
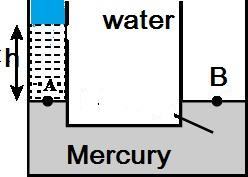
Two communicating vessels contain mercury. The diameter of one vessel is n times larger than the diameter of the other. A column of water of height h is poured into the left vessel. The mercury level will rise in the right hand vessel (s=relative density of mercury and ρ =density of water) by:
$\eqalign{
& {\text{A) }}\dfrac{{{{\text{n}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{h}}}}{{{{{\text{(n + 1)}}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}}} \cr
& {\text{B)}}\dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{{\text{(}}{{\text{n}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + 1)s}}}} \cr
& {\text{C)}}\dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{{{{\text{(n + 1)}}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}}} \cr
& {\text{D)}}\dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{{{\text{n}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{s}}}} \cr} $
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We will follow Pascal's principle, also called Pascal's law, any force applied to a confined fluid is transmitted uniformly in all directions throughout the fluid regardless of the shape of the container.
Complete step by step solution:
If the level in narrow tubes goes down by $h_1$, then in broader tube goes up to $h_2$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow \pi {r^2}h_1 = \pi {(nr)^2}h_2 \cr
& \Rightarrow h_1 = {n^2}h_2 \cr
& {\text{Now pressure at point A = pressure at point B}} \cr
& {\text{h}}\rho {{g = (h_1 + h_2)}}\rho {\text{'g}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\text{h = (}}{{\text{n}}^2}h_2 + h_2)sg \cr
& {\text{also s = }}\dfrac{{\rho {\text{'}}}}{\rho } \cr
& h_2 = \dfrac{h}{{({n^2} + 1)s}} \cr} $
Option B is correct.
Additional Information: A solid surface can exert pressure, but liquids (ie liquid or gas) can also exert pressure. It may sound strange if you think about it because it is hard to imagine hitting a hammer in a nail with liquid. To understand this, imagine sinking to some depth in water. Due to the force of gravity, the water above you will be pulled down and this will increase the pressure on you. If you go deeper, you will have more water, so the weight and pressure will also increase with the water.
The pressure in a fluid depends on the height of the fluid column, but not on the shape of the vessel in which it is contained, when we assume that wherever the fluid is in contact with the vessel wall, the force between it and the wall Perpendicular to the surface.
Note: Pressure exerted by liquid changes with the depth in liquid. Value of pressure is small just below the surface of the liquid, but as we go deeper, the pressure increases with the depth. All liquids have weight and exerts pressure at the bottom of the container. In SI units, the unit of pressure is Pascal (Pa), which is equal to $N / {m^2}$.The primary mathematical expression for pressure is given by: ${\text{pressure = }}\dfrac{{force}}{{area}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
If the level in narrow tubes goes down by $h_1$, then in broader tube goes up to $h_2$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow \pi {r^2}h_1 = \pi {(nr)^2}h_2 \cr
& \Rightarrow h_1 = {n^2}h_2 \cr
& {\text{Now pressure at point A = pressure at point B}} \cr
& {\text{h}}\rho {{g = (h_1 + h_2)}}\rho {\text{'g}} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\text{h = (}}{{\text{n}}^2}h_2 + h_2)sg \cr
& {\text{also s = }}\dfrac{{\rho {\text{'}}}}{\rho } \cr
& h_2 = \dfrac{h}{{({n^2} + 1)s}} \cr} $
Option B is correct.
Additional Information: A solid surface can exert pressure, but liquids (ie liquid or gas) can also exert pressure. It may sound strange if you think about it because it is hard to imagine hitting a hammer in a nail with liquid. To understand this, imagine sinking to some depth in water. Due to the force of gravity, the water above you will be pulled down and this will increase the pressure on you. If you go deeper, you will have more water, so the weight and pressure will also increase with the water.
The pressure in a fluid depends on the height of the fluid column, but not on the shape of the vessel in which it is contained, when we assume that wherever the fluid is in contact with the vessel wall, the force between it and the wall Perpendicular to the surface.
Note: Pressure exerted by liquid changes with the depth in liquid. Value of pressure is small just below the surface of the liquid, but as we go deeper, the pressure increases with the depth. All liquids have weight and exerts pressure at the bottom of the container. In SI units, the unit of pressure is Pascal (Pa), which is equal to $N / {m^2}$.The primary mathematical expression for pressure is given by: ${\text{pressure = }}\dfrac{{force}}{{area}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




