
The product obtained, heating ethanol with conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$at ${{165}^{{\mathrm O}}}-{{170}^{{\mathrm O}}}$, is
A. ${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
B. $C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}$
C. $C{{H}_{3}}COOH$
D. ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}HS{{O}_{4}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Concentrated sulphuric acid $({{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}})$ acts as a dehydrating agent. When alcohol reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid at high temperatures produces alkene as a major product after the removal of water molecules. Here we also have alcohol, ethanol reacts with conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ produces an alkene through dehydration.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When ethyl alcohol or ethanol reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature range ${{165}^{{\mathrm O}}}-{{170}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$ and intramolecular dehydration occurs to form ethane.
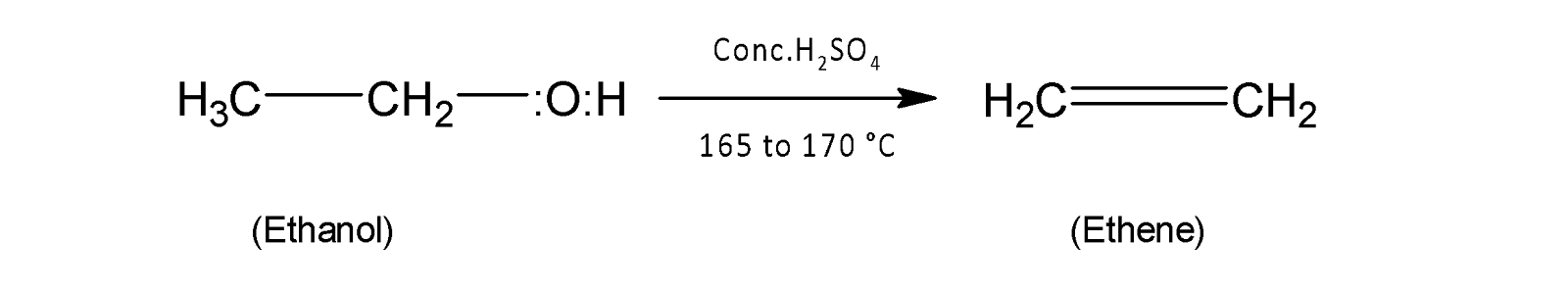
The overall mechanism of acid hydration of alcohol proceeds through three steps. In the first step oxygen of alcohol is protonated.
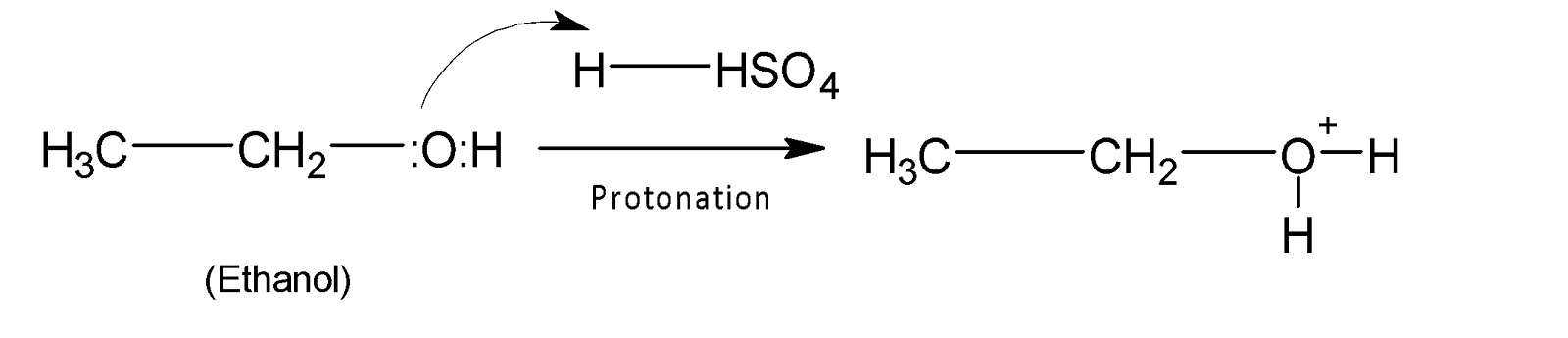
In the second step, a carbocation is formed by the loss of water molecules.
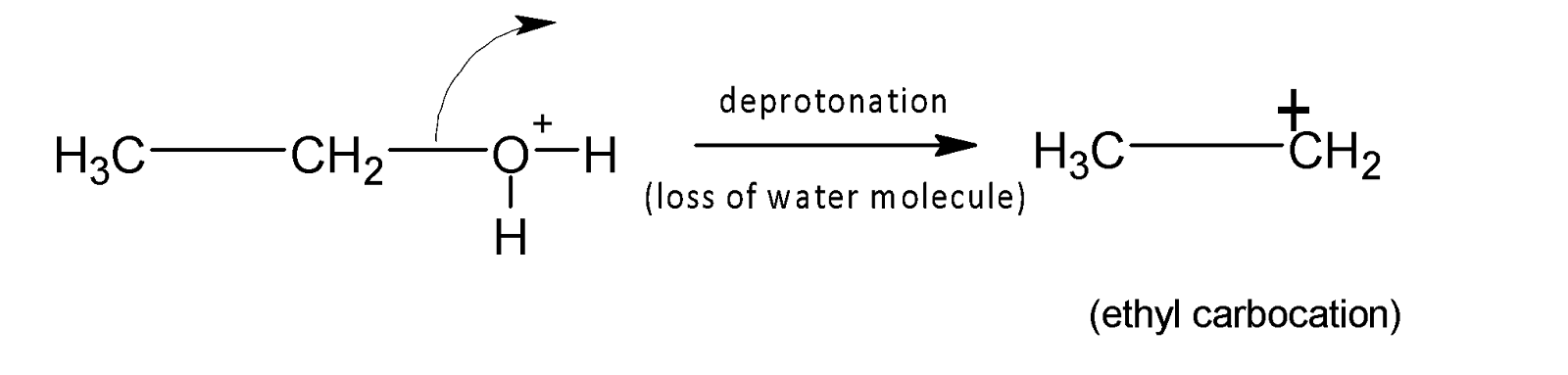
In the third step or final step, an alkene is formed by an elimination reaction with carbocation rearrangement. Here an alkene is formed with the migration of hydride shift from adjacent carbon.
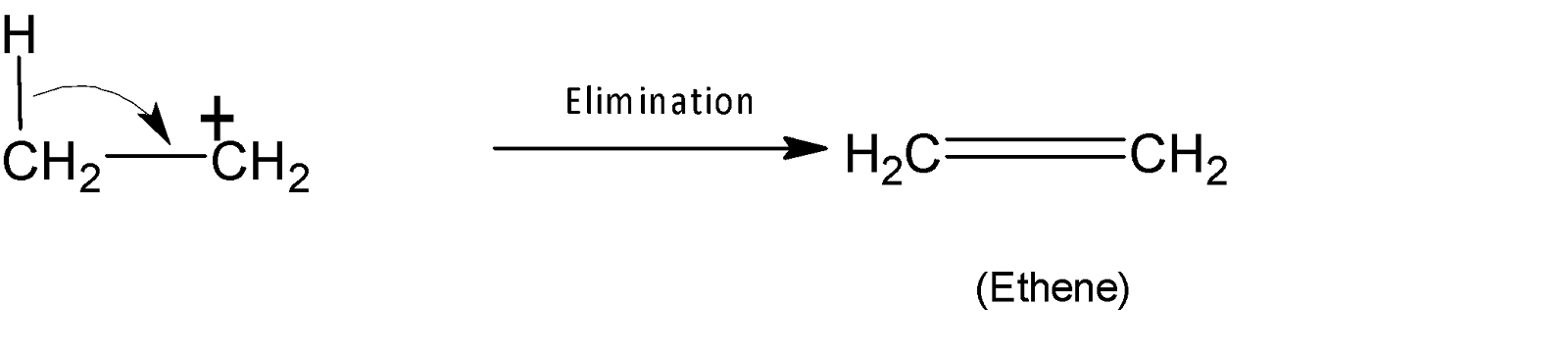
The overall mechanism proceeds through ${{E}_{2}}$ mechanism as ${{E}_{1}}$ pathway is not favoured here. This is because when primary alcohol reacts with the acid, a primary carbocation is generated which is extremely unstable. Through ${{E}_{2}}$elimination, the transition state will be lower in energy and therefore a proton is abstracted from adjacent carbon by a weak nucleophile, $HSO_{4}^{-}$, leading to the formation of alkene.
Therefore when ethanol is heated with conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$at ${{165}^{{\mathrm O}}}-{{170}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$, ethane is formed.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: When hydrogen halide reacts with alcohol a substitution reaction occurs but when Sulphuric acid reacts with alcohol an elimination reaction occurs. Because $HSO_{4}^{-}$is a weak nucleophile and is stabilised through resonance. The negative charge on oxygens delocalized over the molecule and hence is less available for substitution reaction.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When ethyl alcohol or ethanol reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature range ${{165}^{{\mathrm O}}}-{{170}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$ and intramolecular dehydration occurs to form ethane.

The overall mechanism of acid hydration of alcohol proceeds through three steps. In the first step oxygen of alcohol is protonated.

In the second step, a carbocation is formed by the loss of water molecules.

In the third step or final step, an alkene is formed by an elimination reaction with carbocation rearrangement. Here an alkene is formed with the migration of hydride shift from adjacent carbon.

The overall mechanism proceeds through ${{E}_{2}}$ mechanism as ${{E}_{1}}$ pathway is not favoured here. This is because when primary alcohol reacts with the acid, a primary carbocation is generated which is extremely unstable. Through ${{E}_{2}}$elimination, the transition state will be lower in energy and therefore a proton is abstracted from adjacent carbon by a weak nucleophile, $HSO_{4}^{-}$, leading to the formation of alkene.
Therefore when ethanol is heated with conc. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$at ${{165}^{{\mathrm O}}}-{{170}^{{\mathrm O}}}C$, ethane is formed.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: When hydrogen halide reacts with alcohol a substitution reaction occurs but when Sulphuric acid reacts with alcohol an elimination reaction occurs. Because $HSO_{4}^{-}$is a weak nucleophile and is stabilised through resonance. The negative charge on oxygens delocalized over the molecule and hence is less available for substitution reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




