
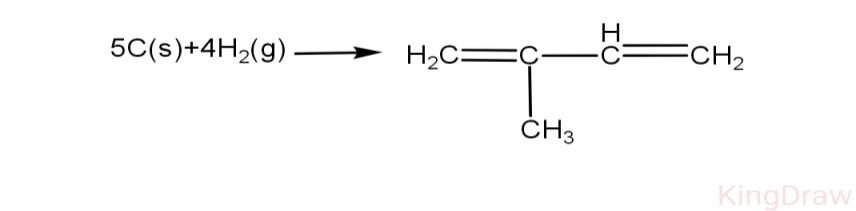
Using bond energy data, calculate heat of formation of isoprene.
Given, C-H, H-H, C-C, C=C and C(s)$\to $C(g) respectively as 98.8 kcal, 104 kcal, 83kcal, 147kcal, 171kcal.
(a) -21 kcal
(b) 21 kcal
(c) 40 kcal
(d) 50 kcal
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: As we know, a chemical reaction involves breaking and forming of chemical bonds. During the formation of the bond, energy is released and during the breaking of a bond, energy is absorbed.
So, the enthalpy changes involving gaseous reactants and gaseous products having covalent bonds can be calculated with the help of bond enthalpies of reactants and products using the following formula.
Heat of Reaction=$\sum{\Delta {{\text{H}}^{\text{o}}}}(\text{reactant bonds)-}\sum{\Delta {{\text{H}}^{\text{o}}}}(\text{products bonds)}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
As it is mentioned in the hint, the bonds between atoms may break, reform or both to either absorb or release energy during chemical reaction. This results in a change to the potential energy of the system. The heat absorbed or released from a system under constant pressure is known as enthalpy and the change in enthalpy that results from a chemical reaction is the enthalpy of reaction. It is generally written as$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{\text{rxn}}}$.
Mathematically, we can think of the enthalpy of reaction as the difference between the potential energy from the product bonds and the energy of the reactant bonds:
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{\text{rxn}}}$=potential energy of product bonds-potential energy of reactant bonds.
As it is given in the question:
\[\text{C-H=98}\text{.8 kcal}\]
\[\text{H-H=104 kcal}\]
\[\text{C-C=83 kcal}\]
\[\text{C=C =147 kcal}\]
\[\text{C(s)}\to \text{C(g)=171 kcal}\]
Reaction:
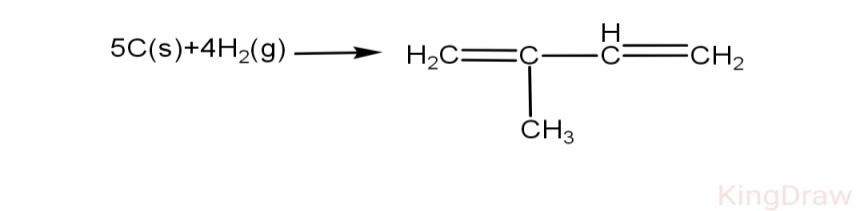
\[\text{5x }\!\![\!\!\text{ C(s)}\to \text{C(g) }\!\!]\!\!\text{ =5x171 kcal=855 kcal}\]
$4{{\text{H}}_{2}}$$\Rightarrow 4\text{x}104=416\text{kcal}$
$\sum{\text{BE(}5\text{C}+4{{\text{H}}_{2}})}\Rightarrow 855+416$
$\sum{\text{BE=C-H}\Rightarrow \text{8x98}\text{.8=790}\text{.4}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C-C=2x83=166 kcal}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C=C= 2x147=294 kcal}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{\text{f}}}=\Delta \text{HB}{{\text{E}}_{\text{r}}}-\Delta \text{HB}{{\text{E}}_{\text{p}}}$= (855+416)-(790.4+166+294)
=1271-1250.4
=20.6 kcal
The closest option from the answer obtained is option (b) 21 kcal.
Note: Please note that the bond energy that is given in the question is for single bonds. Always multiply the stoichiometric coefficient to have the right bond energy for the specific compounds. This can often be a very lengthy calculation if there are a lot of bonds, so you should practice to just look and calculate for the bonds that are changing as in the example.
So, the enthalpy changes involving gaseous reactants and gaseous products having covalent bonds can be calculated with the help of bond enthalpies of reactants and products using the following formula.
Heat of Reaction=$\sum{\Delta {{\text{H}}^{\text{o}}}}(\text{reactant bonds)-}\sum{\Delta {{\text{H}}^{\text{o}}}}(\text{products bonds)}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
As it is mentioned in the hint, the bonds between atoms may break, reform or both to either absorb or release energy during chemical reaction. This results in a change to the potential energy of the system. The heat absorbed or released from a system under constant pressure is known as enthalpy and the change in enthalpy that results from a chemical reaction is the enthalpy of reaction. It is generally written as$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{\text{rxn}}}$.
Mathematically, we can think of the enthalpy of reaction as the difference between the potential energy from the product bonds and the energy of the reactant bonds:
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{\text{rxn}}}$=potential energy of product bonds-potential energy of reactant bonds.
As it is given in the question:
\[\text{C-H=98}\text{.8 kcal}\]
\[\text{H-H=104 kcal}\]
\[\text{C-C=83 kcal}\]
\[\text{C=C =147 kcal}\]
\[\text{C(s)}\to \text{C(g)=171 kcal}\]
Reaction:

\[\text{5x }\!\![\!\!\text{ C(s)}\to \text{C(g) }\!\!]\!\!\text{ =5x171 kcal=855 kcal}\]
$4{{\text{H}}_{2}}$$\Rightarrow 4\text{x}104=416\text{kcal}$
$\sum{\text{BE(}5\text{C}+4{{\text{H}}_{2}})}\Rightarrow 855+416$
$\sum{\text{BE=C-H}\Rightarrow \text{8x98}\text{.8=790}\text{.4}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C-C=2x83=166 kcal}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C=C= 2x147=294 kcal}$
$\Delta {{\text{H}}_{\text{f}}}=\Delta \text{HB}{{\text{E}}_{\text{r}}}-\Delta \text{HB}{{\text{E}}_{\text{p}}}$= (855+416)-(790.4+166+294)
=1271-1250.4
=20.6 kcal
The closest option from the answer obtained is option (b) 21 kcal.
Note: Please note that the bond energy that is given in the question is for single bonds. Always multiply the stoichiometric coefficient to have the right bond energy for the specific compounds. This can often be a very lengthy calculation if there are a lot of bonds, so you should practice to just look and calculate for the bonds that are changing as in the example.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




