
Two masses 5kg and 3kg are suspended from the ends of an unstretchable light string passing over a frictionless pulley. When the masses are released, the force on the pulley due to string connecting 5 kg and 3 kg body is:
A) 30N
B) 75N
C) 15N
D) 60N
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The force that is acting on the pulley due to the masses is termed as tension. The tension in the light string is the axial pull experienced in the direction opposite to that of the pull of the light string. This tension is obtained by drawing the free-body diagram of the setup and calculating all the forces.
Complete step by step solution:
The tension in a string is defined as the stretch or the pull experienced by the string due to forces acting on the either ends of the string that try to extend the length of the string.
When a light string passes over a pulley, whose ends are connected to different masses, the tension is acting on both sides of the pulley. Hence, the force on the pulley will be equal to twice the tension.
Consider a pulley with a string passing over whose ends are connected to masses of 3kg and 5kg respectively.
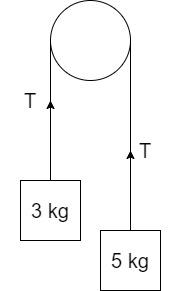
The force on the pulley, which is equal to tension in the string, is denoted by T.
In order to compute the value of T, we have to consider the masses individually, and draw the free-body diagram which contains all the forces acting individually on these masses. Free-body diagram of 3 kg mass:
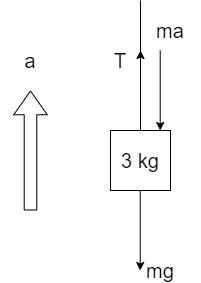
The acceleration is pointed upwards since the mass 5 kg is heavier and it pulls the 3 kg mass in the upward direction over the pulley.
The forces acting on the 3kg mass are:
i) Weight, mg
ii) Tension due to the string, T
iii) Force acting due to the acceleration a, in the direction opposite of the acceleration and equal to ma.
Equating the forces, we get –
$ma + mg = T$
Mass, $m = 3kg$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
$\Rightarrow 3a + 3 \times 10 = T$
$\Rightarrow 3a + 30 = T \to \left( 1 \right)$
Free-body diagram of 5 kg mass:
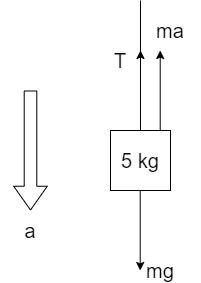
The acceleration is pointed downwards since the mass 5 kg is heavier and it pulls the 3 kg mass in the downward direction over the pulley.
The forces acting on the 5kg mass are:
i) Weight, mg
ii) Tension due to the string, T
iii) Force acting due to the acceleration a, in the direction opposite of the acceleration and equal to ma.
Equating the forces, we get –
$T + ma = mg$
Mass, $m = 5kg$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
$\Rightarrow T + 5a = 5 \times 10$
$\Rightarrow T + 5a = 50$
$\Rightarrow 5a - 50 = - T \to \left( 2 \right)$
Solving the equations (1) and (2) simultaneously –
$\Rightarrow 3a + 30 = T$
$\Rightarrow 5a - 50 = - T$
Adding the above equations, we get –
$\Rightarrow 3a + 5a + 30 - 50 = T - T$
$ \Rightarrow 8a - 20 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{20}}{8}$
Substituting the value of acceleration in equation (1),
$\Rightarrow 3a + 30 = T$
$\Rightarrow 3 \times \dfrac{{20}}{8} + 30 = T$
$ \Rightarrow T = 3 \times 2.5 + 30 = 7.5 + 30 = 37.5N$
The tension in the string is equal to 37.5N
However, the tension is acting on both sides of the pulley. Hence, the force on the pulley will be equal to twice the tension.
Hence, force on the pulley is $2 \times 37.5 = 75N$
The correct option is Option B.
Note: Since it is given in the problem that the string is light, we have not considered the mass of the string. If not, the mass of the string also, has to be considered. However, the mass of the string does not have impact on the tension force generated in the string and hence, it is usually ignored in these calculations.
Complete step by step solution:
The tension in a string is defined as the stretch or the pull experienced by the string due to forces acting on the either ends of the string that try to extend the length of the string.
When a light string passes over a pulley, whose ends are connected to different masses, the tension is acting on both sides of the pulley. Hence, the force on the pulley will be equal to twice the tension.
Consider a pulley with a string passing over whose ends are connected to masses of 3kg and 5kg respectively.

The force on the pulley, which is equal to tension in the string, is denoted by T.
In order to compute the value of T, we have to consider the masses individually, and draw the free-body diagram which contains all the forces acting individually on these masses. Free-body diagram of 3 kg mass:

The acceleration is pointed upwards since the mass 5 kg is heavier and it pulls the 3 kg mass in the upward direction over the pulley.
The forces acting on the 3kg mass are:
i) Weight, mg
ii) Tension due to the string, T
iii) Force acting due to the acceleration a, in the direction opposite of the acceleration and equal to ma.
Equating the forces, we get –
$ma + mg = T$
Mass, $m = 3kg$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
$\Rightarrow 3a + 3 \times 10 = T$
$\Rightarrow 3a + 30 = T \to \left( 1 \right)$
Free-body diagram of 5 kg mass:

The acceleration is pointed downwards since the mass 5 kg is heavier and it pulls the 3 kg mass in the downward direction over the pulley.
The forces acting on the 5kg mass are:
i) Weight, mg
ii) Tension due to the string, T
iii) Force acting due to the acceleration a, in the direction opposite of the acceleration and equal to ma.
Equating the forces, we get –
$T + ma = mg$
Mass, $m = 5kg$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
$\Rightarrow T + 5a = 5 \times 10$
$\Rightarrow T + 5a = 50$
$\Rightarrow 5a - 50 = - T \to \left( 2 \right)$
Solving the equations (1) and (2) simultaneously –
$\Rightarrow 3a + 30 = T$
$\Rightarrow 5a - 50 = - T$
Adding the above equations, we get –
$\Rightarrow 3a + 5a + 30 - 50 = T - T$
$ \Rightarrow 8a - 20 = 0$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{20}}{8}$
Substituting the value of acceleration in equation (1),
$\Rightarrow 3a + 30 = T$
$\Rightarrow 3 \times \dfrac{{20}}{8} + 30 = T$
$ \Rightarrow T = 3 \times 2.5 + 30 = 7.5 + 30 = 37.5N$
The tension in the string is equal to 37.5N
However, the tension is acting on both sides of the pulley. Hence, the force on the pulley will be equal to twice the tension.
Hence, force on the pulley is $2 \times 37.5 = 75N$
The correct option is Option B.
Note: Since it is given in the problem that the string is light, we have not considered the mass of the string. If not, the mass of the string also, has to be considered. However, the mass of the string does not have impact on the tension force generated in the string and hence, it is usually ignored in these calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




