
Which of the following curves represent Henry’s law?
A.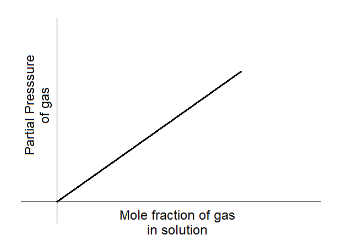
B.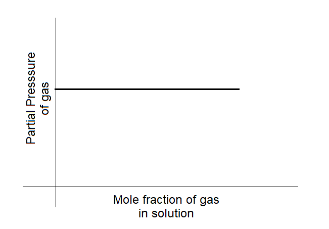
C.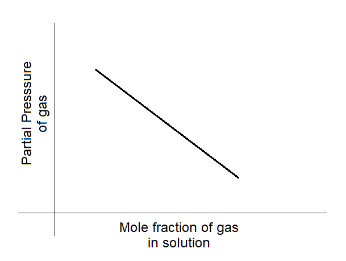
D.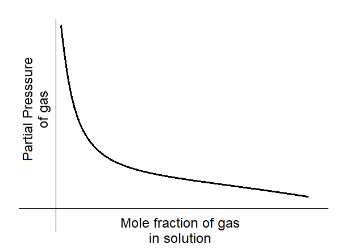
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Henry’s law comes under physical chemistry and it is denoted by Henry’s law constant. It is a type of gas law in which partial pressure of the gas and dissolution of gas is to be considered.
Formula used: Henry’s law is denoted by the given formula;
\[C = kP\] , where \[C\] represents the total concentration of dissolved gas in a liquid, \[k\] represents Henry’s law constant, and \[P\] denotes the partial pressure of the gas.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Henry’s law was given by Sir William Henry. It is a type of gas law that states that the total amount of dissolved gas that is present in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid only when the temperature at which it occurs is kept constant.
Since Henry’s law is denoted as \[C = kP\] ;
Where \[C\] is the total amount of gas in the liquid and \[P\] represents partial pressure of the gas above the liquid, we can conclude that;
\[C \prec P\], hence if pressure increases, the total concentration of dissolved gas in a liquid will also increase.
If the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid is kept constant, the total amount of gas that is dissolved in the liquid will also be constant.
Hence, option A is the correct answer
Note: Henry’s law has its limitations and it is not applicable under certain conditions which are as follows
1. This law is only applicable when all of the molecules and partial pressure are under the state of equilibrium; if the equilibrium is damaged, this law fails.
2. The application of this law also fails to occur when the gases are under extreme pressure.
3. If the dissolved gas and the liquid have a chemical reaction with one another, this law fails.
Formula used: Henry’s law is denoted by the given formula;
\[C = kP\] , where \[C\] represents the total concentration of dissolved gas in a liquid, \[k\] represents Henry’s law constant, and \[P\] denotes the partial pressure of the gas.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Henry’s law was given by Sir William Henry. It is a type of gas law that states that the total amount of dissolved gas that is present in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid only when the temperature at which it occurs is kept constant.
Since Henry’s law is denoted as \[C = kP\] ;
Where \[C\] is the total amount of gas in the liquid and \[P\] represents partial pressure of the gas above the liquid, we can conclude that;
\[C \prec P\], hence if pressure increases, the total concentration of dissolved gas in a liquid will also increase.
If the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid is kept constant, the total amount of gas that is dissolved in the liquid will also be constant.
Hence, option A is the correct answer
Note: Henry’s law has its limitations and it is not applicable under certain conditions which are as follows
1. This law is only applicable when all of the molecules and partial pressure are under the state of equilibrium; if the equilibrium is damaged, this law fails.
2. The application of this law also fails to occur when the gases are under extreme pressure.
3. If the dissolved gas and the liquid have a chemical reaction with one another, this law fails.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




