{O_3}\]
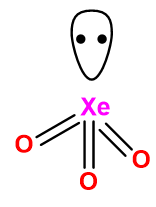
Image: Structure of \[Xe{O_3}\].
Contribution of electrons from the xenon toward bonding \[ = 8\] .
Number of mono-valent atoms \[ = 0\].
By putting all these values in equation 1.
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{8 + 0 - 0 + 0}}{2} = 4\]
The value of 4 will be equal to \[s{p^3}\] hybridization. Therefore, we can easily say that \[Xe{O_3}\]has \[s{p^3}\]hybridization.
By following the same strategy, we can predict the hybridization of \[BC{l_3}\], and \[BB{r_3}\]. That will be \[s{p^2}\] for both the molecules. Whereas \[Xe{F_3}\]compound of xenon does not exist.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (a) will be the correct option:
Note: By using the concept of hybridization we can predict the hybridization of molecules. Whereas the concept of VSEPR theory, the shape of a molecule can be determined. According to VSEPR theory the shape of any molecule can be determined by the repulsion between the lone pair and bond pair.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
During the process of hybridization, the resulting hybridised molecule has a different size, shape, and energy from the unhybridized atomic orbitals. The concept of hybridization is considered as the expansion of the valence bond theory.
By means of the concept of hybridization, we can easily predict the geometry of the molecule. The hybridization process of orbitals involves the proper overlapping. To determine the hybridization of any given molecule we can use the following equation:
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{V + M - C + A}}{2}\] (Eq.1)
Whereas V = number of valence electrons on the central atom
M = a number of monovalent atoms
C = charge on the cation
A =charge on anion
Now using above equation will be used to explore the hybridization of the given molecules
(a) \[Xe{O_3}\]

Image: Structure of \[Xe{O_3}\].
Contribution of electrons from the xenon toward bonding \[ = 8\] .
Number of mono-valent atoms \[ = 0\].
By putting all these values in equation 1.
\[Hybridization(H) = \frac{{8 + 0 - 0 + 0}}{2} = 4\]
The value of 4 will be equal to \[s{p^3}\] hybridization. Therefore, we can easily say that \[Xe{O_3}\]has \[s{p^3}\]hybridization.
By following the same strategy, we can predict the hybridization of \[BC{l_3}\], and \[BB{r_3}\]. That will be \[s{p^2}\] for both the molecules. Whereas \[Xe{F_3}\]compound of xenon does not exist.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (a) will be the correct option:
Note: By using the concept of hybridization we can predict the hybridization of molecules. Whereas the concept of VSEPR theory, the shape of a molecule can be determined. According to VSEPR theory the shape of any molecule can be determined by the repulsion between the lone pair and bond pair.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




