
The shape of $Cl{O_3}^ - $ according to VSEPR model is-
(A) Planar triangle
(B) Pyramidal
(C) Tetrahedral
(D) Square planar
Answer
240.9k+ views
Hint: This question belongs to the chapter Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure. This question demands us to find the shape of compound $Cl{O_3}^ - $, to state the structure we need to place the formula of hybridization. By placing all the required values, we can find our answer.
Complete step by step answer:
> Chlorate is a white crystalline, inorganic in nature. It is water-soluble. The material itself is noncombustible, but can form a very flammable combination with materials which are combustible, which can be explosive if the combustible material is very finely divided. Friction can ignite the mixture. Strong sulfuric acid contact may lead to fires or explosions. Spontaneous decomposition and ignition can result when mixed with ammonium salts. Long exposure to heat or fire can lead to an explosion.
The compound is $Cl{O_3}^ - $.
By placing hybridization formula, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}$ (Number of valence electron on center atom + number of monovalent atom)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {7 + 0 + 1} \right)k$ { here, 7 is the valence electron on chlorine, oxygen is divalent so monovalent 0, 1 is the charge gained}
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( 8 \right) = 4$, so we get $s{p^3}$ hybridization.
4 bonds would have been made but it will be 3 bond pair and 1 lone pair
Figure –
So, the shape of the compound $Cl{O_3}^ - $ would be pyramidal.
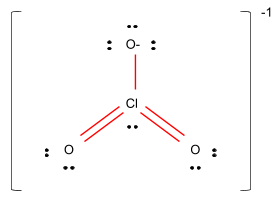
Hence, it is clear that option B is the correct option.
Note: Chlorate is a monovalent anion derived from chloric acid deprotonation. It's a mere inorganic anion and oxoanion chlorine. It is a chloric acid conjugate base.
Complete step by step answer:
> Chlorate is a white crystalline, inorganic in nature. It is water-soluble. The material itself is noncombustible, but can form a very flammable combination with materials which are combustible, which can be explosive if the combustible material is very finely divided. Friction can ignite the mixture. Strong sulfuric acid contact may lead to fires or explosions. Spontaneous decomposition and ignition can result when mixed with ammonium salts. Long exposure to heat or fire can lead to an explosion.
The compound is $Cl{O_3}^ - $.
By placing hybridization formula, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}$ (Number of valence electron on center atom + number of monovalent atom)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {7 + 0 + 1} \right)k$ { here, 7 is the valence electron on chlorine, oxygen is divalent so monovalent 0, 1 is the charge gained}
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( 8 \right) = 4$, so we get $s{p^3}$ hybridization.
4 bonds would have been made but it will be 3 bond pair and 1 lone pair
Figure –
So, the shape of the compound $Cl{O_3}^ - $ would be pyramidal.

Hence, it is clear that option B is the correct option.
Note: Chlorate is a monovalent anion derived from chloric acid deprotonation. It's a mere inorganic anion and oxoanion chlorine. It is a chloric acid conjugate base.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




