
Two capacitors each having a capacitor $C$ and breakdown voltage $V$ are joined in series. The effective capacitance and maximum working voltage of the combination is:
(A) $2C,2V$
(B) $\dfrac{C}{2},\dfrac{V}{2}$
(C) $2C,V$
(D) \[\dfrac{C}{2},2V\]
Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: We know for a given capacitor, charge \[Q\] on a capacitor is proportional to potential difference \[V\], between the plates.
\[Q = CV\]
And, for series combination charges on capacitors remain the same.
Complete Step by Step Answer
Figure, shows two capacitors connected in series. The capacitance is \[C\] and \[C\].
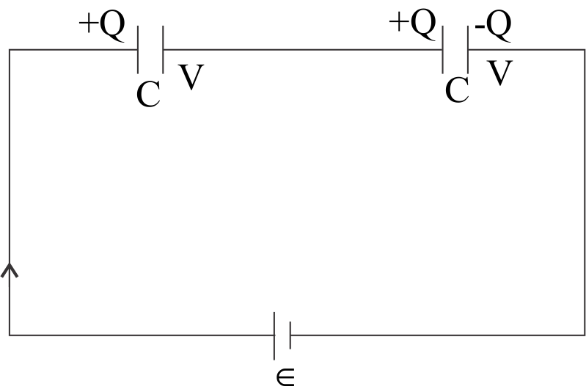
Now, let us take the potential of the right plate of the second plate to be zero. The potential of the left plate of the first capacitor is \[E\]. Since, the breakdown voltage of capacitors is \[V\]. Therefore capacitor \[1\],
\[E - V = \dfrac{Q}{C}...........(i)\]
Similarly, for other capacitor,
\[V - 0 = \dfrac{Q}{C}...........(ii)\]
Adding equation \[(i)\] and \[(ii)\]
\[E = Q\left( {\dfrac{1}{C} + \dfrac{1}{C}} \right)\,.........\,(iii)\]
If the equivalent capacitance of the combination is \[{C_{eq}}\].
\[{C_{eq}} = \dfrac{Q}{E}\,..........\,(iv)\]
Using equation \[(iii)\] and \[(iv)\] we get,
\[{C_{eq}} = \dfrac{C}{2}\,\]
And, the maximum working voltage is \[E\].
Hence, \[E = V + V = 2V\]
Hence, Option (D) is correct
Note:
Charge on series combination remains same but voltage changes with respect to the capacitance whereas voltage on parallel combination remains same but charge varies in accordance to capacitance.
\[Q = CV\]
And, for series combination charges on capacitors remain the same.
Complete Step by Step Answer
Figure, shows two capacitors connected in series. The capacitance is \[C\] and \[C\].

Now, let us take the potential of the right plate of the second plate to be zero. The potential of the left plate of the first capacitor is \[E\]. Since, the breakdown voltage of capacitors is \[V\]. Therefore capacitor \[1\],
\[E - V = \dfrac{Q}{C}...........(i)\]
Similarly, for other capacitor,
\[V - 0 = \dfrac{Q}{C}...........(ii)\]
Adding equation \[(i)\] and \[(ii)\]
\[E = Q\left( {\dfrac{1}{C} + \dfrac{1}{C}} \right)\,.........\,(iii)\]
If the equivalent capacitance of the combination is \[{C_{eq}}\].
\[{C_{eq}} = \dfrac{Q}{E}\,..........\,(iv)\]
Using equation \[(iii)\] and \[(iv)\] we get,
\[{C_{eq}} = \dfrac{C}{2}\,\]
And, the maximum working voltage is \[E\].
Hence, \[E = V + V = 2V\]
Hence, Option (D) is correct
Note:
Charge on series combination remains same but voltage changes with respect to the capacitance whereas voltage on parallel combination remains same but charge varies in accordance to capacitance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




