
The structural formula of methyl aminomethane is
(a) \[{(C{H_3})_2}CHN{H_2}\]
(b) \[{(C{H_3})_3}N\]
(c) \[{(C{H_3})_2}NH\]
(d) \[C{H_3}N{H_2}\]
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Amines are belonging to the class of organic molecules, which contains nitrogen atoms. Amines are formed by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms of ammonia molecules (\[N{H_3}\]) by the alkyl and aryl groups.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amines are present in various biomolecules such as proteins, vitamins, hormones, etc. They are also used in industries for making detergents and various kinds of drugs.
Amines are derivatives of ammonia. Depending upon the number of alkyl or aryl groups, the amines can be classified as primary (\[{1^ \circ }\]), secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]), and tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]).
Primary (\[{1^ \circ }\]): If only one alkyl or aryl group is attached to the nitrogen atom of ammonia then it is called Primary or \[{1^ \circ }\] amine.
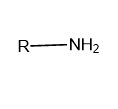
Image: General structure of primary amine, where R represents the aryl and alkyl group.
Secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]): If two alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom of ammonia then it is called secondary or \[{2^ \circ }\]amine.
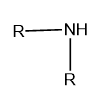
Image: General structure of secondary amine, where R represents the aryl and alkyl group.
Tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]): If three alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom of ammonia then it is called tertiary or \[{3^ \circ }\] amine.
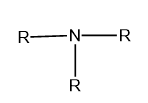
Image: General structure of tertiary amine, where R represents the aryl and alkyl group.
The naming of amines:
According to IUPAC the naming of aliphatic amines can be done by writing the name alkyl before the name of amine and therefore the name of amine will be alkylamine i.e., alkyl part + amine =methylamine.
For example, The IUPAC name of \[C{H_3}N{H_2}\] can be done by adding the name of the alkyl group i.e., \[ - C{H_3}\] group before the name of amine. Hence the name of \[C{H_3}N{H_2}\]will be methylamine.
In the case of secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]) and tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]) amine, the prefixes di and tri are used before the name of the alkyl group.
If the secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]) and tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]) amine have a different alkyl group, then the alkyl amino alkane name is used. The alkyl notation has a short carbon chain whereas the alkane notation contains the longest carbon chain. E.g, \[C{H_3}C{H_2}NHC{H_3}\] can be named as methyl aminoethane.
Hence, from the above discussion. Option (c) will be the correct answer because the \[{(C{H_3})_2}NH\]has the same carbon chain (\[ - C{H_3}\]) therefore its name can be written as methyl aminomethane.
Note: In some cases, the amines contain more than one amino group. Then the location of the amino group is defined by the numbering of the carbon atoms in the parent chain. The numbering will start from where the carbon atom bearing \[ - N{H_2}\] group gets the lowest numbers. Therefore, prefixes along with the number of the amino group and their position in the molecule.
For example, \[N{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - N{H_2}\] can be named as ethane 1, 2-diamine.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Amines are present in various biomolecules such as proteins, vitamins, hormones, etc. They are also used in industries for making detergents and various kinds of drugs.
Amines are derivatives of ammonia. Depending upon the number of alkyl or aryl groups, the amines can be classified as primary (\[{1^ \circ }\]), secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]), and tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]).
Primary (\[{1^ \circ }\]): If only one alkyl or aryl group is attached to the nitrogen atom of ammonia then it is called Primary or \[{1^ \circ }\] amine.

Image: General structure of primary amine, where R represents the aryl and alkyl group.
Secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]): If two alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom of ammonia then it is called secondary or \[{2^ \circ }\]amine.

Image: General structure of secondary amine, where R represents the aryl and alkyl group.
Tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]): If three alkyl or aryl groups are attached to the nitrogen atom of ammonia then it is called tertiary or \[{3^ \circ }\] amine.

Image: General structure of tertiary amine, where R represents the aryl and alkyl group.
The naming of amines:
According to IUPAC the naming of aliphatic amines can be done by writing the name alkyl before the name of amine and therefore the name of amine will be alkylamine i.e., alkyl part + amine =methylamine.
For example, The IUPAC name of \[C{H_3}N{H_2}\] can be done by adding the name of the alkyl group i.e., \[ - C{H_3}\] group before the name of amine. Hence the name of \[C{H_3}N{H_2}\]will be methylamine.
In the case of secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]) and tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]) amine, the prefixes di and tri are used before the name of the alkyl group.
If the secondary (\[{2^ \circ }\]) and tertiary (\[{3^ \circ }\]) amine have a different alkyl group, then the alkyl amino alkane name is used. The alkyl notation has a short carbon chain whereas the alkane notation contains the longest carbon chain. E.g, \[C{H_3}C{H_2}NHC{H_3}\] can be named as methyl aminoethane.
Hence, from the above discussion. Option (c) will be the correct answer because the \[{(C{H_3})_2}NH\]has the same carbon chain (\[ - C{H_3}\]) therefore its name can be written as methyl aminomethane.
Note: In some cases, the amines contain more than one amino group. Then the location of the amino group is defined by the numbering of the carbon atoms in the parent chain. The numbering will start from where the carbon atom bearing \[ - N{H_2}\] group gets the lowest numbers. Therefore, prefixes along with the number of the amino group and their position in the molecule.
For example, \[N{H_2} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - N{H_2}\] can be named as ethane 1, 2-diamine.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




