
Which is more stable carbocation?
A. 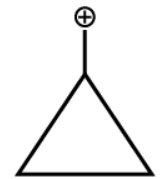
B. \[Ph-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,{{H}_{2}}\]
C. \[C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,H-C{{H}_{3}}\]
D. \[C{{H}_{3}}=CH-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,{{H}_{2}}\]
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: Carbocation is a carbon atom containing positive charge or an empty p orbital. Now try recalling how carbocation is formed, well it is formed when a covalent bond breaks up by heterolytic cleavage, where the more electronegative atom takes away both the bonding electron while the carbon loses its electron and acquires positive charge.
Complete step by step solution:
The correct answer is Cyclopropylmethyl carbocation.
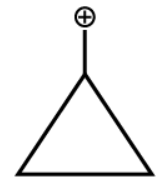
Let us see how it is the most stable carbocation:
- The percentage p character is greater in the cyclopropyl ring as compared to other cyclic compounds as the bond angle here is almost 60 degrees. And we know when the bond angle decreases the percentage p character increases.
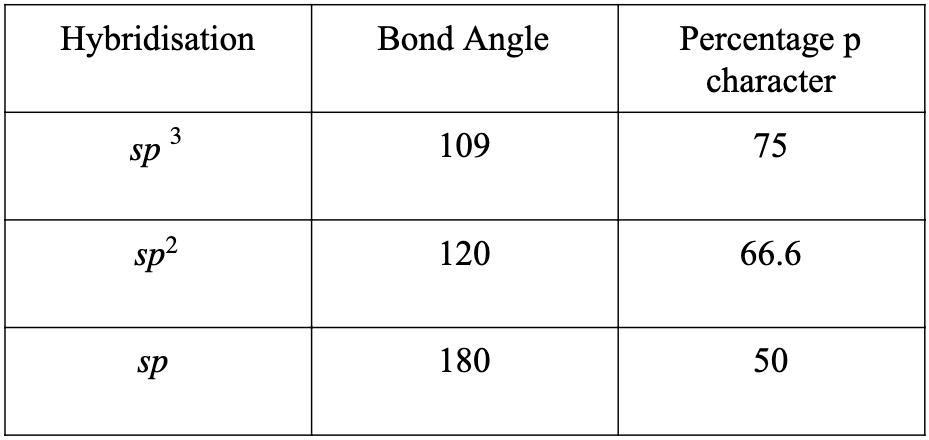
- The cationic carbon has a vacant p orbital, that means it can easily accept an electron.
- Now there will be an interaction of the cyclopropyl bonding orbitals with the vacant p orbital of the cationic carbon.
- The electrons of the bonding orbital have a relatively higher energy than the normal Sigma electrons as the bond formed is called bent bond, which is an intermediate of sigma and pi bond.
- Now this Sigma electron expands outwardly due to strain in the angle.
- Therefore, the electron cloud of the cationic carbon is surrounded by the cloud of the expanded electron cloud making it a more stable carbocation.
Now lets know why other options are not correct:
b) In benzyl carbocation even though there exists a resonance, its phenyl pi system is not as much nucleophilic as the inner bonds of the cyclopropane.
c) In secondary propyl carbocation there exists a hyperconjugation, still the positive charge is kind of trapped.
d) In propene carbocation it will be stabilised by the pi bond resonance with the adjacent carbon, but still won’t attain as much stability as the bent bonds of the cyclopropyl methyl carbocation.
So, the correct answer is cyclopropyl methyl carbocation which is option (a).
Note: Although all the structures given in the option are stable, Cyclopropylmethyl carbocation is exceptionally stable because of its structure and properties. So, be careful while answering.
The stability order of aliphatic carbocations is tertiary > secondary > primary while in allylic carbocation stability varies as resonance gets involved there.
Complete step by step solution:
The correct answer is Cyclopropylmethyl carbocation.

Let us see how it is the most stable carbocation:
- The percentage p character is greater in the cyclopropyl ring as compared to other cyclic compounds as the bond angle here is almost 60 degrees. And we know when the bond angle decreases the percentage p character increases.

- The cationic carbon has a vacant p orbital, that means it can easily accept an electron.
- Now there will be an interaction of the cyclopropyl bonding orbitals with the vacant p orbital of the cationic carbon.
- The electrons of the bonding orbital have a relatively higher energy than the normal Sigma electrons as the bond formed is called bent bond, which is an intermediate of sigma and pi bond.
- Now this Sigma electron expands outwardly due to strain in the angle.
- Therefore, the electron cloud of the cationic carbon is surrounded by the cloud of the expanded electron cloud making it a more stable carbocation.
Now lets know why other options are not correct:
b) In benzyl carbocation even though there exists a resonance, its phenyl pi system is not as much nucleophilic as the inner bonds of the cyclopropane.
c) In secondary propyl carbocation there exists a hyperconjugation, still the positive charge is kind of trapped.
d) In propene carbocation it will be stabilised by the pi bond resonance with the adjacent carbon, but still won’t attain as much stability as the bent bonds of the cyclopropyl methyl carbocation.
So, the correct answer is cyclopropyl methyl carbocation which is option (a).
Note: Although all the structures given in the option are stable, Cyclopropylmethyl carbocation is exceptionally stable because of its structure and properties. So, be careful while answering.
The stability order of aliphatic carbocations is tertiary > secondary > primary while in allylic carbocation stability varies as resonance gets involved there.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




