
The phenomenon by which the incident light falling on a surface is sent back into the same medium is known as
A. Reflection
B. Refraction
C. Dispersion
D. None
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Optical phenomena happen when light waves interact with matter. Examples of this are Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, etc.
Complete Step by step solution:
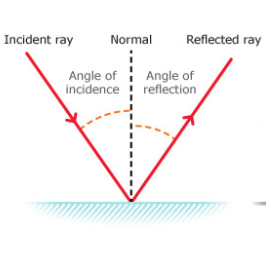
Reflection is the phenomenon by which any incident wave-front falling on a surface is sent back into the same medium where it originated. There are three laws of reflection that are
(i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) Angle of incidence is equal to Angle of reflection.
(iii) The reflected ray and the incident ray are on the opposite sides of the normal.
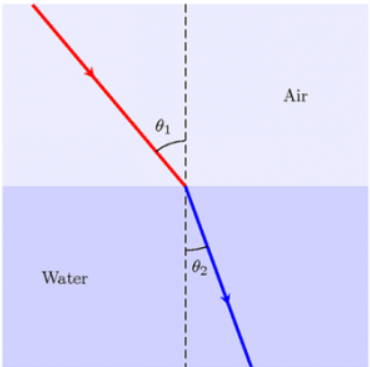
Refraction is the phenomenon of bending of a light wave or change in its direction when it is going from one medium to another. A lens is a refractive surface used for many purposes, such as magnification.
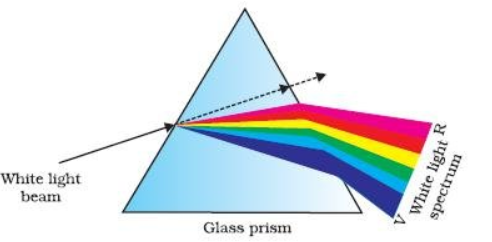
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the white light when passed through a glass prism splits into its spectrum of colours. This phenomenon along with refraction is responsible for the formation of rainbows in the sky.
So the answer to the given question is Reflection, option (A)
Note: Reflection is the bouncing back of light in the same medium when incident on any surface.
Refraction is the bending of light when it goes from one medium to another.
Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its spectrum of colours when passed through a glass prism.
Complete Step by step solution:

Reflection is the phenomenon by which any incident wave-front falling on a surface is sent back into the same medium where it originated. There are three laws of reflection that are
(i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) Angle of incidence is equal to Angle of reflection.
(iii) The reflected ray and the incident ray are on the opposite sides of the normal.

Refraction is the phenomenon of bending of a light wave or change in its direction when it is going from one medium to another. A lens is a refractive surface used for many purposes, such as magnification.

Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the white light when passed through a glass prism splits into its spectrum of colours. This phenomenon along with refraction is responsible for the formation of rainbows in the sky.
So the answer to the given question is Reflection, option (A)
Note: Reflection is the bouncing back of light in the same medium when incident on any surface.
Refraction is the bending of light when it goes from one medium to another.
Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its spectrum of colours when passed through a glass prism.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




