
Which of the following compounds will show the maximum enol content?
(A) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}$
(B) $C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
(C) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}CON{H_2}$
(D) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COO{C_2}{H_5}$
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: The extent of enol content is explained on the basis of orifice hydrogen and intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
Keto and enol form a compound are isomers.
These isomers are called tautomerism and isomerision is known as tautomerism.
Tautomers are isomers of a compound which differ in portion of protons and electrons.
When a reaction involves simple intermolecular proton transfer is called tautomerism.
Example:
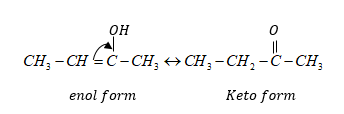
Both isomers form by simple transfer of proton within a molecule.
In the following example $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}$enol content is maximum due to intermolecular h-bonding and resonance stabilization.
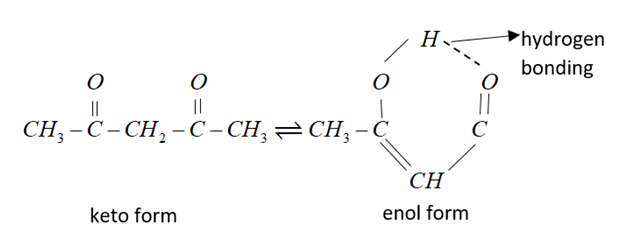
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (A) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}.$
Its IUPAC name is pentane-2,4-dione.
Enol content is high in carbon with electron withdrawing group > carbonyl carbon > number of atoms of hydrogen.
Keto is electrophilic and enol is nucleophilic.
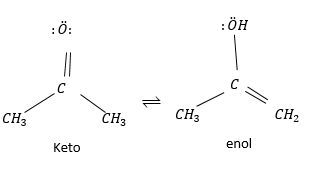
Under most condition keto form is covered. This form is important for aldehydes and ketones but not so much for carboxylic acid ester and amides under normal condition.
[A] Already draw enol form
[B]
Cannot draw enol form so $He$ enol content present in acetone. Atomic form is prominent.
[C] $C{H_3} - COC{H_2}CON{H_2}$
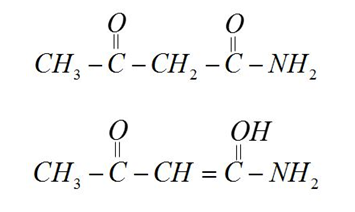
$ - N{H_2}$group decreases enol content in compound
[D] $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COO{C_2}{H_5}$
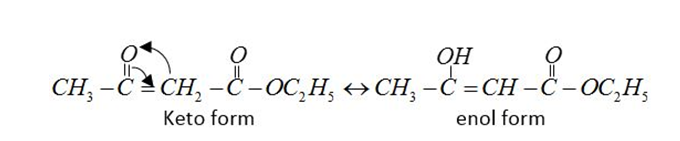
Ethoxide$( - 06.25)$group decreases enolic content.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (A) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}.$
Note: Under normal condition keto form is fevered. Because keto form has $C - H,C - C$ and $C - O$bond whereas enol has $C = C,C = O$ and $O = H$ bond. The sum of first three is about $359lcal/mol$ and second three is $347kcal/mol.$
Complete step by step answer:
Keto and enol form a compound are isomers.
These isomers are called tautomerism and isomerision is known as tautomerism.
Tautomers are isomers of a compound which differ in portion of protons and electrons.
When a reaction involves simple intermolecular proton transfer is called tautomerism.
Example:
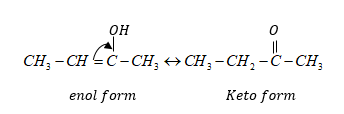
Both isomers form by simple transfer of proton within a molecule.
In the following example $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}$enol content is maximum due to intermolecular h-bonding and resonance stabilization.

Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (A) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}.$
Its IUPAC name is pentane-2,4-dione.
Enol content is high in carbon with electron withdrawing group > carbonyl carbon > number of atoms of hydrogen.
Keto is electrophilic and enol is nucleophilic.

| Electrophilic | Nucleophilic |
| Keto form is electrophilic in nature and reacts with carbonyl carbon. It is acidic at -carbon atom and hydrogen bond acceptor. | Enol from is nucleophilic in nature and reacts with electrophiles at -carbon atom. It is acidic at (O-H) and hydrogen bond donor and acceptor. |
Under most condition keto form is covered. This form is important for aldehydes and ketones but not so much for carboxylic acid ester and amides under normal condition.
[A] Already draw enol form
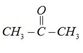
[B]
Cannot draw enol form so $He$ enol content present in acetone. Atomic form is prominent.
[C] $C{H_3} - COC{H_2}CON{H_2}$
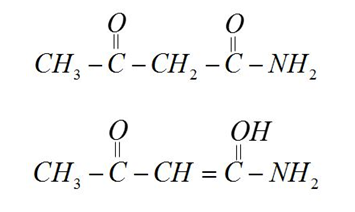
$ - N{H_2}$group decreases enol content in compound
[D] $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COO{C_2}{H_5}$
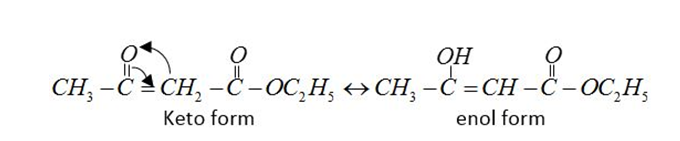
Ethoxide$( - 06.25)$group decreases enolic content.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (A) $C{H_3}COC{H_2}COC{H_3}.$
Note: Under normal condition keto form is fevered. Because keto form has $C - H,C - C$ and $C - O$bond whereas enol has $C = C,C = O$ and $O = H$ bond. The sum of first three is about $359lcal/mol$ and second three is $347kcal/mol.$
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




