
Which of the following acids is isomeric with phthalic acid
A.Succinic acid
B.Salicylic acid
C.$1,4-$benzene dicarboxylic acid
D.Methyl benzoic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Generally isomers are different compounds that have an identical molecular formula but the atoms are attached differently. Here we have four acidic compounds given in the option and first, we have to draw the chemical structures of all four compounds along with phthalic acid.
Complete answer:The word ‘’isomers’’ is taken from the Greek word ‘isos’ which means equal and ‘meros’ which means parts. Isomers are chemical compounds that have identical parts but have different attachments of atoms in space. But isomers are excluded from any different arrangements that are simply due to the molecule rotating as a whole or rotating about any particular bonds.
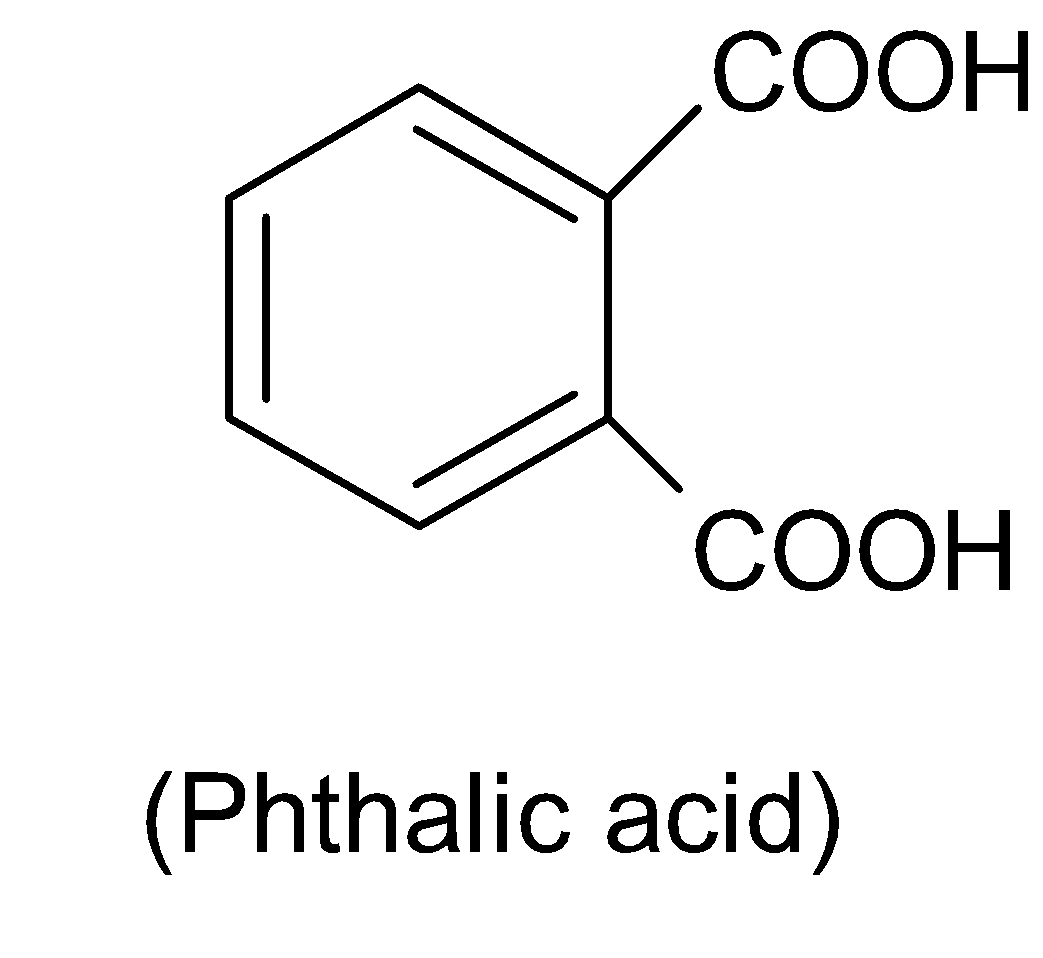
Phthalic acid has a chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(COOH)}_{2}}$and the IUPAC name of this compound is $1,2-$benzene dicarboxylic acid. The structure of phthalic acid is shown below:
The chemical formula of succinic acid ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{(COOH)}_{2}}$ and its structure is
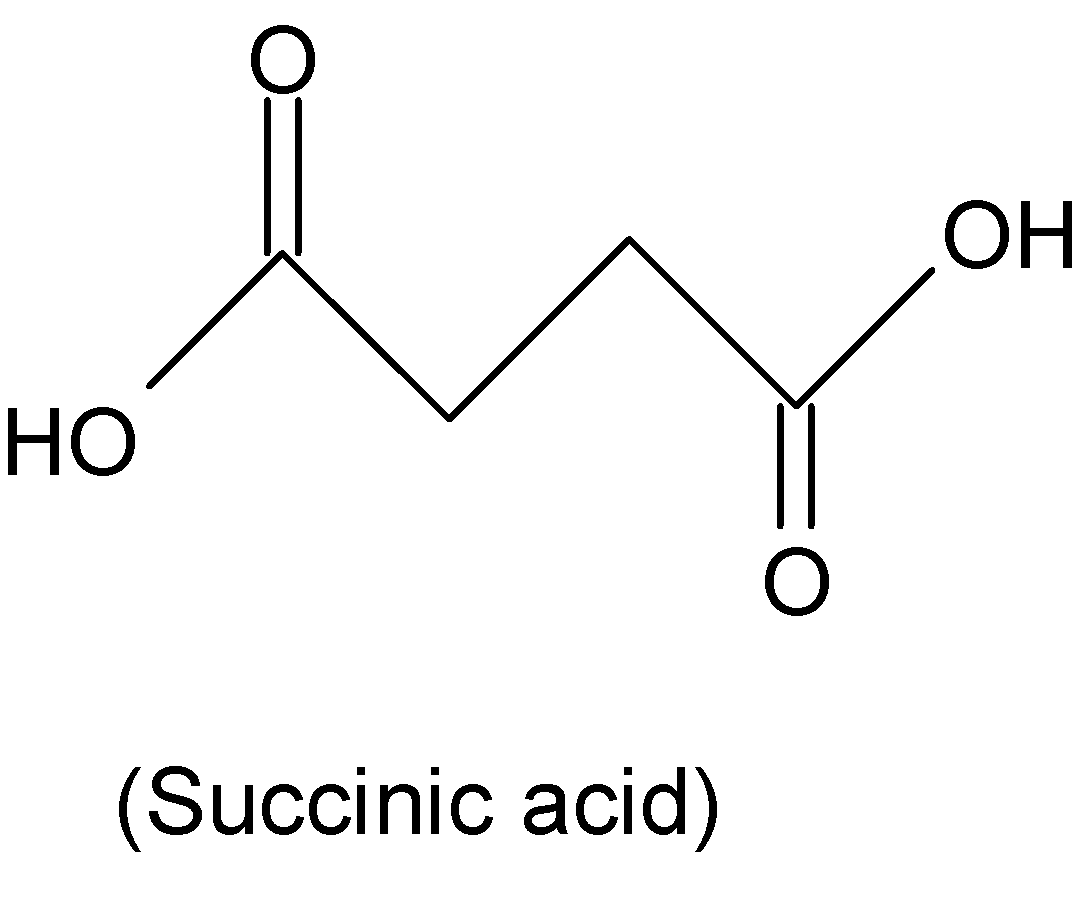
Hence succinic acid has different chemical formula from that of phthalic acid, so it is not an isomer of phthalic acid.
Salicylic acid has a chemical formula $HO{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}COOH$and the structure can be drawn in the following way:
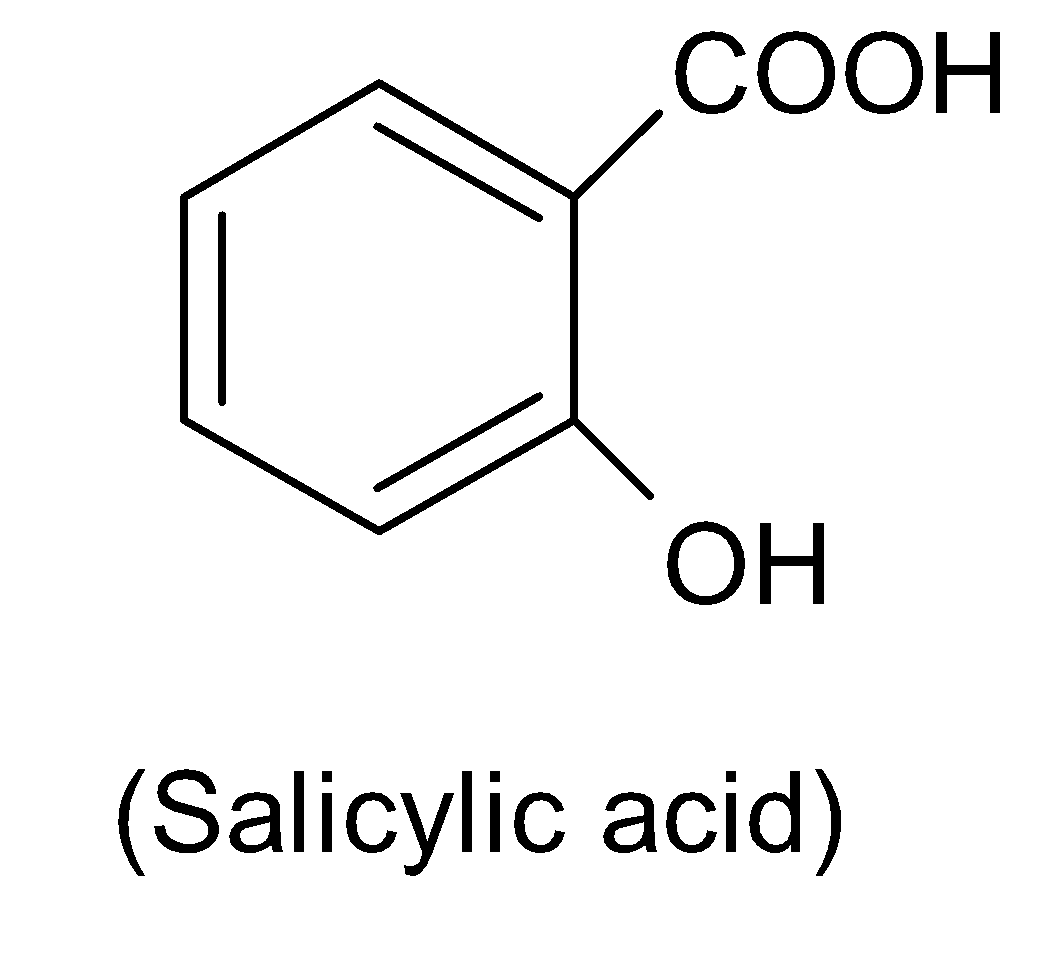
Again it is not an isomer of phthalic acid.
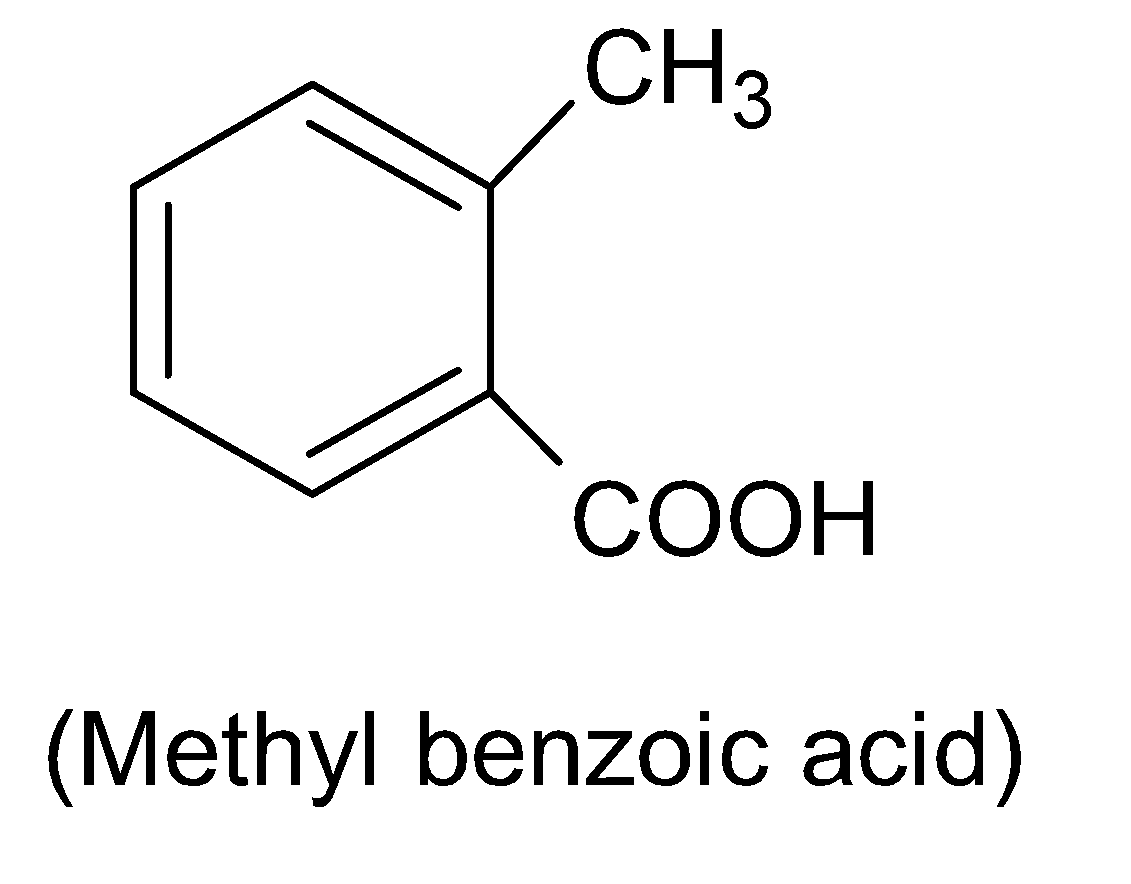
Methyl benzoic acid is not an isomer of phthalic acid as it has a chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}COOH$.
In (C), we have $1,4-$benzene dicarboxylic acid has a chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(COOH)}_{2}}$ and the structure is shown below:
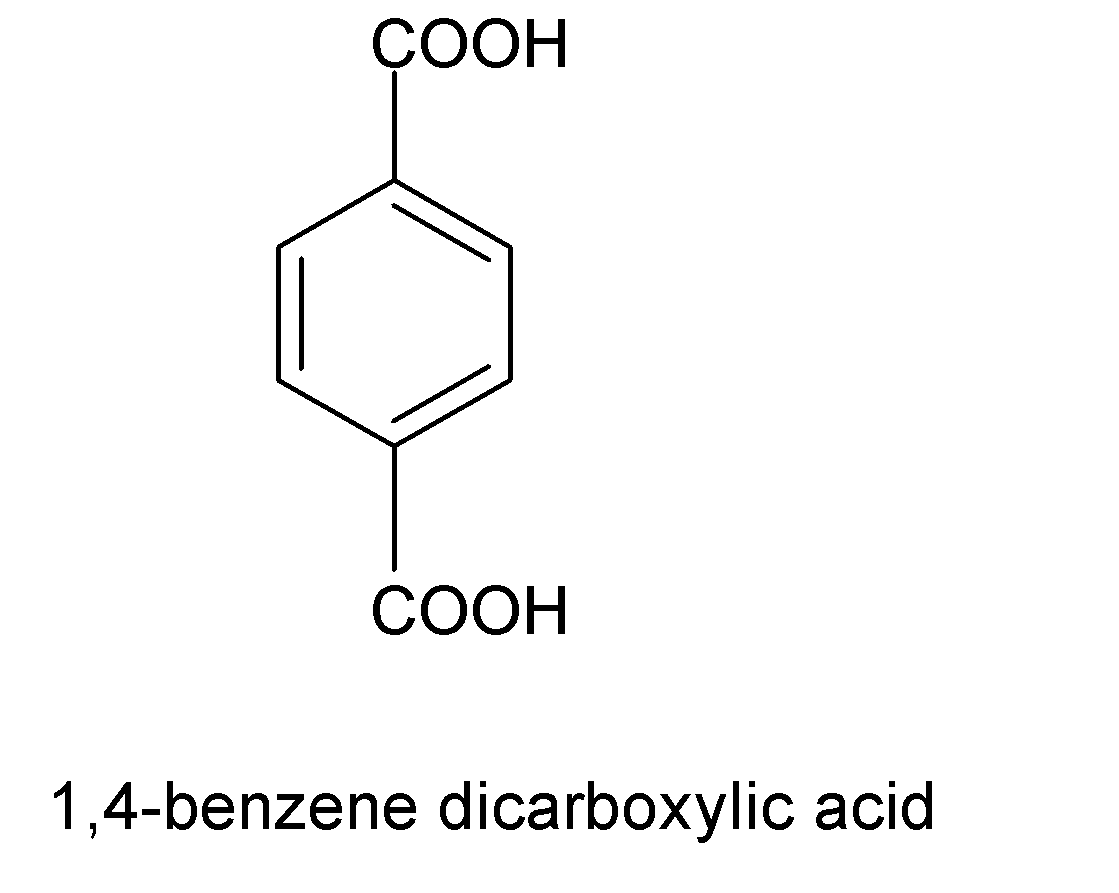
Therefore $1,4-$benzene dicarboxylic acid is an isomer of phthalic acid as it has a similar chemical formula but a different arrangement of $-COOH$ groups.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Isomers can be classified into two categories, constitutional and stereoisomers. When molecules have the same molecular formula but have different atomic arrangements and when molecules have identical formulas molecular formulas and functional structures but with different spatial arrangements of atoms are called stereoisomers.
Complete answer:The word ‘’isomers’’ is taken from the Greek word ‘isos’ which means equal and ‘meros’ which means parts. Isomers are chemical compounds that have identical parts but have different attachments of atoms in space. But isomers are excluded from any different arrangements that are simply due to the molecule rotating as a whole or rotating about any particular bonds.
Phthalic acid has a chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(COOH)}_{2}}$and the IUPAC name of this compound is $1,2-$benzene dicarboxylic acid. The structure of phthalic acid is shown below:

The chemical formula of succinic acid ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}{{(COOH)}_{2}}$ and its structure is

Hence succinic acid has different chemical formula from that of phthalic acid, so it is not an isomer of phthalic acid.
Salicylic acid has a chemical formula $HO{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}COOH$and the structure can be drawn in the following way:

Again it is not an isomer of phthalic acid.
Methyl benzoic acid is not an isomer of phthalic acid as it has a chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}COOH$.

In (C), we have $1,4-$benzene dicarboxylic acid has a chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{4}}{{(COOH)}_{2}}$ and the structure is shown below:

Therefore $1,4-$benzene dicarboxylic acid is an isomer of phthalic acid as it has a similar chemical formula but a different arrangement of $-COOH$ groups.
Thus, option (C) is correct.
Note: Isomers can be classified into two categories, constitutional and stereoisomers. When molecules have the same molecular formula but have different atomic arrangements and when molecules have identical formulas molecular formulas and functional structures but with different spatial arrangements of atoms are called stereoisomers.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




