
Two mutually perpendicular wires carry charge densities $\lambda_{4}$ and $\lambda_{2}$. The electric line of force makes angle a with the second wire then finds $\lambda_{4} / \lambda_{2}$.
(in terms of angle $a$ ).
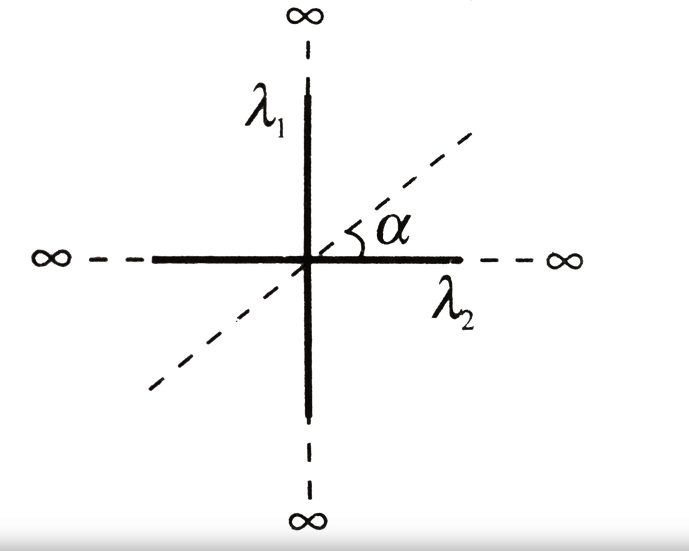
A) $\cot ^{2} \alpha$
B) $\cot \alpha $
C) $\tan ^{2} \alpha$
D) $\tan \alpha $
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the external electric field is a fundamental requirement for electrospinning and an important factor governing the fibre diameter. Melt-electrospinning involves the stretching of predominantly non conducting liquid under the influence of an applied electric field. On Earth, flowing of liquid metal in the outer core of the planet generates electric currents. The rotation of Earth on its axis causes these electric currents to form a magnetic field which extends around the planet. The magnetic field is extremely important to sustaining life on Earth.
Complete step by step answer
We know that the electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge. The direction of the field is taken to be the direction of the force it would exert on a positive test charge. The electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.
The space around an electric charge in which its influence can be felt is known as the electric field. The electric field Intensity at a point is the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. Electric Field Intensity is a vector quantity.
Electric fields (e-fields) are an important tool in understanding how electricity begins and continues to flow. Electric fields describe the pulling or pushing force in a space between charges. The electric fields of single charges. A negative charge has an inward electric field because it attracts positive charges.
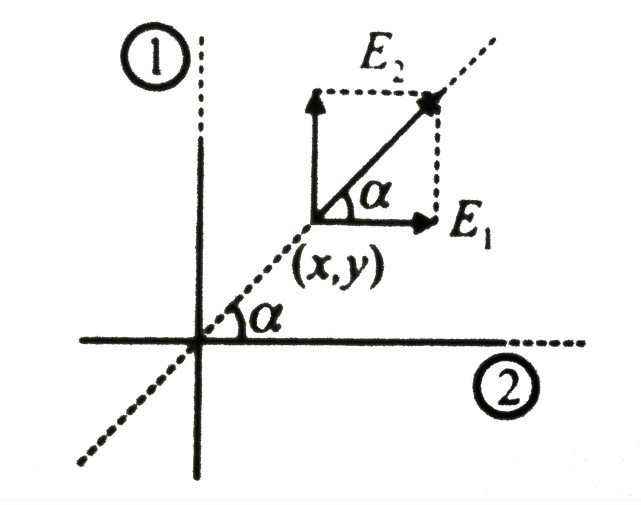
$E_{1}=\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0} x}$ and ${{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{q}}}{2\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}y}$
$\dfrac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=\left(\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{\lambda_{2}}\right)\left(\dfrac{y}{x}\right)$
$\dfrac{1}{\tan \alpha}=\left(\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{\lambda_{2}}\right) \tan \alpha$ or $\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{\lambda_{2}}=\cot ^{2} \alpha$
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: We can say that the electric field lines flow from positive to negative charges. Such sources are well suited for surface applications such as wound healing, corneal repair or even brain and spinal stimulation with closely-separated, inserted electrodes. Electric field is not negative. It is a vector and thus has negative and positive directions. An electron being negatively charged experiences a force against the direction of the field. For a positive charge, the force is along the field. A measure of the strength of an electric field at a given point in space, equal to the force the field would induce on a unit electric charge at that point.
Complete step by step answer
We know that the electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge. The direction of the field is taken to be the direction of the force it would exert on a positive test charge. The electric field is radially outward from a positive charge and radially in toward a negative point charge.
The space around an electric charge in which its influence can be felt is known as the electric field. The electric field Intensity at a point is the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. Electric Field Intensity is a vector quantity.
Electric fields (e-fields) are an important tool in understanding how electricity begins and continues to flow. Electric fields describe the pulling or pushing force in a space between charges. The electric fields of single charges. A negative charge has an inward electric field because it attracts positive charges.

$E_{1}=\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0} x}$ and ${{E}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{\lambda }_{q}}}{2\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}y}$
$\dfrac{E_{1}}{E_{2}}=\left(\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{\lambda_{2}}\right)\left(\dfrac{y}{x}\right)$
$\dfrac{1}{\tan \alpha}=\left(\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{\lambda_{2}}\right) \tan \alpha$ or $\dfrac{\lambda_{1}}{\lambda_{2}}=\cot ^{2} \alpha$
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: We can say that the electric field lines flow from positive to negative charges. Such sources are well suited for surface applications such as wound healing, corneal repair or even brain and spinal stimulation with closely-separated, inserted electrodes. Electric field is not negative. It is a vector and thus has negative and positive directions. An electron being negatively charged experiences a force against the direction of the field. For a positive charge, the force is along the field. A measure of the strength of an electric field at a given point in space, equal to the force the field would induce on a unit electric charge at that point.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




