
Which of the following compounds is not formed in the iodoform reaction of acetone?
(A) ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ I }$
(B) ${ ICH }_{ 2 }{ CO }{ C }{ H }_{ 2 }$
(C) ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }{ { I }_{ 2 } }$
(D) ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ C }{ { I }_{ 3 } }$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Iodoform reaction of acetone will lead to the products - acetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ O }{ H }$) (sodium acetate) and iodoform (${ CH }I_{ 3 }$). On writing the mechanism of the reaction, we can find certain stable intermediates are also formed. None of these intermediates contains a C=C bond. So, among the options given, the compound with C=C is the answer.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
-Structure of acetone is given below:
-Iodoform reaction is used to identify the presence of carbonyl compounds in compounds.
-Here in the iodoform reaction of acetone, the acetone will be reacted by ${ I }_{ 2 }$ in the presence of NaOH to form acetic acid (sodium acetate) and iodoform.
-When we look at the mechanism of this reaction, we can see many intermediates formed in between.
-Given below is the diagrammatic representation of the mechanism of iodoform reaction of acetone.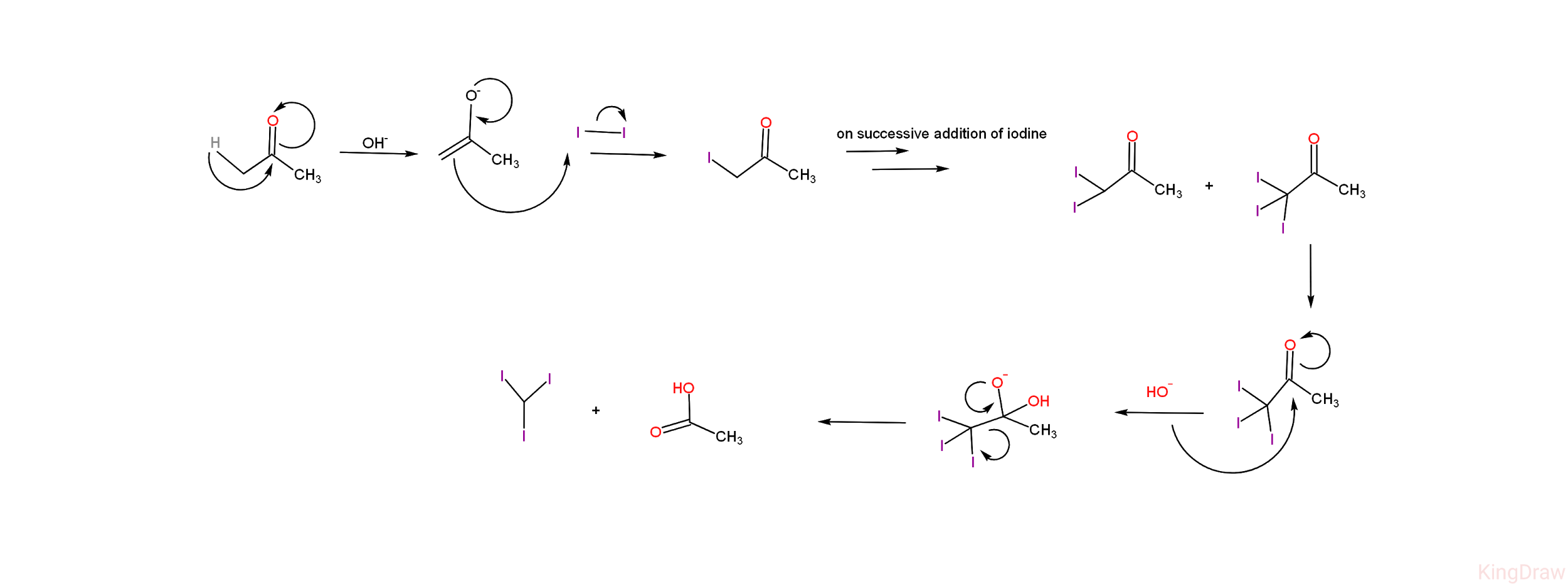 -From the mechanism, we can see that the iodoform reaction of acetone leads to the products - iodoform (${ CH }I_{ 3 }$) and acetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ O }{ H }$ ).
-From the mechanism, we can see that the iodoform reaction of acetone leads to the products - iodoform (${ CH }I_{ 3 }$) and acetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ O }{ H }$ ).
-Apart from the final products, there are certain stable intermediates formed in the reaction - i.e, on addition of iodine on acetate ion, it leads to the formation of 1-iodoacetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ I }$) and on successive addition of iodine , two more compounds are formed which are 1,1-di iodoacetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }{ { I }_{ 2 } }$ ) and 1,1,1- tri iodoacetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ C }{ { I }_{ 3 } }$)
-So, these compounds ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ I }$,${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }{ { I }_{ 2 } }$ , ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ C }{ { I }_{ 3 } }$are formed in the iodoform reaction of acetone, which are satisfied by Option (A), option (C) and option (D).
-In the question, it has been asked which among the options are not formed in the iodoform reaction of acetone and that compound is Option (B)${ ICH }_{ 2 }{ CO }{ C }{ H }_{ 2 }$.
Therefore, the correct answer here is Option (B)${ ICH }_{ 2 }{ CO }{ C }{ H }_{ 2 }$.
Note: Iodoform reaction occurs when there is an $\alpha $- hydrogen in that compound, and this $\alpha $ - hydrogen will be substituted with iodine leading to the formation of iodoform. In the case of acetone, there are three $\alpha $ - hydrogens present in the compound, so all the three $\alpha $ - hydrogens are replaced by iodine successively and thereby these stable intermediates are formed.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
-Structure of acetone is given below:

-Iodoform reaction is used to identify the presence of carbonyl compounds in compounds.
-Here in the iodoform reaction of acetone, the acetone will be reacted by ${ I }_{ 2 }$ in the presence of NaOH to form acetic acid (sodium acetate) and iodoform.
-When we look at the mechanism of this reaction, we can see many intermediates formed in between.
-Given below is the diagrammatic representation of the mechanism of iodoform reaction of acetone.
 -From the mechanism, we can see that the iodoform reaction of acetone leads to the products - iodoform (${ CH }I_{ 3 }$) and acetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ O }{ H }$ ).
-From the mechanism, we can see that the iodoform reaction of acetone leads to the products - iodoform (${ CH }I_{ 3 }$) and acetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ O }{ H }$ ).-Apart from the final products, there are certain stable intermediates formed in the reaction - i.e, on addition of iodine on acetate ion, it leads to the formation of 1-iodoacetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ I }$) and on successive addition of iodine , two more compounds are formed which are 1,1-di iodoacetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }{ { I }_{ 2 } }$ ) and 1,1,1- tri iodoacetic acid (${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ C }{ { I }_{ 3 } }$)
-So, these compounds ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }_{ 2 }{ I }$,${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ CH }{ { I }_{ 2 } }$ , ${ CH }_{ 3 }{ CO }{ C }{ { I }_{ 3 } }$are formed in the iodoform reaction of acetone, which are satisfied by Option (A), option (C) and option (D).
-In the question, it has been asked which among the options are not formed in the iodoform reaction of acetone and that compound is Option (B)${ ICH }_{ 2 }{ CO }{ C }{ H }_{ 2 }$.
Therefore, the correct answer here is Option (B)${ ICH }_{ 2 }{ CO }{ C }{ H }_{ 2 }$.
Note: Iodoform reaction occurs when there is an $\alpha $- hydrogen in that compound, and this $\alpha $ - hydrogen will be substituted with iodine leading to the formation of iodoform. In the case of acetone, there are three $\alpha $ - hydrogens present in the compound, so all the three $\alpha $ - hydrogens are replaced by iodine successively and thereby these stable intermediates are formed.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




