
The process by which the vegetable ghee can be made from the cooking oil is called as :
A. Hydrogenation
B. Distillation
C. Crystallization
D. Oxidation
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Vegetable ghee is an unsaturated fatty acid or oil. And cooking oil are saturated fatty acids or oils. Fatty acids are basically a carboxylic acid of a hydrocarbon. This type of hydrocarbons are with very high carbon numbers. Fatty acids are units of fat or oil.
Complete step by step solution:
\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]
The above reaction is a simple hydrogenation reaction.
Now, the vegetable ghee can be made from the cooking oil by hydrogenation.
Hydrogenation reaction of unsaturated fatty acids is basically the reaction where the hydrogen gets added in the double bond of the alkene or alkyne in presence of nickel. Nickel acts like a catalyst in solid state. That is why this catalysis is also known as heterogeneous catalyst.
So, the correct option is A.
Note:
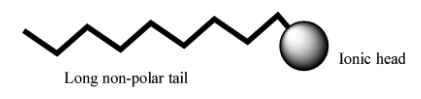
The hydrocarbon of fatty acids has two parts , one is the polar part and other one is the nonpolar part. The polar part is basically hydrophilic .i.e. that part has affection towards water or it can be said that it is soluble in water. But the other part is hydrophobic .i.e. that part repels water or it can be said that it does not soluble in water.
In these two parts one part which is polar is called polar head. And the part which is non polar is called tail. Also, the nonpolar part is a large chain of carbon like tail
The structure of the fatty acid shown below.
Complete step by step solution:
\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} \to {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}\]
The above reaction is a simple hydrogenation reaction.
Now, the vegetable ghee can be made from the cooking oil by hydrogenation.
Hydrogenation reaction of unsaturated fatty acids is basically the reaction where the hydrogen gets added in the double bond of the alkene or alkyne in presence of nickel. Nickel acts like a catalyst in solid state. That is why this catalysis is also known as heterogeneous catalyst.
So, the correct option is A.
Note:
The hydrocarbon of fatty acids has two parts , one is the polar part and other one is the nonpolar part. The polar part is basically hydrophilic .i.e. that part has affection towards water or it can be said that it is soluble in water. But the other part is hydrophobic .i.e. that part repels water or it can be said that it does not soluble in water.
In these two parts one part which is polar is called polar head. And the part which is non polar is called tail. Also, the nonpolar part is a large chain of carbon like tail
The structure of the fatty acid shown below.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




