
The pipe shows the volume flow rate of an ideal liquid at a certain time and its direction. What is the value of \[Q\] in \[\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{s}\] ? ( Assume steady state and equal area of cross- section at each point).
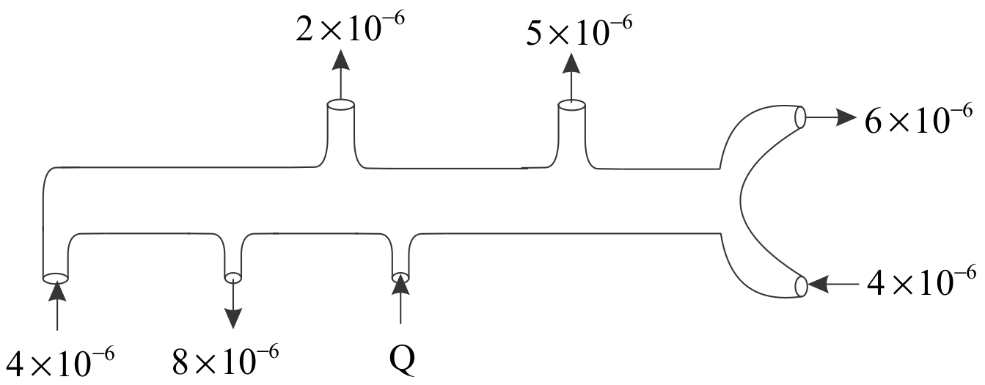
(A) $10 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
(B) $11 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
(C) $13 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
(D) $18 \times {10^{ - 6}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Apply the equation of continuity at all sections . The volume flowing inside the pipe will be equal to the volume flowing outside the pipe . All other values ( at each opening ) are given and this is how it can be calculated .
Complete step by step solution: The above problem will be solved by applying a continuity equation. The equation of continuity is based on conservation of mass . It states that the volume entering the pipe will be equal to the volume exiting the pipe ( if there aren’t any frictional losses) .
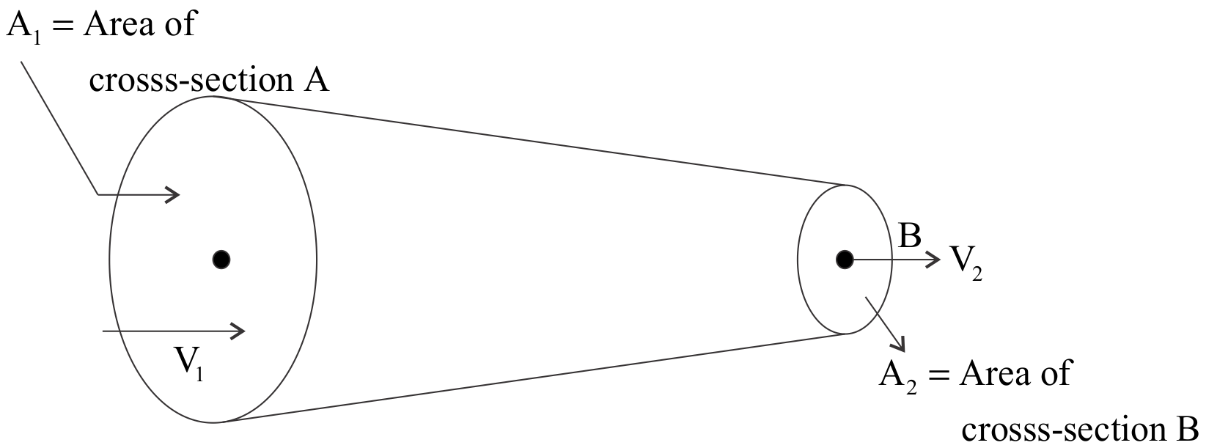
Suppose we have two sections A and B as shown in the diagram .
${V_1},{V_2}$ are the velocities of each section A and B respectively .
${A_1},{A_2}$ are the corresponding areas of cross- sections .
So according to equation of continuity:
${A_1}{V_1} = {A_2}{V_2}$ ……..(i)
The flow rate of liquid is expressed in terms of area and velocity. So eq(i) can be written as :
${Q_1} = {Q_2}$
In the above question, flow rate through each cross- section is given .
Flow rate incoming= flow rate outgoing
We have:
$
{Q_{in}} = {Q_{out}} \\
(4 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (4 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + Q = (2 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (5 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (8 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (6 \times {10^{ - 6}}) \\
Q = 13 \times {10^{ - 6}} \\
$
We have got the answer . The correct option is C.
Note: We need to keep in mind that in this derivation we have neglected the loss due to friction . If friction were to be present there will be slight loss in the volume of the liquid .
Complete step by step solution: The above problem will be solved by applying a continuity equation. The equation of continuity is based on conservation of mass . It states that the volume entering the pipe will be equal to the volume exiting the pipe ( if there aren’t any frictional losses) .

Suppose we have two sections A and B as shown in the diagram .
${V_1},{V_2}$ are the velocities of each section A and B respectively .
${A_1},{A_2}$ are the corresponding areas of cross- sections .
So according to equation of continuity:
${A_1}{V_1} = {A_2}{V_2}$ ……..(i)
The flow rate of liquid is expressed in terms of area and velocity. So eq(i) can be written as :
${Q_1} = {Q_2}$
In the above question, flow rate through each cross- section is given .
Flow rate incoming= flow rate outgoing
We have:
$
{Q_{in}} = {Q_{out}} \\
(4 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (4 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + Q = (2 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (5 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (8 \times {10^{ - 6}}) + (6 \times {10^{ - 6}}) \\
Q = 13 \times {10^{ - 6}} \\
$
We have got the answer . The correct option is C.
Note: We need to keep in mind that in this derivation we have neglected the loss due to friction . If friction were to be present there will be slight loss in the volume of the liquid .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




