
To get DDT, chlorobenzene has to react with one of the following compound in the presence of conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]
A. Trichloroethane
B. Dichloroacetaone
C. Dichloroacetaldehyde
D. Trichloroacetaldehyde
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:DDT or Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane is an organochlorine and a crystalline chemical compound, can be prepared through electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. To get DDT we have to use chlorinated compounds with an electrophilic carbon centre on which chlorobenzene can attack. From the four given options we have to find out the most electrophilic carbon centre.
Complete step-by-step answer:An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction proceeds through an organic coupling reaction. Here for preparing DDT, chlorobenzene acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophilic carbon centre in the presence of sulphuric acid.
Among the four given options, the most electrophilic carbon centre is present on trichloroacetaldehyde as there is one electronegative oxygen atom and three chlorine atoms are attached with the carbon atom, making it the most electron deficient centre.
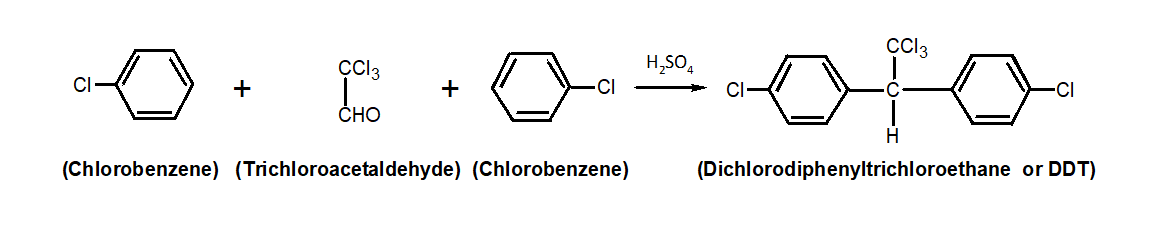
Therefore by repeatedly combining one mole of trichloroacetaldehyde or chloral and two equivalents of chlorobenzene with an acidic catalyst, we may prepare DDT.
In order to create dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, chlorobenzene interacts with chloral in the presence of a strong sulfuric acid solution. Chloral and chlorobenzene react with \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]to produce Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. The overall reaction is shown as follows:
Option ‘D’ is correct
Note: The main driving force behind the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction for the preparation of DDT is the activation of electrophile using acid catalyst (Here sulphuric acid) to form acylium ion and reformation of the delocalised ring of electrons of benzene by losing a proton from the six membered ring.
Complete step-by-step answer:An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction proceeds through an organic coupling reaction. Here for preparing DDT, chlorobenzene acts as a nucleophile and attacks on the electrophilic carbon centre in the presence of sulphuric acid.
Among the four given options, the most electrophilic carbon centre is present on trichloroacetaldehyde as there is one electronegative oxygen atom and three chlorine atoms are attached with the carbon atom, making it the most electron deficient centre.
Therefore by repeatedly combining one mole of trichloroacetaldehyde or chloral and two equivalents of chlorobenzene with an acidic catalyst, we may prepare DDT.
In order to create dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, chlorobenzene interacts with chloral in the presence of a strong sulfuric acid solution. Chloral and chlorobenzene react with \[{H_2}S{O_4}\]to produce Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. The overall reaction is shown as follows:

Option ‘D’ is correct
Note: The main driving force behind the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction for the preparation of DDT is the activation of electrophile using acid catalyst (Here sulphuric acid) to form acylium ion and reformation of the delocalised ring of electrons of benzene by losing a proton from the six membered ring.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




