
When two pairs of electrons are shared, bond is.
(a) Single covalent bond
(b) Double covalent bond
(c) Dative bond
(d) Triple bond
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The mutual sharing of electrons between the participating atoms leads to the formation of a covalent bond. The electron pair which involves in the formation of a covalent bond is called a shared pair and bonding pair electrons. During the covalent bond formation, the sharing of electrons occurs to achieve the noble gas electronic configuration.
Complete step by step solution:A covalent bond is formed between the atom of the same elements (\[{H_2},C{l_2}\]and \[{O_2}\])or between the atom of two different elements having almost same electronegativity difference (\[{H_2}O,C{H_4}\]and \[N{H_3}\]).
Atoms share their electron pair to achieve inert noble gas electronic configuration or to gain stability.
The following is the Lewis Dot Structure of the \[CC{l_4}\]molecule, showing the covalent bond formation by sharing electrons between chlorine and a carbon atom. The Lewis Dot Structure also represents that each atom is following the octet rule.
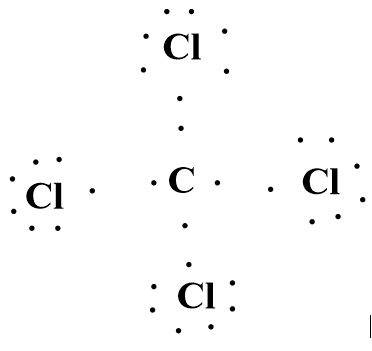
Image: Lewis Dot Structure of the \[CC{l_4}\]molecule.
The covalent bond can be divided into three types based on the sharing of electron pairs.
(1) Single bond: Formed when sharing of only one electron takes place between two atoms.
For e.g., \[HCl\]has a single bond formed by the sharing of a single electron from hydrogen as well as from a chlorine atom.
(2) Double bond: Formed when two pairs of electrons are involved in sharing between two atoms.
For e.g., \[C{O_2}\]have two double bonds formed between carbon and oxygen atom
(3) Triple bond: Formed when three pairs of electrons are involved in sharing between two atoms. For e.g., Dinitrogen (.\[{N_2}\]) consists of a triple bond.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: Compared to ionic compounds covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Covalent compounds are best soluble in non-polar solvents.
Unlike ionic compounds, covalent compounds are considered as directional in nature i.e., they have a proper direction of overlapping.
Complete step by step solution:A covalent bond is formed between the atom of the same elements (\[{H_2},C{l_2}\]and \[{O_2}\])or between the atom of two different elements having almost same electronegativity difference (\[{H_2}O,C{H_4}\]and \[N{H_3}\]).
Atoms share their electron pair to achieve inert noble gas electronic configuration or to gain stability.
The following is the Lewis Dot Structure of the \[CC{l_4}\]molecule, showing the covalent bond formation by sharing electrons between chlorine and a carbon atom. The Lewis Dot Structure also represents that each atom is following the octet rule.

Image: Lewis Dot Structure of the \[CC{l_4}\]molecule.
The covalent bond can be divided into three types based on the sharing of electron pairs.
(1) Single bond: Formed when sharing of only one electron takes place between two atoms.
For e.g., \[HCl\]has a single bond formed by the sharing of a single electron from hydrogen as well as from a chlorine atom.
(2) Double bond: Formed when two pairs of electrons are involved in sharing between two atoms.
For e.g., \[C{O_2}\]have two double bonds formed between carbon and oxygen atom
(3) Triple bond: Formed when three pairs of electrons are involved in sharing between two atoms. For e.g., Dinitrogen (.\[{N_2}\]) consists of a triple bond.
Therefore from the above explanation we can say option (b) will be the correct option:
Note: Compared to ionic compounds covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Covalent compounds are best soluble in non-polar solvents.
Unlike ionic compounds, covalent compounds are considered as directional in nature i.e., they have a proper direction of overlapping.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




