
Which is the path of rays of light when it enters with oblique incidence from water to air?
(A)
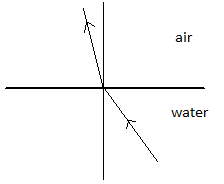
(B)
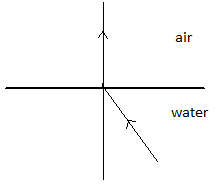
(C)
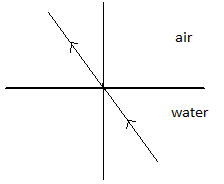
(D)
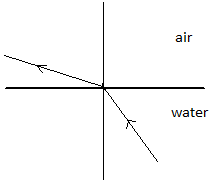
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We know that refraction is the bending of light rays when they travel from one material medium to another. Refraction of light is mainly caused because of the change in speed of the light wave upon crossing a boundary.
Complete answer:
If a ray of light passes across the boundary from a material in which it travels with a fast speed into a material in which it travels at a slower speed, then the light ray will bend towards the normal line.
Similarly when a ray of light passes across the boundary from a material in which its speed is slower compared to a material in which its speed is much faster, then the ray of light will bend away from the normal.
In the question given above it is clear that the ray of light is travelling from a denser medium (in which its speed is much less) into a rarer medium (in which its speed is much more). Thus, the light ray should bend away from the normal line.
When we carefully analyse the figures given in options (A), (B) and (C) we see that all three of them do not fit into our description of bending of a refracted ray of light. Thus, only option (D) displays a ray of light which bends away from the normal while travelling from a denser medium (in which its speed is much less) into a rarer medium (in which its speed is much more).
Thus, (D) is the correct answer to this question.
Note: The tendency of a ray of light to bend one direction or another is dependent upon whether the light wave speeds up or slows down upon crossing the boundary. The speed of a light wave is dependent upon the optical density of the material through which it moves. For this reason, the direction that the path of a light wave bends depends on whether the light wave is traveling from a more dense (slow) medium to a less dense (fast) medium or from a less dense medium to a more dense medium.
Complete answer:
If a ray of light passes across the boundary from a material in which it travels with a fast speed into a material in which it travels at a slower speed, then the light ray will bend towards the normal line.
Similarly when a ray of light passes across the boundary from a material in which its speed is slower compared to a material in which its speed is much faster, then the ray of light will bend away from the normal.
In the question given above it is clear that the ray of light is travelling from a denser medium (in which its speed is much less) into a rarer medium (in which its speed is much more). Thus, the light ray should bend away from the normal line.
When we carefully analyse the figures given in options (A), (B) and (C) we see that all three of them do not fit into our description of bending of a refracted ray of light. Thus, only option (D) displays a ray of light which bends away from the normal while travelling from a denser medium (in which its speed is much less) into a rarer medium (in which its speed is much more).
Thus, (D) is the correct answer to this question.
Note: The tendency of a ray of light to bend one direction or another is dependent upon whether the light wave speeds up or slows down upon crossing the boundary. The speed of a light wave is dependent upon the optical density of the material through which it moves. For this reason, the direction that the path of a light wave bends depends on whether the light wave is traveling from a more dense (slow) medium to a less dense (fast) medium or from a less dense medium to a more dense medium.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




