
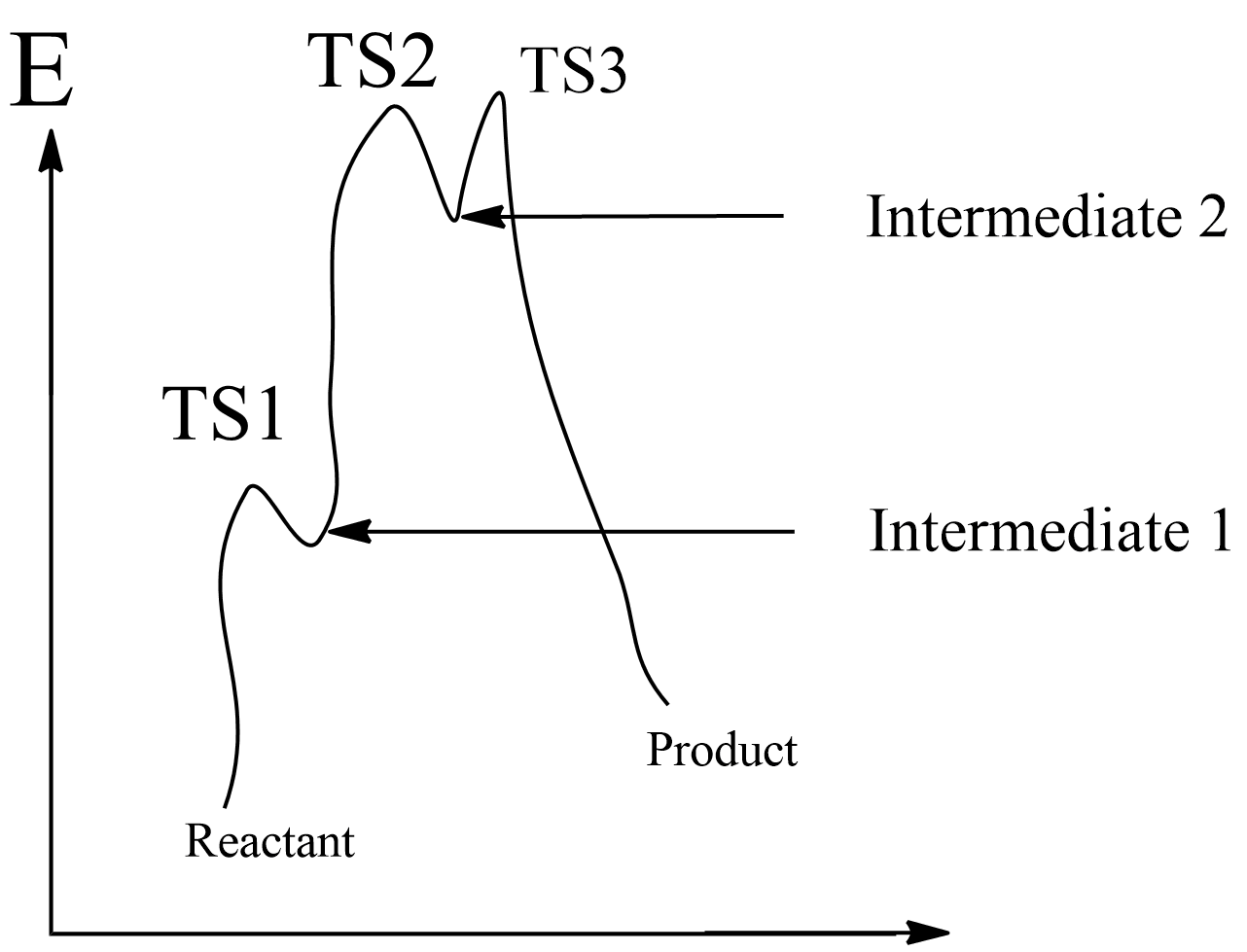
Transition state 2 (TS2) is structurally most likely as a/an:
(A) intermediate 2
(B) product
(C) intermediate 1
(D) transition state (TS3)
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along with the reaction coordinate. The transition state is unstable with a high energy state and some amount of energy approaches the next step of the reaction. whether transition state is closer to reactants exothermic reaction favours or closer to products endothermic reaction favours.
Complete step by step solution:
According to Hammond’s postulate states that the transition state of a reaction resembles either reactants or the products to whichever closer in energy.
In an exothermic reaction, the transition state is closer to reactants, then less energy required during the formation of products. Hence according to Hammond’s postulate, in an exothermic reaction, the transition state resembles reactants.
In an endothermic reaction, the transition state is closer to the products than to the reactants in energy. So, more energy is required at the formation of products. Therefore, according to Hammond’s postulate, in an endothermic reaction, the transition state resembles the products.
In the given reaction with three transition states TS1, TS2, and TS3, which exist with two intermediates as intermediate 1 and intermediate 2 based on their energy level. Generally, the transition state tries to bring stability with less energy difference.
Hence, according to Hammond’s postulate, the transition state resembles that species which is energetically near to it, hence, transition state 2 will resemble intermediate 2.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A: intermediate 2.
Note: Activation energy and transition state are different in kinetic reactions. Activation energy means the energy required for a reaction to occur catalysis by increasing the rate of reaction by lowering its activation energy. The transition state is an intermediate state during a chemical reaction that has higher energy than the reactants or the products.
Complete step by step solution:
According to Hammond’s postulate states that the transition state of a reaction resembles either reactants or the products to whichever closer in energy.
In an exothermic reaction, the transition state is closer to reactants, then less energy required during the formation of products. Hence according to Hammond’s postulate, in an exothermic reaction, the transition state resembles reactants.
In an endothermic reaction, the transition state is closer to the products than to the reactants in energy. So, more energy is required at the formation of products. Therefore, according to Hammond’s postulate, in an endothermic reaction, the transition state resembles the products.
In the given reaction with three transition states TS1, TS2, and TS3, which exist with two intermediates as intermediate 1 and intermediate 2 based on their energy level. Generally, the transition state tries to bring stability with less energy difference.
Hence, according to Hammond’s postulate, the transition state resembles that species which is energetically near to it, hence, transition state 2 will resemble intermediate 2.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A: intermediate 2.
Note: Activation energy and transition state are different in kinetic reactions. Activation energy means the energy required for a reaction to occur catalysis by increasing the rate of reaction by lowering its activation energy. The transition state is an intermediate state during a chemical reaction that has higher energy than the reactants or the products.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




